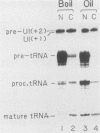
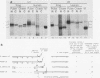
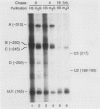
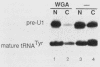Abstract
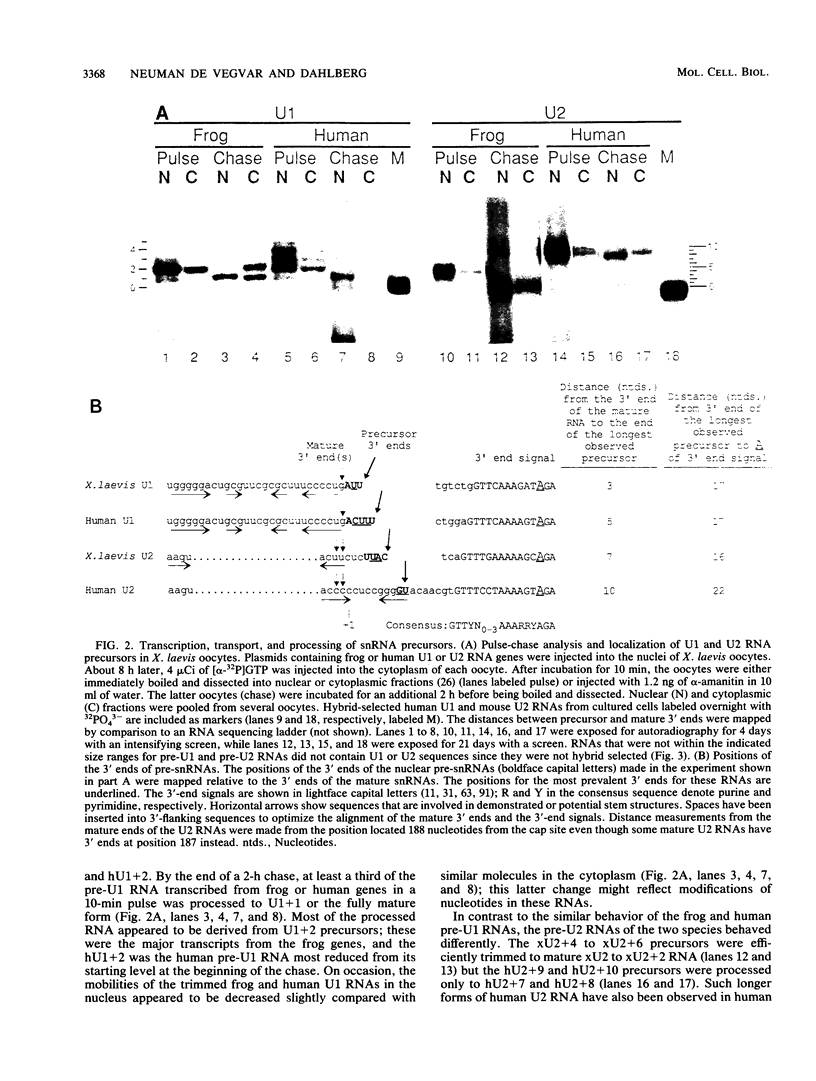
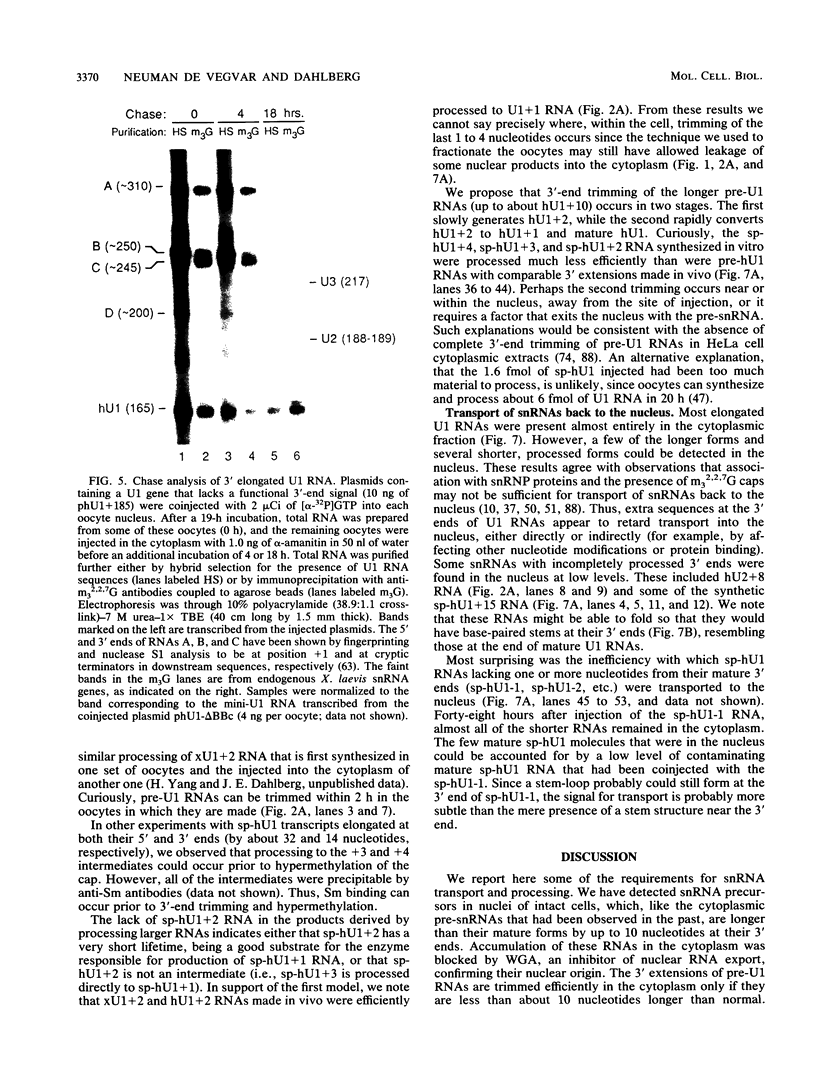
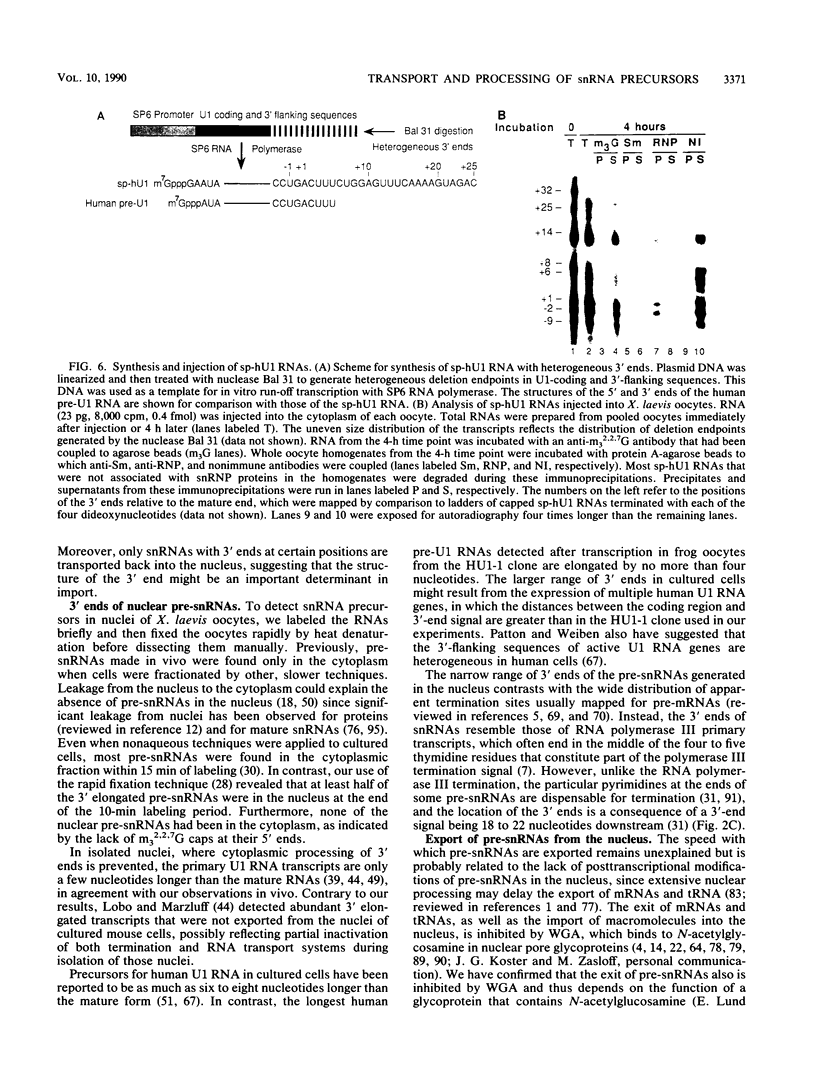
We have analyzed the structures and locations of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) precursors at various stages in their synthesis and maturation. In the nuclei of pulse-labeled Xenopus laevis oocytes, we detected snRNAs that were longer than their mature forms at their 3' ends by up to 10 nucleotides. Analysis of the 5' caps of these RNAs and pulse-chase experiments showed that these nuclear snRNAs were precursors of the cytoplasmic pre-snRNAs that have been observed in the past. Synthesis of pre-snRNAs was not abolished by wheat germ agglutinin, which inhibits export of the pre-snRNAs from the nucleus, indicating that synthesis of these RNAs is not obligatorily coupled to their export. Newly synthesized U1 RNAs could be exported from the nucleus regardless of the length of the 3' extension, but pre-U1 RNAs that were elongated at their 3' ends by more than about 10 nucleotides were poor substrates for trimming in the cytoplasm. The structure at the 3' end was critical for subsequent transport of the RNA back to the nucleus. This requirement ensures that truncated and incompletely processed U1 RNAs are excluded from the nucleus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod V. D., Kramer F. R. Transcription from bacteriophage T7 and SP6 RNA polymerase promoters in the presence of 3'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate chain terminators. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5716–5723. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglia F. A., Maul G. G. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein release and nucleoside triphosphatase activity are inhibited by antibodies directed against one nuclear matrix glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Gallinaro H., Lazar E., Jacob M. The conformation of chicken, rat and human U1A RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):841–858. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Haendler B., Jacob M. U2 RNA shares a structural domain with U1, U4, and U5 RNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharappa S. C., Smith J. H., Eliceiri G. L. Biosynthesis of small nuclear RNAs in human cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Nov;117(2):169–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dathan N., Frank R., Philipson L., Mattaj I. W. Formation of the 3' end on U snRNAs requires at least three sequence elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Feldherr C. M., Smuckler E. A. Nucleocytoplasmic RNA transport. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Jul;67(2):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02370167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone D. E., Keene J. D. Viral transcription is necessary and sufficient for vesicular stomatitis virus to inhibit maturation of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4172–4180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4172-4180.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Schulz B., Scheer U., Peters R. Inhibition of nuclear accumulation of karyophilic proteins in living cells by microinjection of the lectin wheat germ agglutinin. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Lienhard S., Parisot R. F. Intracellular transport of microinjected 5S and small nuclear RNAs. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):572–577. doi: 10.1038/295572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L. Formation of low molecular weight RNA species in HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Feb;102(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L., Sayavedra M. S. Small RNAs in the nucleus and cytoplasm of HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):507–512. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Busch H. Site-specific cleavage by T1 RNase of U-1 RNA in u-1 ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney R. J., Sauterer R. A., Feeney J. L., Zieve G. W. Cytoplasmic assembly and nuclear accumulation of mature small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5776–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kornberg T. B., Kirschner M. W. Small nuclear RNA transcription and ribonucleoprotein assembly in early Xenopus development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):62–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco L. D., Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. Rapid inhibition of processing and assembly of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins after infection with vesicular stomatitis virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A., Parisot R., Newmeyer D., De Robertis E. M. Small nuclear U-ribonucleoproteins in Xenopus laevis development. Uncoupled accumulation of the protein and RNA components. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O., Mous J., Birnstiel M. L. Processing and nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of histone gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8539–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilloud E., Clarkson S. G. A dispersed tyrosine tRNA gene from Xenopus laevis with high transcriptional activity in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):486–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr, Eliceiri G. L. Intracellular distribution of low molecular weight RNA species in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):398–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA is directed by a conserved sequence located downstream of the coding region. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1827–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt A. M., Patton J. R., Pederson T. U2 small nuclear RNP assembly in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4817–4828. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt A. M., Pederson T. Accurate and efficient 3' processing of U2 small nuclear RNA precursor in a fractionated cytoplasmic extract. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3131–3137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings D. A., Mattaj I. W. Mutant U2 snRNAs of Xenopus which can form an altered higher order RNA structure are unable to enter the nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Oct;172(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. The two embryonic U1 RNA genes of Xenopus laevis have both common and gene-specific transcription signals. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription boundaries of U1 small nuclear RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2332–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Sri-Widada J., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Structural organization of ribonucleoproteins containing small nuclear RNAs from HeLa cells. Proteins interact closely with a similar structural domain of U1, U2, U4 and U5 small nuclear RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):623–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Marzluff W. F. Synthesis of U1 RNA in isolated mouse cell nuclei: initiation and 3'-end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4290–4296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Bostock C. J., Dahlberg J. E. The transcription of Xenopus laevis embryonic U1 snRNA genes changes when oocytes mature into eggs. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):47–56. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. In vitro synthesis of vertebrate U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):287–292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. True genes for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Copy number, polymorphism, and methylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2013–2021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore S. J., Wieben E. D., Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Precursors of U4 small nuclear RNA. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1140–1144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore S. J., Wieben E. D., Pederson T. Intracellular site of U1 small nuclear RNA processing and ribonucleoprotein assembly. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):188–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Zeller R. Xenopus laevis U2 snRNA genes: tandemly repeated transcription units sharing 5' and 3' flanking homology with other RNA polymerase II transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Schopfer K., Wilhelm J. A., Nyffenegger T., Parisot R. F., De Robertis E. M. Molecular characterization of ribonucleoprotein antigens bound by antinuclear antibodies. A diagnostic evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1283. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munns T. W., Liszewski M. K., Tellam J. T., Sims H. F., Rhoads R. E. Antibody-nucleic acid complexes. Immunospecific retention of globin messenger ribonucleic acid with antibodies specific for 7-methylguanosine. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):2922–2928. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Transcription of a gene for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Smith F. I., Palese P. Rapid RNA sequencing using double-stranded template DNA, SP6 polymerase, and 3'-deoxynucleotide triphosphates. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):167–171. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. G., Wieben E. D. U1 precursors: variant 3' flanking sequences are transcribed in human cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):175–182. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Patterson R. J., Pederson T. Reconstitution of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4030–4037. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R. Compilation of small RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r61–r72. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wolin S., Guthrie C. A subset of yeast snRNA's contains functional binding sites for the highly conserved Sm antigen. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):328–331. doi: 10.1126/science.2948278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohleder A., Wieben E. Solid-phase processing of U2 snRNA precursors. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):5910–5914. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauterer R. A., Feeney R. J., Zieve G. W. Cytoplasmic assembly of snRNP particles from stored proteins and newly transcribed snRNA's in L929 mouse fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jun;176(2):344–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Bachmann M., Diehl-Seifert B., Müller W. E. Transport of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1987;34:89–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Falke D., Weise K., Bachmann M., Carmo-Fonseca M., Zaubitzer T., Müller W. E. Change of processing and nucleocytoplasmic transport of mRNA in HSV-1-infected cells. Virus Res. 1989 May;13(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Friese U., Bachmann M., Zaubitzer T., Müller W. E. Energy requirement and kinetics of transport of poly(A)-free histone mRNA compared to poly(A)-rich mRNA from isolated L-cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):149–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Gouilloud E., Clarkson S. G. Oocyte and somatic tyrosine tRNA genes in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1190–1198. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian J. A., Drinkard L., Zasloff M. tRNA nuclear transport: defining the critical regions of human tRNAimet by point mutagenesis. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Mattaj I. W. Fungal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins share properties with plant and vertebrate U-snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):469–476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Pettersson U., Dahlberg J. E. Human U2 and U1 RNA genes use similar transcription signals. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3295–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. Properties of a distal regulatory element controlling transcription of the U2 small nuclear RNA. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. Protein binding sites are conserved in U1 small nuclear RNA from insects and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1217–1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Nenninger J. M., Pederson T. Ribonucleoprotein organization of eukaryotic RNA. XXXII. U2 small nuclear RNA precursors and their accurate 3' processing in vitro as ribonucleoprotein particles. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff B., Willingham M. C., Hanover J. A. Nuclear protein import: specificity for transport across the nuclear pore. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):318–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Imamoto-Sonobe N., Yamaizumi M., Uchida T. Reversible inhibition of protein import into the nucleus by wheat germ agglutinin injected into cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Dec;173(2):586–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Sequences required for 3' end formation of human U2 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W. Cytoplasmic maturation of the snRNAs. J Cell Physiol. 1987 May;131(2):247–254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A., Feeney R. J. Newly synthesized small nuclear RNAs appear transiently in the cytoplasm. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Subnuclear particles containing a small nuclear RNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):501–523. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]