Abstract
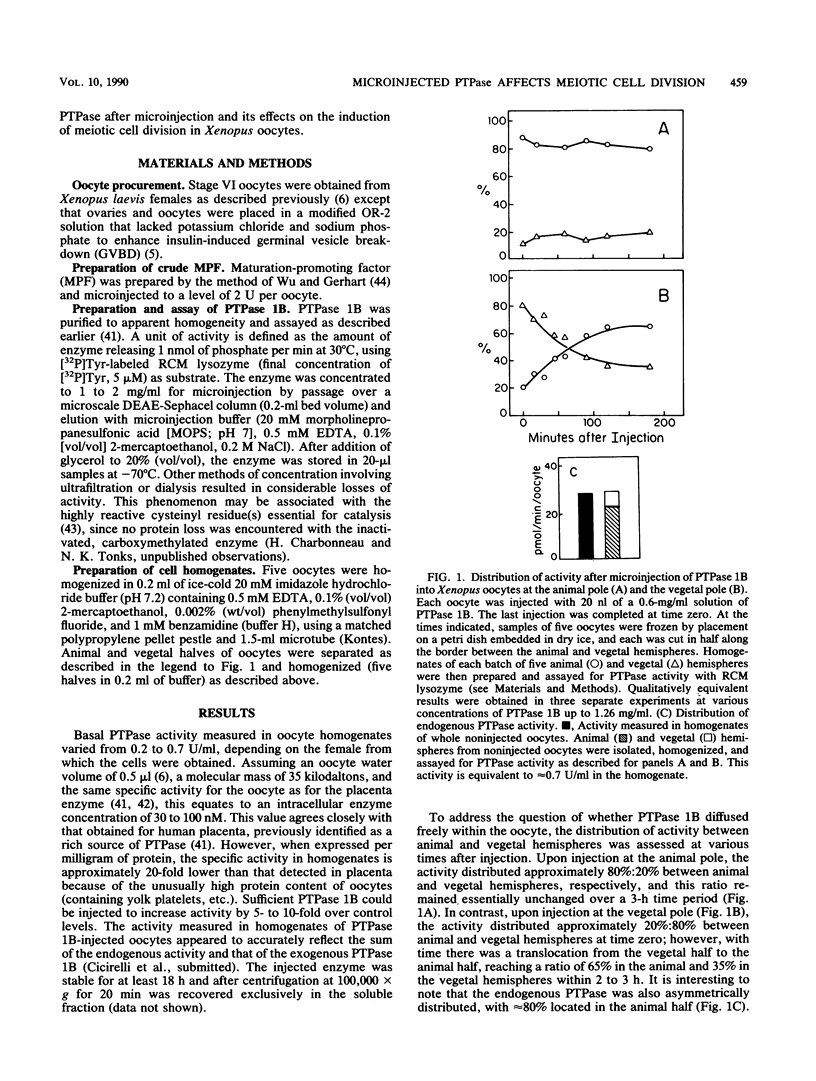
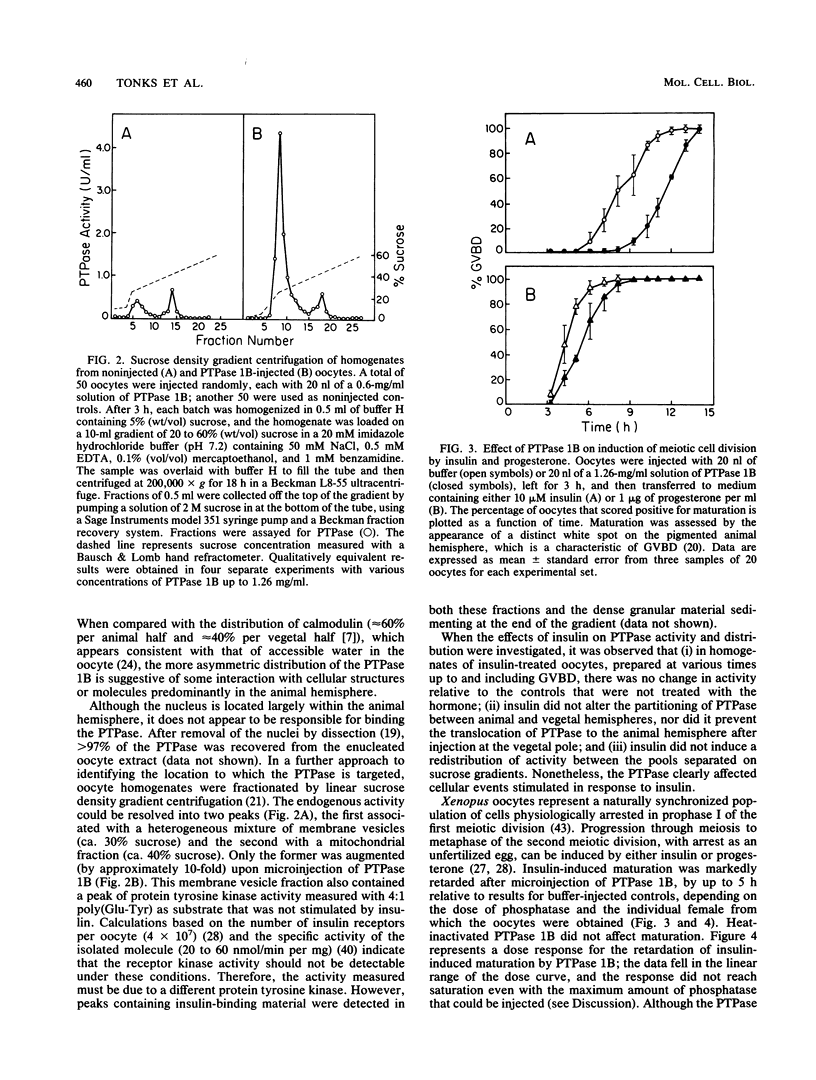
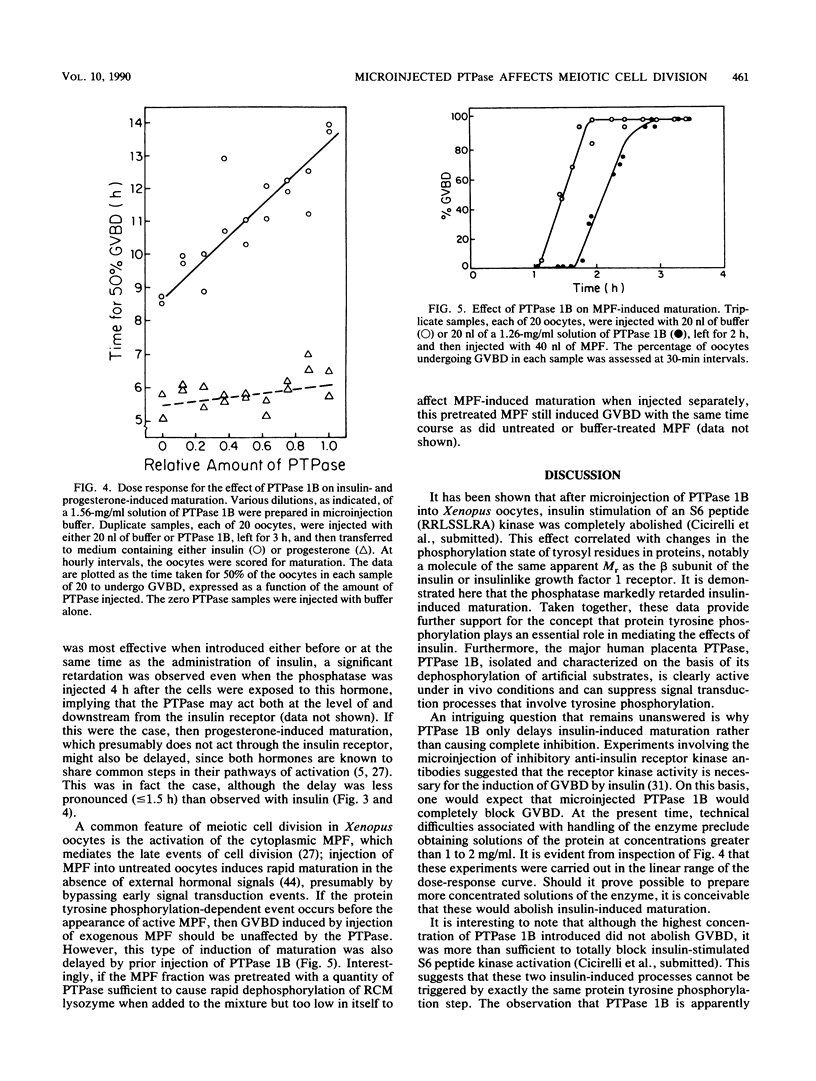
Homogeneous preparations of a protein phosphatase that is specific for phosphotyrosyl residues (protein tyrosine phosphatase [PTPase] 1B) were isolated from human placenta and microinjected into Xenopus oocytes. This resulted in an increase in activity of up to 10-fold over control levels, as measured in homogenates with use of an artificial substrate (reduced carboxamidomethylated and maleylated lysozyme). Microinjected PTPase was stable for at least 18 h. It is distributed within the oocyte in a manner similar to the endogenous activity and is suggestive of an interaction with cellular structures or molecules located predominantly in the animal hemisphere. The phosphatase markedly retarded (by up to 5 h) maturation induced by insulin. This, in conjunction with the demonstration that PTPase 1B abolished insulin stimulation of an S6 peptide (RRLSSLRA) kinase concomitant with a decrease in the phosphorylation of tyrosyl residues in a protein with the same apparent Mr as the beta subunit of the insulin and insulinlike growth factor 1 receptors (M. F. Cicirelli, N. K. Tonks, C. D. Diltz, E. H. Fischer, and E. G. Krebs, submitted for publication), provides further support for an essential role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in insulin action. Furthermore, maturation was significantly retarded even when the PTPase was injected 2 to 4 h after exposure of the cells to insulin. PTPase 1B also retarded maturation induced by progesterone and maturation-promoting factor, which presumably do not act through the insulin receptor. These data point to a second site of action of the PTPase in the pathway of meiotic cell division, downstream of the insulin receptor and following the appearance of active maturation-promoting factor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H. The leukocyte common antigen (CD45): a putative receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Insulin and progesterone activate a common synthetic ribosomal protein S6 peptide kinase in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Robinson K. R., Smith L. D. Internal pH of Xenopus oocytes: a study of the mechanism and role of pH changes during meiotic maturation. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Smith L. D. Calmodulin synthesis and accumulation during oogenesis and maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1986 Jan;113(1):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debant A., Clauser E., Ponzio G., Filloux C., Auzan C., Contreres J. O., Rossi B. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 does not alter the mitogenic effect of the hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8032–8036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor that activate glucose transport but not insulin receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3448–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherzi R., Russell D. S., Taylor S. I., Rosen O. M. Reevaluation of the evidence that an antibody to the insulin receptor is insulinmimetic without activating the protein tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16900–16905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Methods for nuclear transplantation in amphibia. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huchon D., Crozet N., Cantenot N., Ozon R. Germinal vesicle breakdown in the Xenopus laevis oocyte: description of a transient microtubular structure. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1981;21(1):135–148. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19810112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Smith L. D., Richter J., Larkins B. A. Subcellular compartmentalization of maize storage proteins in Xenopus oocytes injected with zein messenger RNAs. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):292–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Lane M. D. Activation of glucose uptake by insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. T., Reynhout J. K., Horowitz S. B. Regional water changes during oocyte meiotic maturation: evidence of ooplasmic segregation. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Kyes J. L., Maller J. L. Metaphase protein phosphorylation in Xenopus laevis eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):760–768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Koontz J. W. A study of the induction of cell division in amphibian oocytes by insulin. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 30;85(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Pike L. J., Freidenberg G. R., Cordera R., Stith B. J., Olefsky J. M., Krebs E. G. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 following microinjection of insulin receptor-kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):459–461. doi: 10.1038/320459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Kaplan J. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of p60c-src by p34cdc2-associated protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):775–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Acute insulin action requires insulin receptor kinase activity: introduction of an inhibitory monoclonal antibody into mammalian cells blocks the rapid effects of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Autophosphorylation and kinase activity of insulin receptor in diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):E542–E550. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.5.E542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. In vivo regulation of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes. Stimulation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10644–10650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Hedo J. A. Insulin receptor phosphorylation may not be a prerequisite for acute insulin action. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1301–1304. doi: 10.1126/science.6367041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Demonstration that the leukocyte common antigen CD45 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8695–8701. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Characterization of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6731–6737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6722–6730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the maturation-promoting factor from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I., Gorden P., Roth J. The role of antireceptor antibodies in stimulating phosphorylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4396–4400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



