Abstract
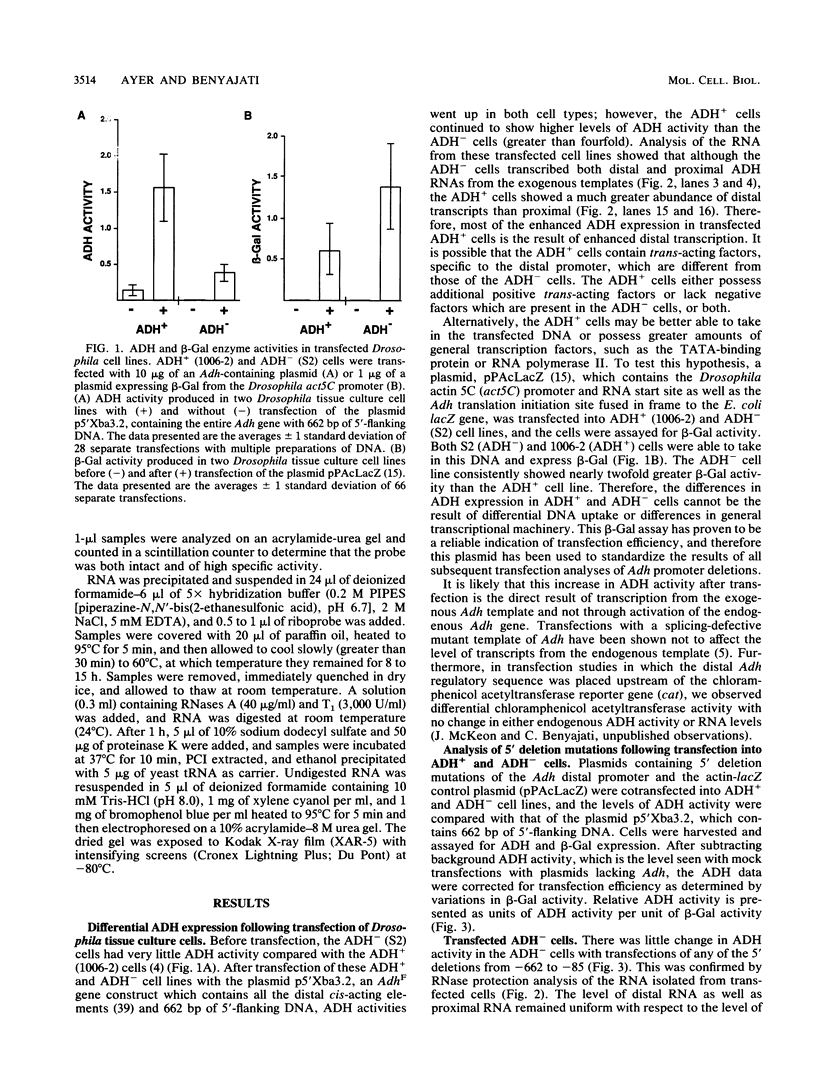
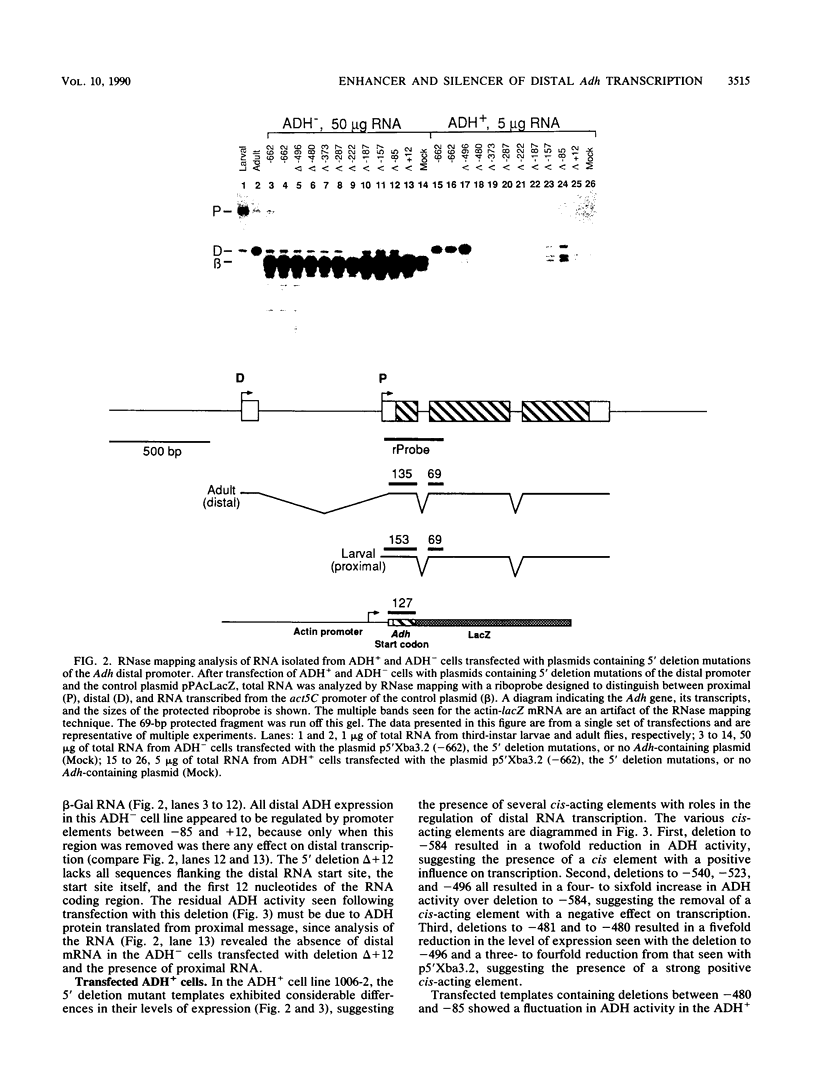
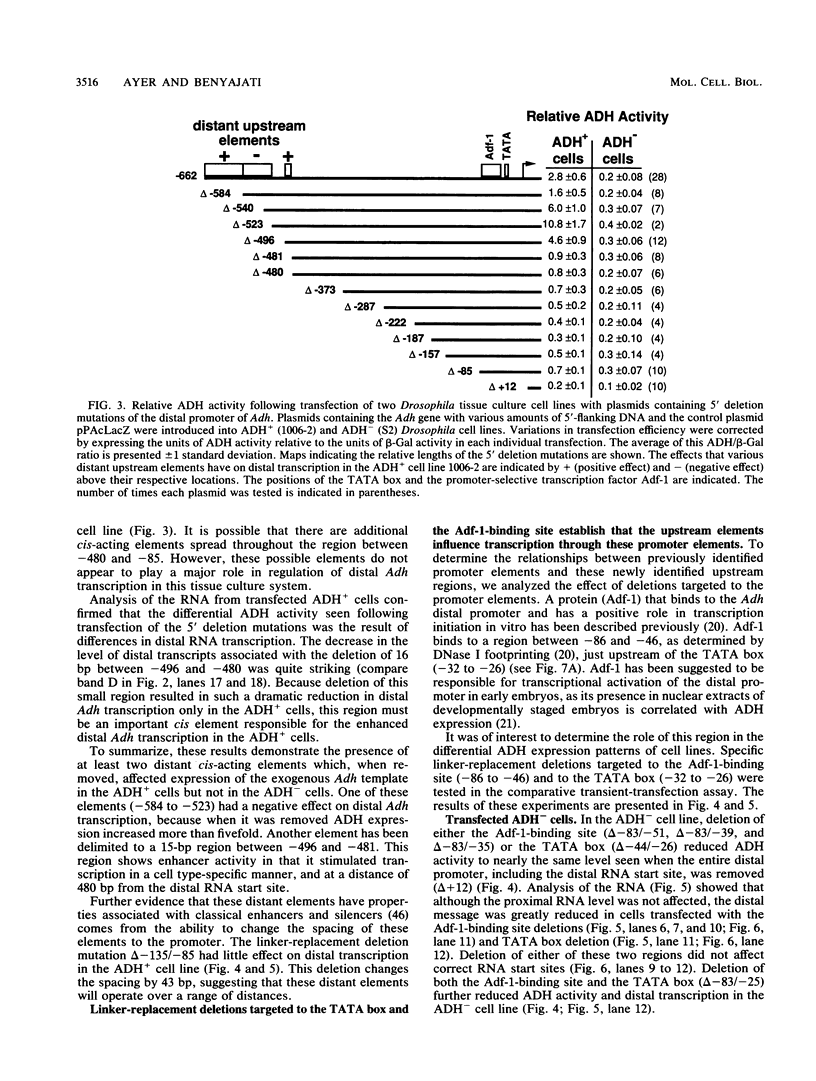
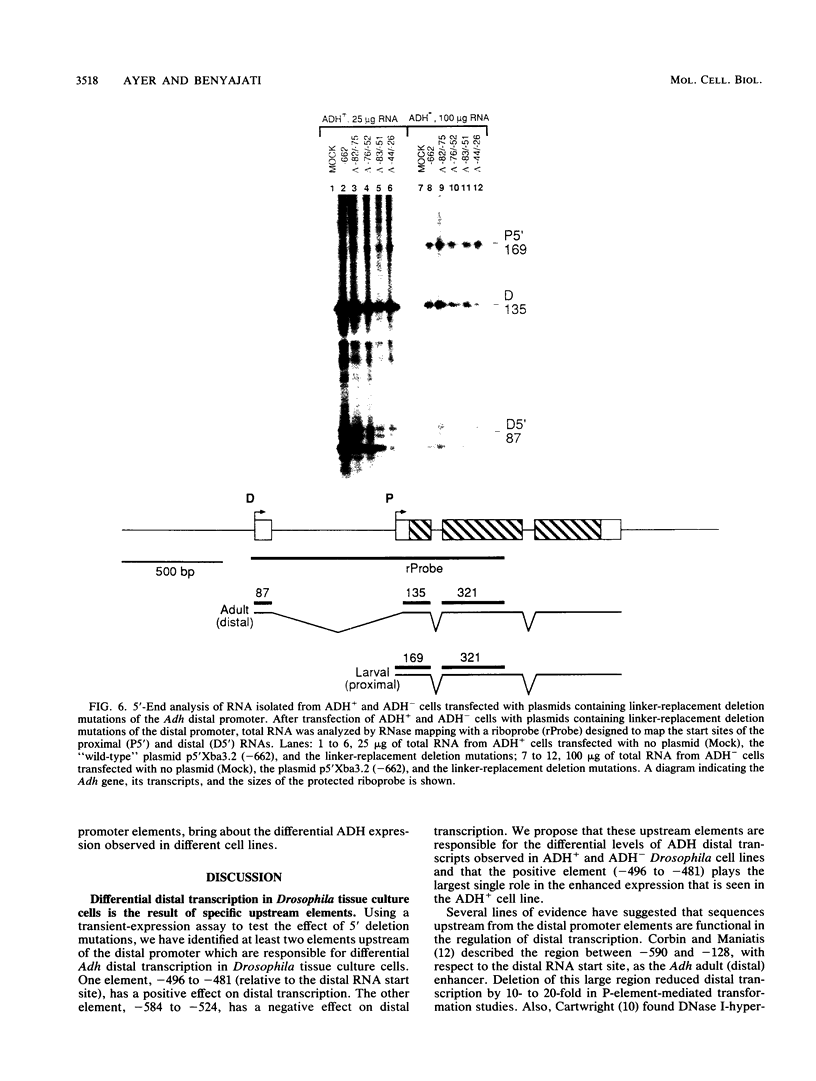
The distal promoter of Adh is differentially expressed in Drosophila tissue culture cell lines. After transfection with an exogenous Adh gene, there was a specific increase in distal alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) transcripts in ADH-expressing (ADH+) cells above the levels observed in transfected ADH-nonexpressing (ADH-) cells. We used deletion mutations and a comparative transient-expression assay to identify the cis-acting elements responsible for enhanced Adh distal transcription in ADH+ cells. DNA sequences controlling high levels of distal transcription were localized to a 15-base-pair (bp) region nearly 500 bp upstream of the distal RNA start site. In addition, a 61-bp negative cis-acting element was found upstream from and adjacent to the enhancer. When this silencer element was deleted, distal transcription increased only in the ADH+ cell line. These distant upstream elements must interact with the promoter elements, the Adf-1-binding site and the TATA box, as they only influenced transcription when at least one of these two positive distal promoter elements was present. Internal deletions targeted to the Adf-1-binding site or the TATA box reduced transcription in both cell types but did not affect the transcription initiation site. Distal transcription in transfected ADH- cells appears to be controlled primarily through these promoter elements and does not involve the upstream regulatory elements. Evolutionary conservation in distantly related Drosophila species suggests the importance of these upstream elements in correct developmental and tissue-specific expression of ADH.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson P. W., Mills L. E., Starmer W. T., Sullivan D. T. Structure and evolution of the Adh genes of Drosophila mojavensis. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):713–723. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Ayer S., McKeon J., Ewel A., Huang J. Roles of cis-acting elements and chromatin structure in Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7903–7920. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Dray J. F. Cloned Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase genes are correctly expressed after transfection into Drosophila cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1701–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. D., Dickinson W. J. Complex developmental regulation of the Drosophila affinidisjuncta alcohol dehydrogenase gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. D., Rowan R. G., Rabinow L., Dickinson W. J. Isolation and initial characterization of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene from Drosophila affinidisjuncta. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):436–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L. Developmental switch in chromatin structure associated with alternate promoter usage in the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3097–3101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Identification of cis-regulatory elements required for larval expression of the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):637–646. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Role of transcriptional interference in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh promoter switch. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):279–282. doi: 10.1038/337279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. The role of specific enhancer-promoter interactions in the Drosophila Adh promoter switch. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2191–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewel A., Jackson J. R., Benyajati C. Alternative DNA-protein interactions in variable-length internucleosomal regions associated with Drosophila Adh distal promoter expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1771–1781. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Regulatory elements involved in Drosophila Adh gene expression are conserved in divergent species and separate elements mediate expression in different tissues. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Drosophila nuclear proteins bind to regions of alternating C and T residues in gene promoters. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1487–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2781290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Tjian R. Temporal pattern of alcohol dehydrogenase gene transcription reproduced by Drosophila stage-specific embryonic extracts. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):410–415. doi: 10.1038/331410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Complexities of gene regulation by cAMP. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Heberlein U., Ashburner M. The Adh gene promoters of Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila orena are functionally conserved and share features of sequence structure and nuclease-protected sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moye-Rowley W. S., Harshman K. D., Parker C. S. Yeast YAP1 encodes a novel form of the jun family of transcriptional activator proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):283–292. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. In vitro analysis of the Antennapedia P2 promoter: identification of a new Drosophila transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1615–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. Novel Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologous to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4265–4273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for the regulation of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:515–520. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. G., Brennan M. D., Dickinson W. J. Developmentally regulated RNA transcripts coding for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila affinidisjuncta. Genetics. 1986 Oct;114(2):405–433. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. G., Dickinson W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic region encoding alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila affinidisjuncta. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):43–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02143496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. How do different transcription factors binding the same DNA sequence sort out their jobs? Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simcox A. A., Sobeih M. M., Shearn A. Establishment and characterization of continuous cell lines derived from temperature-sensitive mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01534735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofer W., Martin P. F. Analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:203–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.3399892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Factor substitution in a human HSP70 gene promoter: TATA-dependent and TATA-independent interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Porton B., Shen L. Y., Eckhardt L. A. Role of the octamer motif in hybrid cell extinction of immunoglobulin gene expression: extinction is dominant in a two enhancer system. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]