Abstract
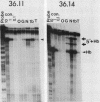
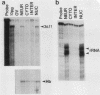
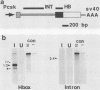
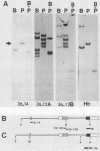
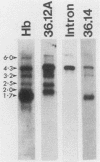
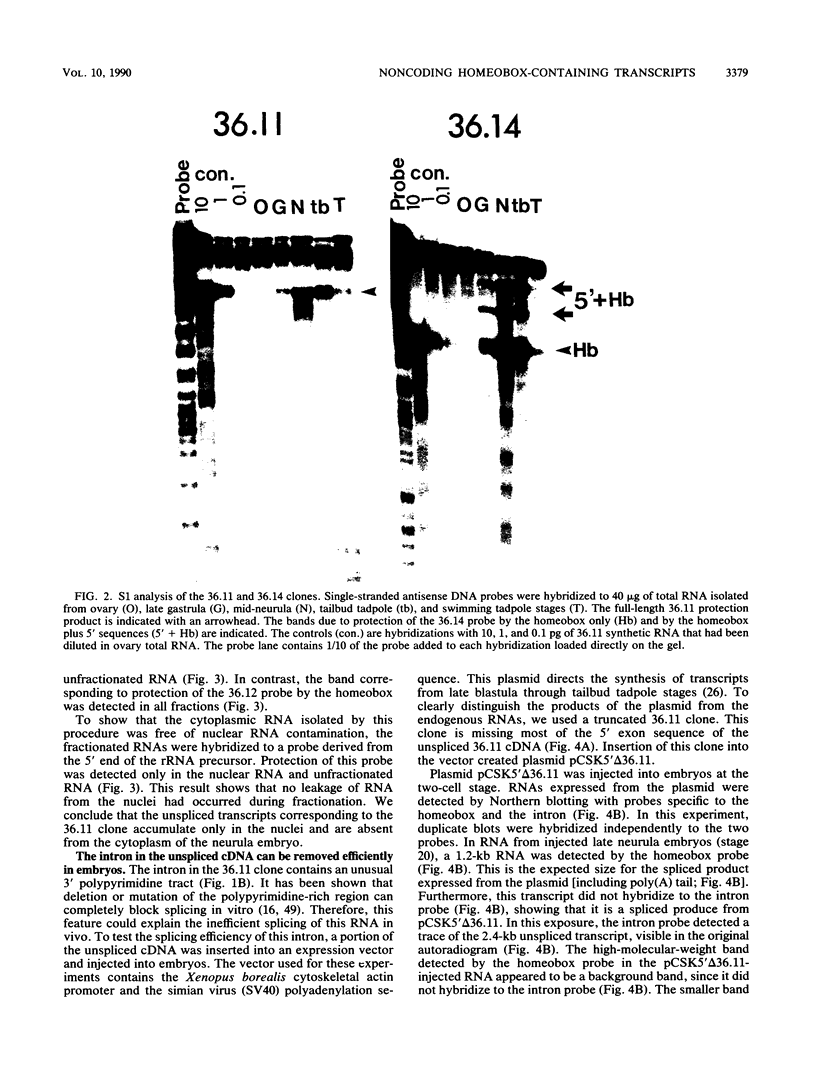
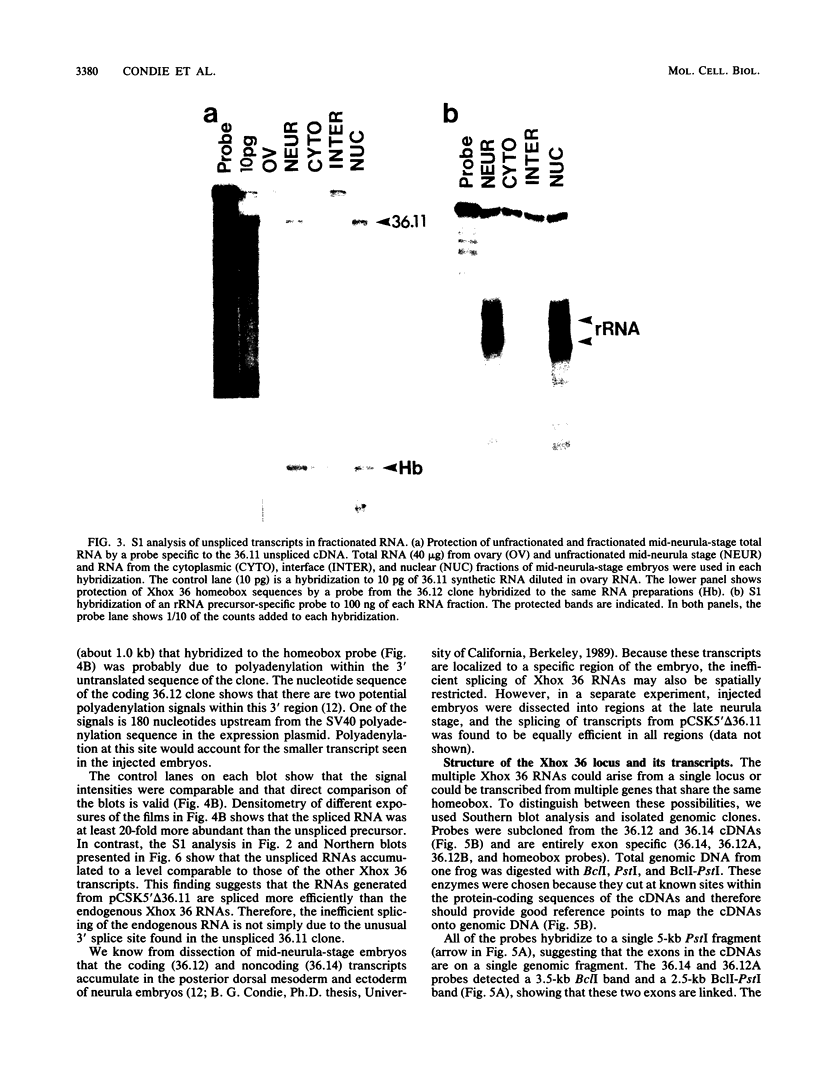
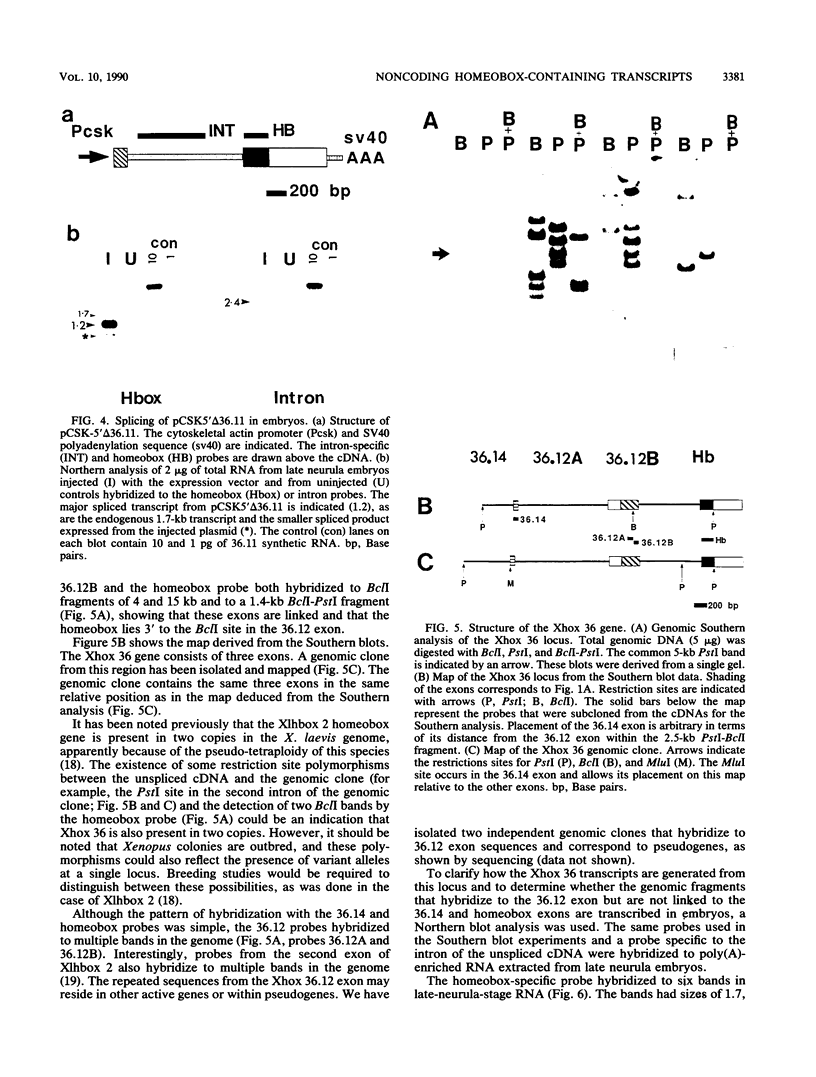
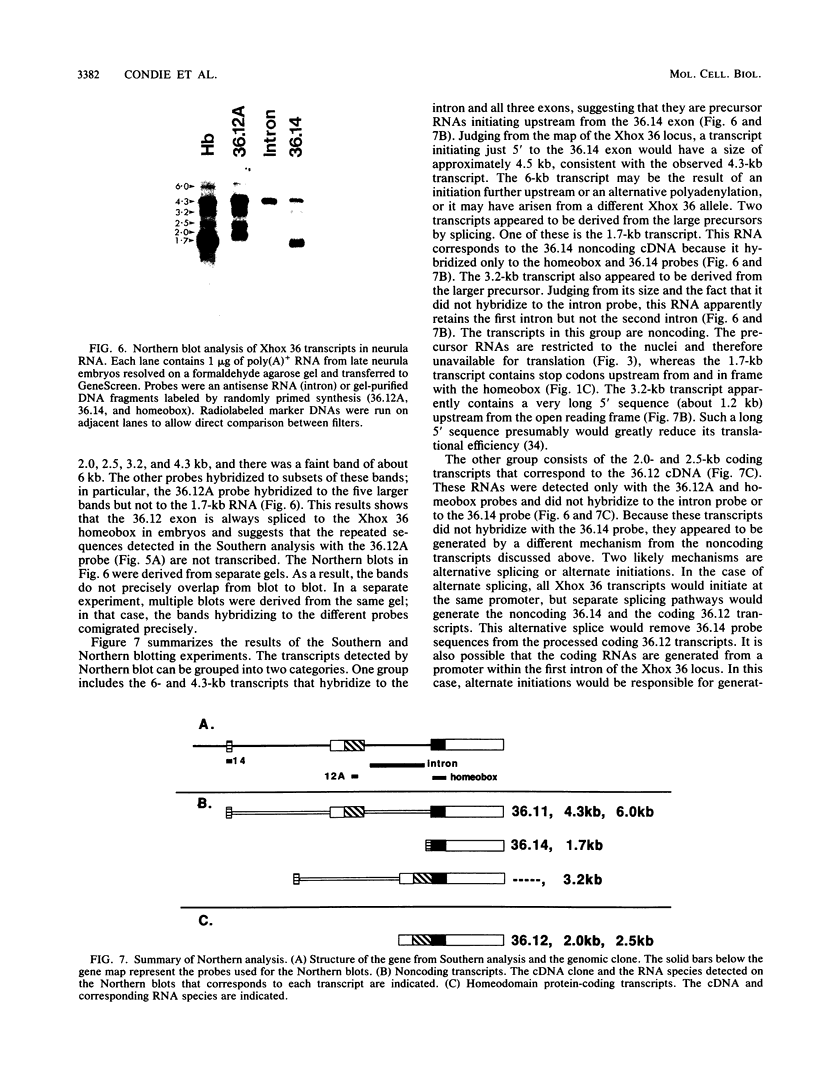
Multiple Xhox 36 transcripts accumulate in Xenopus embryos from gastrula to early tadpole stages. The transcripts were characterized by sequencing cDNA clones and by S1 protection and Northern (RNA) blotting of embryonic RNA with probes derived from the cDNAs. The Xhox 36 RNAs included unspliced precursor transcripts that accumulated in the embryonic nuclei, spliced transcripts that contained multiple stop codons in frame with the homeobox, and less abundant coding mRNAs. These transcripts were generated either by alternative splicing or multiple initiations from a single Xhox 36 gene. The sequence of a cDNA clone of the unspliced transcript showed that the intron contained a noncanonical 3' splice site. However, the intron was spliced efficiently when expressed from a plasmid injected into Xenopus embryos, suggesting that the inefficient splicing of the endogenous RNA is not due to the unusual 3' splice site. The accumulation of noncoding and unspliced transcripts suggests multiple levels of regulation in the embryonic expression of the Xhox 36 gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balling R., Mutter G., Gruss P., Kessel M. Craniofacial abnormalities induced by ectopic expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1.1 in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Featherstone M. S., Hill R. E., Hall A., Galliot B., Duboule D. Hox-1.6: a mouse homeo-box-containing gene member of the Hox-1 complex. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2977–2986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermingham J. R., Jr, Scott M. P. Developmentally regulated alternative splicing of transcripts from the Drosophila homeotic gene Antennapedia can produce four different proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3211–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs R. T., Gregor P., Idriss S., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Regulation of sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster via alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):739–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brivanlou A. H., Harland R. M. Expression of an engrailed-related protein is induced in the anterior neural ectoderm of early Xenopus embryos. Development. 1989 Jul;106(3):611–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Fate of amplified nucleoli in Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):458–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M. Translational control in homoeobox mRNAs? Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):701–702. doi: 10.1038/330701c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., Malacinski G. M. Localization of Xenopus homoeo-box gene transcripts during embryogenesis and in the adult nervous system. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Goetz J., Wright C. V., Fritz A., Hardwicke J., De Robertis E. M. Differential utilization of the same reading frame in a Xenopus homeobox gene encodes two related proteins sharing the same DNA-binding specificity. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2139–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Püschel A. W., Dony C., Voss S. D., Gruss P. Post-transcriptional regulation of a murine homeobox gene transcript in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Differentiation. 1987;35(3):206–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie B. G., Harland R. M. Posterior expression of a homeobox gene in early Xenopus embryos. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):93–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Oliver G., Wright C. V. Determination of axial polarity in the vertebrate embryo: homeodomain proteins and homeogenetic induction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A. F., Cho K. W., Wright C. V., Jegalian B. G., De Robertis E. M. Duplicated homeobox genes in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;131(2):584–588. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A. F., Martin G., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M. Site-specific inversions in repeated Xenopus laevis homeobox gene 2 sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9058–9058. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A., De Robertis E. M. Xenopus homeobox-containing cDNAs expressed in early development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1453–1469. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J. Homoeobox gene Hox-1.5 expression in mouse embryos: earliest detection by in situ hybridization is during gastrulation. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Miller J. R., Powell D. J., Duboule D. Homoeobox gene expression in mouse embryos varies with position by the primitive streak stage. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):662–664. doi: 10.1038/324662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J. Mouse homeobox gene transcripts occupy different but overlapping domains in embryonic germ layers and organs: a comparison of Hox-3.1 and Hox-1.5. Development. 1988 May;103(1):135–144. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Lorimer J., McVey J. H., Tuddenham E. G., Krumlauf R. Characterization of a murine homeo box gene, Hox-2.6, related to the Drosophila Deformed gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1424–1438. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Fairman S., Mohun T. J., Brennan S. Activation of muscle-specific actin genes in Xenopus development by an induction between animal and vegetal cells of a blastula. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):913–922. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Misher L. Stability of RNA in developing Xenopus embryos and identification of a destabilizing sequence in TFIIIA messenger RNA. Development. 1988 Apr;102(4):837–852. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Microinjection of synthetic Xhox-1A homeobox mRNA disrupts somite formation in developing Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):687–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Tabin C. J., Melton D. A. Embryonic expression and nuclear localization of Xenopus homeobox (Xhox) gene products. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1237–1244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Expression of homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):773–782. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Spatially restricted patterns of expression of the homeobox-containing gene Hox 2.1. during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):159–174. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Open reading frames and translational control. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):117–118. doi: 10.1038/332117c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld K., Saint R. B., Beachy P. A., Harte P. J., Peattie D. A., Hogness D. S. Structure and expression of a family of Ultrabithorax mRNAs generated by alternative splicing and polyadenylation in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):243–258. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A profusion of controls. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):1–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Developmental regulation of a gastrula-specific gene injected into fertilized Xenopus eggs. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3463–3471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Different transcripts of the Drosophila Abd-B gene correlate with distinct genetic sub-functions. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3233–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Early retinoic acid-induced F9 teratocarcinoma stem cell gene ERA-1: alternate splicing creates transcripts for a homeobox-containing protein and one lacking the homeobox. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3906–3917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon G. G., Perry R. P. C mu-containing transcripts initiate heterogeneously within the IgH enhancer region and contain a novel 5'-nontranslatable exon. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):475–478. doi: 10.1038/318475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshitz H. D., Peattie D. A., Hogness D. S. Novel transcripts from the Ultrabithorax domain of the bithorax complex. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):307–322. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Belote J. M., Boggs R. T. Ectopic expression of the female transformer gene product leads to female differentiation of chromosomally male Drosophila. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):887–895. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Brennan S., Dathan N., Fairman S., Gurdon J. B. Cell type-specific activation of actin genes in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):716–721. doi: 10.1038/311716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. M. Mix.1, a homeobox mRNA inducible by mesoderm inducers, is expressed mostly in the presumptive endodermal cells of Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):965–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Bimodal and graded expression of the Xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 during embryonic development. Development. 1989 May;106(1):173–183. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Involvement of the Xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 in pattern formation along the anterior-posterior axis. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Role of the 3' splice site consensus sequence in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):732–734. doi: 10.1038/317732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe C. R., Fritz A., De Robertis E. M., Gurdon J. B. A homeobox-containing marker of posterior neural differentiation shows the importance of predetermination in neural induction. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe P. T., Miller J. R., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Gaunt S. J. Isolation and expression of a new mouse homeobox gene. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):397–407. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.2.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Pannese M., Acampora D., D'Esposito M., Boncinelli E. At least three human homeoboxes on chromosome 12 belong to the same transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5379–5390. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher V. L., Gaiser J. C., Garber R. L. Alternative RNA splicing that is spatially regulated: generation of transcripts from the Antennapedia gene of Drosophila melanogaster with different protein-coding regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4143–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Behringer R. R., Mostoller M. P., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice overexpressing the mouse homoeobox-containing gene Hox-1.4 exhibit abnormal gut development. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):464–467. doi: 10.1038/337464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Fritz A., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. A Xenopus laevis gene encodes both homeobox-containing and homeobox-less transcripts. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4083–4094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Hardwicke J., Collins R. H., De Robertis E. M. Interference with function of a homeobox gene in Xenopus embryos produces malformations of the anterior spinal cord. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90871-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Oliver G., De Robertis E. M. Vertebrate homeodomain proteins: families of region-specific transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Banerji J., Schaffner W. Analysis of the transcriptional enhancer effect. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):911–919. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]