Abstract
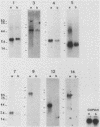
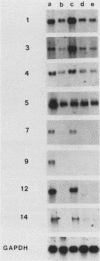
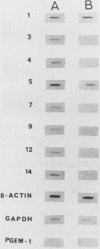
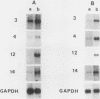
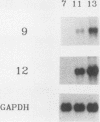
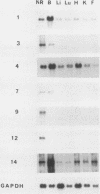
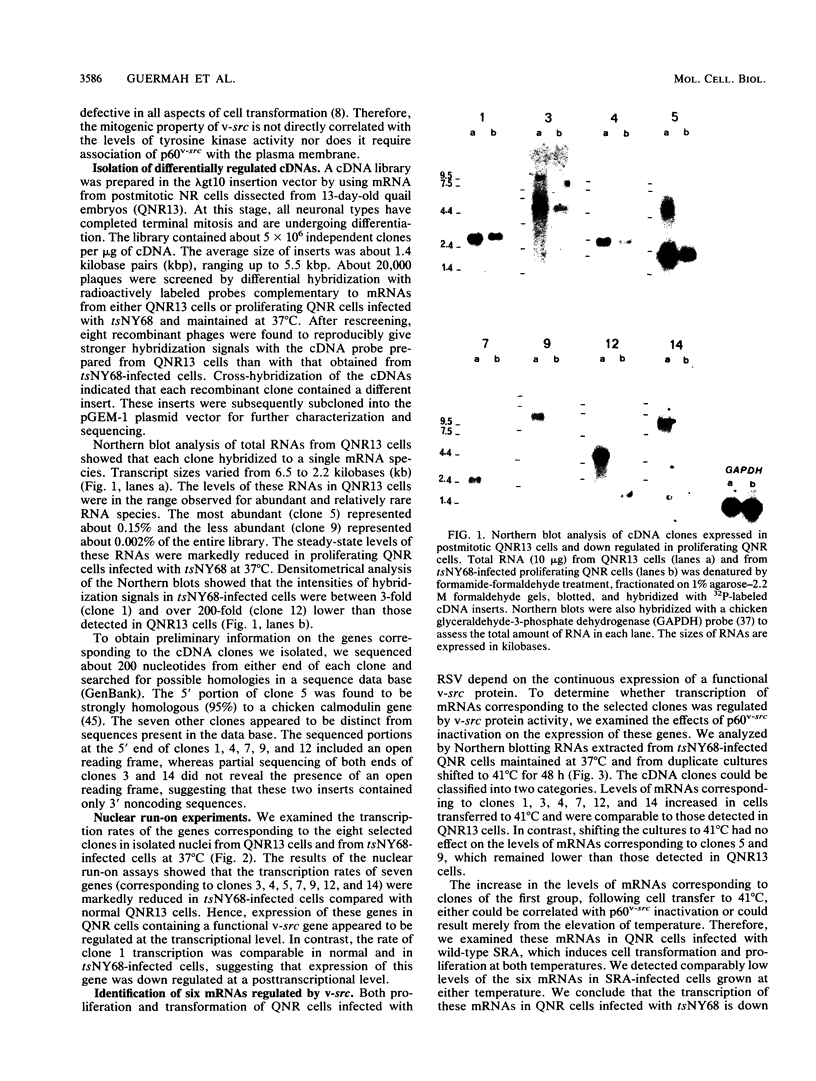
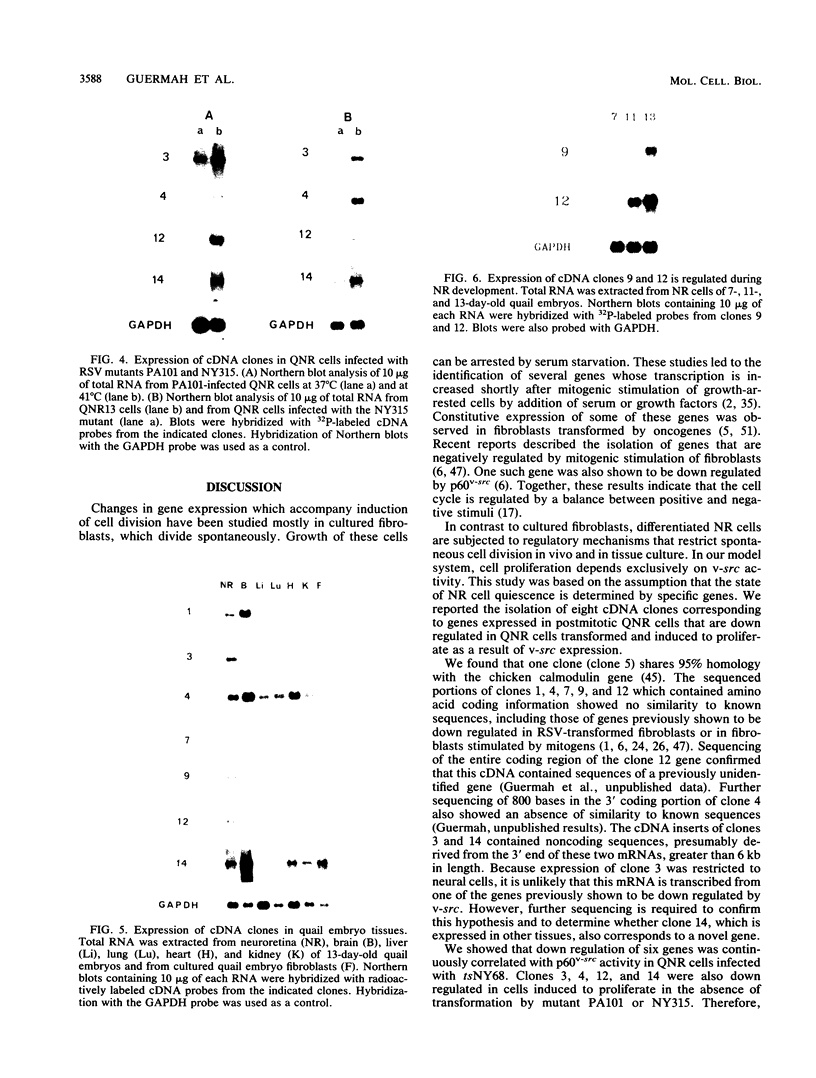
The avian neuroretina (NR) is composed of photoreceptors and different neurons that are derived from proliferating precursor cells. Neuronal differentiation takes place after terminal mitosis. We have previously shown that differentiating NR cells can be induced to proliferate by infection with Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and that cell multiplication requires expression of a functional v-src gene. We speculated that the quiescence of NR cells could be determined by specific genes. Cell proliferation could then result from the negative regulation of these genes by the v-src protein. By differential hybridization of a cDNA library, we isolated eight clones corresponding to genes expressed in postmitotic NR cells from 13-day-old quail embryos, transcriptional levels of which are significantly reduced in NR cells induced to proliferate by tsNY68, an RSV mutant with temperature-sensitive mitogenic activity. Partial sequencing analysis indicated that one RNA encoded the calmodulin gene, whereas the other seven showed no similarity to known sequences. By using v-src mutants that induce NR cell proliferation in the absence of transformation, we showed that transcription of six genes was negatively regulated by the v-src protein and that of four genes was correlated with NR cell quiescence. We also report that a subset of genes are specifically transcribed in neural cells and developmentally regulated in the NR. These results indicate that the v-src protein regulates expression of genes likely to play a role in the control of neural cell growth or differentiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Alwine J. C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Use of recombinant plasmids to characterize collagen RNAs in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4935–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P. A., Alcorta D., Simmons D. L., Luk K. C., Erikson R. L. Constitutive expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide homologous to biologically active human platelet protein in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P. A., Yannoni Y., Simmons D. L., Erikson R. L. Rapid repression of quiescence-specific gene expression by epidermal growth factor, insulin, and pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Laugier D., Cross F. R., Jove R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. The membrane-binding domain and myristylation of p60v-src are not essential for stimulation of cell proliferation. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1678-1681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Pessac B. Growth stimulation of chicl embryo neuroretinal cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus: relationship to viral replication and morphological transformation. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):336–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Poirier F., Dambrine G., Mignatti P., Combes P., Pessac B. Expression of viral oncogenes in differentiating chick embryo neuroretinal cells infected with avian tumor viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):983–990. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Poirier F., Dambrine G., Pessac B. A transformation defective mutant of Rous sarcoma virus inducing chick embryo neuroretinal cell proliferation. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combes P. C., Privat A., Pessac B., Calothy G. Differentiation of chick embryo neuroretina cells in monolayer cultures. An ultrastructural study. I. Seven-day retina. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Dec 13;185(2):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00220661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W., Sager R. Suppression of tumorigenicity in hybrids of normal and oncogene-transformed CHEF cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisanti-Combes P., Lorinet A. M., Girard A., Pessac B., Wasseff M., Calothy G. Expression of neuronal markers in chick and quail embryo neuroretina cultures infected with Rous sarcoma virus. Cell Differ. 1982 Jan;11(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(82)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisanti-Combes P., Pessac B., Calothy G. Choline acetyl transferase activity in chick embryo neuroretinas during development in ovo and in monolayer cultures. Dev Biol. 1978 Jul;65(1):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Sobel M. E., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Effects of transformation on fibronectin gene expression using cloned fibronectin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks M., Weintraub H. Multiple tropomyosin polypeptides in chicken embryo fibroblasts: differential repression of transcription by Rous sarcoma virus transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1823–1833. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Garber E. A., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Biochemical properties of p60v-src mutants that induce different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):849–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.849-857.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Mayer B. J., Iba H., Laugier D., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Genetic analysis of p60v-src domains involved in the induction of different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):840–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.840-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koufos A., Hansen M. F., Lampkin B. C., Workman M. L., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Cavenee W. K. Loss of alleles at loci on human chromosome 11 during genesis of Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):170–172. doi: 10.1038/309170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Identification of a set of genes expressed during the G0/G1 transition of cultured mouse cells. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3145–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R. Expression of the mRNA coding for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jove R., Krane J. F., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa H. Genetic lesions involved in temperature sensitivity of the src gene products of four Rous sarcoma virus mutants. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):858–867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.858-867.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessac B., Calothy G. Transformation of chick embryo neuroretinal cells by Rous sarcoma virus in vitro: induction of cell proliferation. Science. 1974 Aug;185(4152):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4152.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessac B., Girard A., Romey G., Crisanti P., Lorinet A. M., Calothy G. A neuronal clone derived from a Rous sarcoma virus-transformed quail embryo neuroretina established culture. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):616–618. doi: 10.1038/302616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Calothy G., Karess R. E., Erikson E., Hanafusa H. Role of p60src kinase activity in the induction of neuroretinal cell proliferation by rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):780–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.780-789.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Jullien P., Dezelee P., Dambrine G., Esnault E., Benatre A., Calothy G. Role of the mitogenic property and kinase activity of p60src in tumor formation by Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):325–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.325-332.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Ts'ui K. F., Tanaka T., Lagacé L., Stein J. P., Lai E. C., Means A. R. Chicken calmodulin genes. A species comparison of cDNA sequences and isolation of a genomic clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11864–11870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., King R. M., Philipson L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Voss R., Hall V., Bodmer W. F., Jass J. R., Jeffreys A. J., Lucibello F. C., Patel I., Rider S. H. Chromosome 5 allele loss in human colorectal carcinomas. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):616–619. doi: 10.1038/328616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Der C. J., Doersen C. J., Nishimi R. Y., Peehl D. M., Weissman B. E., Wilkinson J. E. Human cell hybrids: analysis of transformation and tumorigenicity. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):252–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7053574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus induces a novel gene with homology to a mitogenic platelet protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]