Abstract
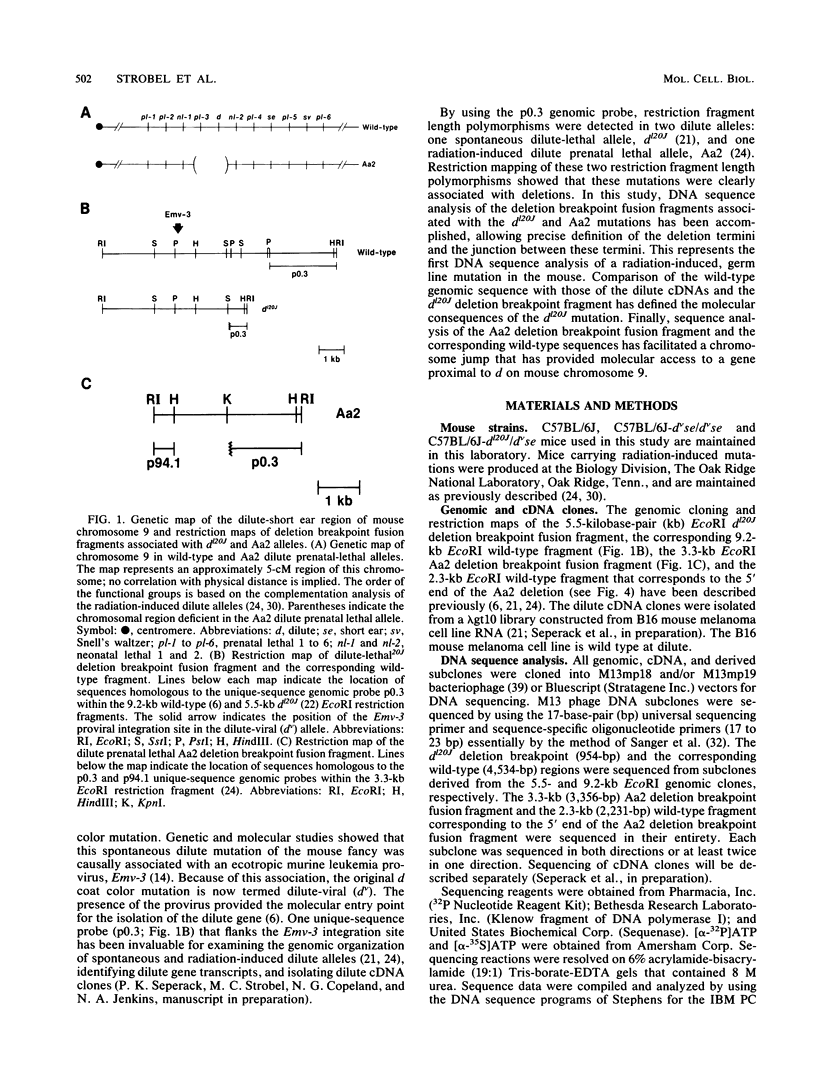
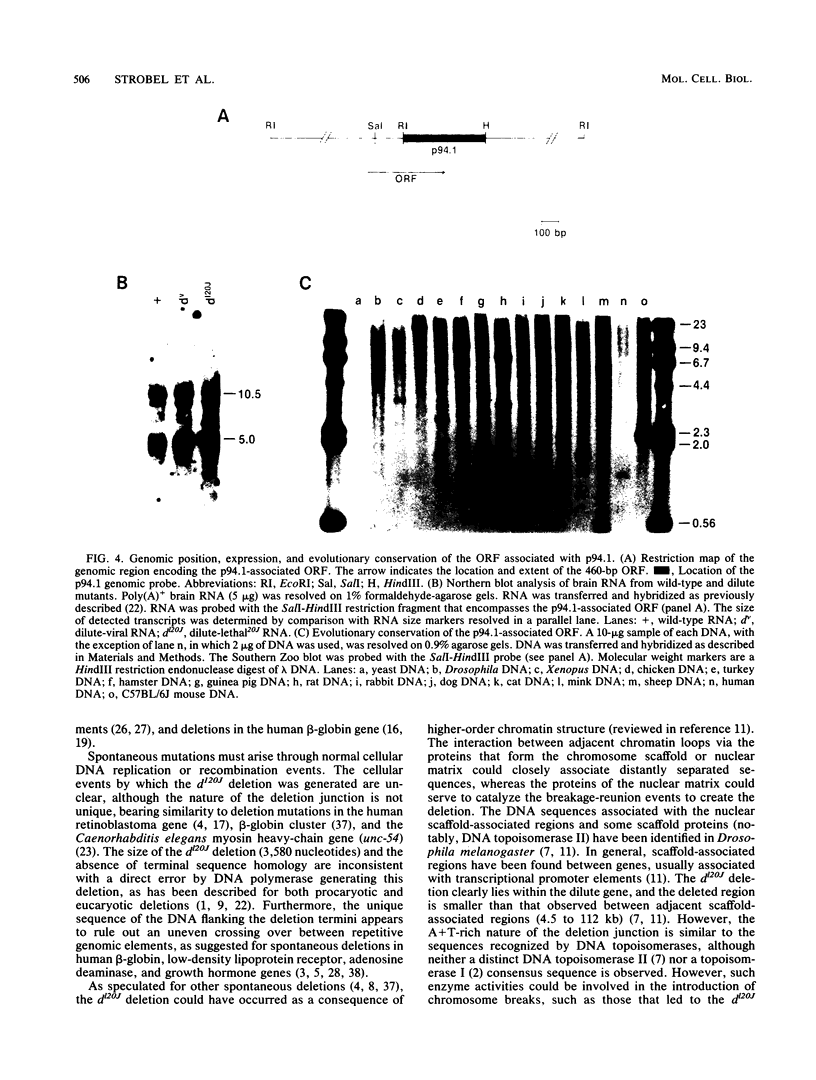
The dilute (d) coat color locus of mouse chromosome 9 has been identified by more than 200 spontaneous and mutagen-induced recessive mutations. With the advent of molecular probes for this locus, the molecular lesion associated with different dilute alleles can be recognized and precisely defined. In this study, two dilute mutations, dilute-lethal20J (dl20J) and dilute prenatal lethal Aa2, have been examined. Using a dilute locus genomic probe in Southern blot analysis, we detected unique restriction fragments in dl20J and Aa2 DNA. Subsequent analysis of these fragments showed that they represented deletion breakpoint fusion fragments. DNA sequence analysis of each mutation-associated deletion breakpoint fusion fragment suggests that both genomic deletions were generated by nonhomologous recombination events. The spontaneous dl20J mutation is caused by an interstitial deletion that removes a single coding exon of the dilute gene. The correlation between this discrete deletion and the expression of all dilute-associated phenotypes in dl20J homozygotes defines the dl20J mutation as a functional null allele of the dilute gene. The radiation-induced Aa2 allele is a multilocus deletion that, by complementation analysis, affects both the dilute locus and the proximal prenatal lethal-3 (pl-3) functional unit. Molecular analysis of the Aa2 deletion breakpoint fusion fragment has provided access to a previously undefined gene proximal to d. Initial characterization of this new gene suggests that it may represent the genetically defined pl-3 functional unit.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkvens T. M., Gerritsen E. J., Oldenburg M., Breukel C., Wijnen J. T., van Ormondt H., Vossen J. M., van der Eb A. J., Meera Khan P. Severe combined immune deficiency due to a homozygous 3.2-kb deletion spanning the promoter and first exon of the adenosine deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9365–9378. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Lee E. Y., Peccei A., Lee W. H. Human retinoblastoma gene: long-range mapping and analysis of its deletion in a breast cancer cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1628–1634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Herrera R. E., Vosberg H. P., Nordheim A. DNA topoisomerase II cleaves at specific sites in the 5' flanking region of c-fos proto-oncogenes in vitro. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2257–2265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Francke U. A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):556–558. doi: 10.1038/329556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosovsky A. J., de Boer J. G., de Jong P. J., Drobetsky E. A., Glickman B. W. Base substitutions, frameshifts, and small deletions constitute ionizing radiation-induced point mutations in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):185–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. W., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Dilute-coat-color locus of mice: nucleotide sequence analysis of the d+2J and d+Ha revertant alleles. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2899–2904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. W., Jones R. W., Wood W. G., Weatherall D. J. Analysis of an inversion within the human beta globin gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2897–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Bookstein R., Young L. J., Lin C. J., Rosenfeld M. G., Lee W. H. Molecular mechanism of retinoblastoma gene inactivation in retinoblastoma cell line Y79. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6017–6021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoMonaco M. B., Lee W. R., Chang S. H. Identification of an X-ray induced deletion mutant flanked by direct repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7641–7641. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S., Smithies O. A Chinese G gamma + (A gamma delta beta)zero thalassemia deletion: comparison to other deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster and sequence analysis of the breakpoints. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6559–6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C L, Silvers W K. The Effects of Genotype and Cell Environment on Melanoblast Differentiation in the House Mouse. Genetics. 1956 May;41(3):429–450. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. J., Seperack P. K., Strobel M. C., Swing D. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Dilute suppressor dsu acts semidominantly to suppress the coat color phenotype of a deletion mutation, dl20J, of the murine dilute locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8131–8135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Hartley D., Phear G., Tear G., Meuth M. Spontaneous deletion formation at the aprt locus of hamster cells: the presence of short sequence homologies and dyad symmetries at deletion termini. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulak R. A., Anderson P. Structures of spontaneous deletions in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3748–3754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL E. S. A quantitative histological study of the pigment found in the coat color mutants of the house mouse; estimates of the total volume of pigment. Genetics. 1948 May;33(3):228–236. doi: 10.1093/genetics/33.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Russell L. B., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Molecular genetic analysis of the dilute-short ear (d-se) region of the mouse. Genetics. 1986 Feb;112(2):321–342. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Lehrman M. A., Südhof T. C., Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The LDL receptor in familial hypercholesterolemia: use of human mutations to dissect a membrane protein. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):811–819. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Definition of functional units in a small chromosomal segment of the mouse and its use in interpreting the nature of radiation-induced mutations. Mutat Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Information from specific-locus mutants on the nature of induced and spontaneous mutations in the mouse. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;209B:437–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Russell L. B., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Allelic variation within the Emv-15 locus defines genomic sequences closely linked to the agouti locus on mouse chromosome 2. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):85–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vnencak-Jones C. L., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Molecular basis of human growth hormone gene deletions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong P. J., Grosovsky A. J., Glickman B. W. Spectrum of spontaneous mutation at the APRT locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells: an analysis at the DNA sequence level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]