Abstract
Background
The insertion element IS630 found in Aeromonas salmonicida belongs to the IS630-Tc1-mariner superfamily of transposons. It is present in multiple copies and represents approximately half of the IS present in the genome of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449.
Results
By using High Copy Number IS630 Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (HCN-IS630-RFLP), strains of various subspecies of Aeromonas salmonicida showed conserved or clustering patterns, thus allowing their differentiation from each other. Fingerprints of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida showed the highest homogeneity while ‘atypical’ A. salmonicida strains were more heterogeneous. IS630 typing also differentiated A. salmonicida from other Aeromonas species. The copy number of IS630 in Aeromonas salmonicida ranges from 8 to 35 and is much lower in other Aeromonas species.
Conclusions
HCN-IS630-RFLP is a powerful tool for subtyping of A. salmonicida. The high stability of IS630 insertions in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida indicates that it might have played a role in pathoadaptation of A. salmonicida which has reached an optimal configuration in the highly virulent and specific fish pathogen A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida.
Keywords: Aeromonas salmonicida, HCN-IS630-RFLP, IS element, Subtyping, Tc1 Mariner transposon, Salmonidae, Pathoadaptation
Background
Aeromonas salmonicida is one of the predominant bacterial species found in fish and water samples [1]. While some Aeromonas species are able to cause opportunistic disease in warm- and cold blooded vertebrates, A. salmonicida seems to be specific for fish. Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida a specific primary pathogen of Salmonidae (salmon, trout and char) has been known for decades to cause furunculosis. This bacterial septicaemia has a significant economic impact on aquaculture operations as well as on the wild stock of salmonids and some other fish species [2]. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology recognizes five subspecies of A. salmonicida: salmonicida, achromogenes, smithia, pectinolytica and masoucida[3]. Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida is referred to as typical Aeromonas salmonicida by reason that these strains are very homogeneous and considered to be clonal [4,5]. Clinical strains that cannot be assigned to any of the known subspecies are referred to as A. salmonicida ‘atypical’. In recent years, it has been recognized that ‘atypical’ strains cause diseases in salmonidae and other fish species that differ from furunculosis. Therefore their importance is being increasingly recognized. The most common clinical manifestation observed, following infections with such strains, is chronic skin ulceration [6]. Due to a convoluted history of nomenclature and taxonomy of Aeromonas sp., clear assignment of strains using currently available methods remains sometimes confusing and controversial which makes epidemiological studies difficult [7]. Intraspecies phenotypic variability also makes phenotypic identification challenging on the species level [8]. A variety of molecular genetic methods have been employed for genetic classification of Aeromonads including mol% G + C composition, DNA-DNA relatedness studies, restriction fragment length polymorphism, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, plasmid analysis, ribotyping, multilocus sequence typing, PCR and more [3,5]. Combination of 16S rDNA-RFLP analysis and sequencing of the gene rpoD was proposed as a suitable approach for the correct assignment of Aeromonas strains [9]. Moreover, analyzing strains by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) with an extraction method revealed 100% genus-level accuracy and 91.4% accuracy at species level [10]. However, this method was not able to discriminate A. salmonicida at the subspecies level.
Currently, no molecular approach gives a clear genotypic distinction of strains among A. salmonicida species. For this reason we elaborated a molecular genetic technique to achieve an adequate subtyping of all Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies. This method, named High Copy Number IS-Element based Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (HCN-IS-RFLP), has been successfully applied in numerous epidemiological studies for other pathogenic bacteria [11-15].
Results
Optimization of HCN-IS630-RFLP conditions
IS630 was selected because it is the IS element with the highest copy number in the genome of A. salmonicida[16]. Primers internal to the highly conserved IS630 genes [GenBank: ABO88357.1] were designed to generate a probe on an intact IS fragment from the A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida JF2267 genome. To obtain the most distinct banding pattern, the digestion by several restriction enzymes on a set of sequenced genomes (A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449, A. hydrophila ATCC7966 and A. veronii B565) was predicted by computer analysis. XhoI that does not cut within our probe for IS630 revealed a good resolution with a clear banding pattern and was therefore selected. A size window of 1375 bp to 21226 bp was defined on all southern blots as some hybridizing patterns with very large or small fragments were not sufficiently resolved (Figure 1). The genomic DNA sequence of A. salmonicida strain A449 [GenBank: CP000644.1] predicted that the probe would hybridize with 35 copies of IS630 on XhoI fragments ranging from 1277 bp to 17948 bp (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Figure 1.
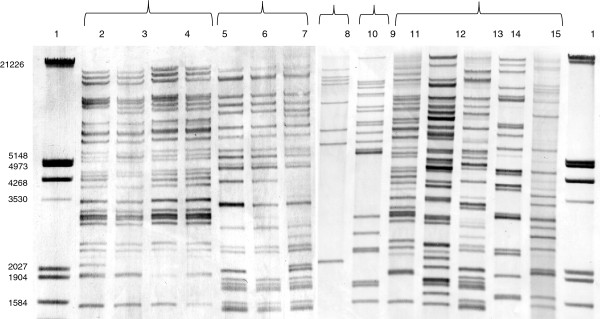
Southern blot of Xho-I digested DNAs from different A. salmonicida strains hybridized with an IS630-specific probe. Lanes 1 and 16, molecular size marker (sizes are indicated on the left in kilobase pairs); lanes 2 to 5 and 11, A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida (JF2267, JF3224, JF3996, JF3507, JF3121 [formerly identified as atypical]); lanes 6 to 8 and 13, A. salmonicida subsp. achromogenes (JF3115, JF3116, JF2997, JF3123 [formerly identified as atypical]); lane 9, A. salmonicida subsp. pectinolytica (JF3120); lane 10, A. salmonicida subsp. masoucida (JF3118); lanes 12, 14 and 15, A. salmonicida atypical (JF3122, JF3124, JF3125).
We analyzed the IS630 RFLP-fingerprints of 87 Aeromonas sp. strains of various geographical origins, which comprised 31 A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, 4 subsp. achromogenes, 4 subsp. smithia, 2 subsp. masoucida, one subsp. pectinolytica, 12 A. salmonicida atypical strains, 8 A. popoffii, 5 A. sobria and A. bestiarum, 2 A. hydrophila, one A. trota, A. enteropelogenes, A. simiae, A. eucrenophila, A. ichthiosmia, A. jandaei, A. molluscorum, A. bivalvium, A. allosaccharophila, A. media, A. veronii, A. caviae and A. culicicola (Table 1). The fingerprints (Figure 1) of the analyzed strains were subjected to similarity analysis and are shown in Figure 2.
Table 1.
Aeromonas strains used in this study
| JF N° | Synonyme | Species | Subspecies | Origin | Identified virulence characteristics | Pigment production (Day 6) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JF2996 |
Austin98 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Sediment in Riccarton Loch, Scotland |
ascV-, ascU-, aexT+, aopP+, aopO-, aopH+ |
+++ |
[17,18] |
| JF3507 |
ATCC 33658 T, NCIMB 1102 T |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Salmo salar, Scotland |
ascV-, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD- |
+++ |
[18-20] |
| JF3327 |
F330/04 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Arctic char, Switzerland, 2004 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF3517 |
4757 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Turbot, Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF2267 |
Fi 94 G |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Arctic char, Switzerland, 1999 |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
+++ |
[17,18,20] |
| JF2869 |
CCUG 47405 (A) |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Arctic char (Savelinus alpinus) |
aexT+, SacrD 3′+ |
++++ |
- |
| JF3223 |
Fi 210 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
White fish, Switzerland, 1997 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF3224 |
R04/170 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Brown trout, Switzerland, 2004 |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++++ |
[17,18] |
| JF3518 |
4704 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Turbot, Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF2509 |
CC72 - D640 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Atlantic salmon, Canada, before 1960 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
++++ |
[18,20] |
| JF3519 |
3294 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Arctic char, Switzerland, 1986 |
ascV-, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH- |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF2506 |
CC 27–80/9-1 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Atlantic salmon Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
++++ |
[18,20] |
| JF2507 |
CC 29 - 74/2 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Atlantic salmon, Scotland |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
++++ |
[18,20] |
| JF2508 |
CC 63- D-615 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Atlantic salmon, Canada |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
++++ |
[18,20] |
| JF2510 |
CC 23/8019-5 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Atlantic salmon Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
++++ |
[18,20] |
| JF3521 |
2265 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Wild atlantic salmon, Norway 1991 |
ascV-, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH- |
++++ |
[18] |
| JF3496 |
F05/160 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Wild brown trout, Switzerland, 2005 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
+++ |
[18] |
| JF3844 |
F06/417 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Arctic char, Switzerland, 2006 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
+++ |
[18] |
| JF2505 |
MT 44/SS 10 |
salmonicida |
- |
non virulent for trout, Canada |
A+, LPS+, acrD- |
+++ |
[20] |
| JF3791 |
F06/385 |
salmonicida |
- |
Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus, Switzerland, 2006 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP-aopO+, aopH+ |
+++ |
[18] |
| JF4111 |
F07/357(NiA) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus, Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4112 |
F07/357 (NiB) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus, Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4113 |
F07/357 (NiC) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus, Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF3121 |
As209 |
salmonicida |
salmonicida [formerly atypical] |
Wolf fish, UK |
ascV-, ascU- |
+++ |
[17] |
| JF4714 |
IMD1520 |
salmonicida |
- |
Thymallus thymallus (skin), Switzerland, 2009 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4715 |
IMD 1521 |
salmonicida |
- |
Thymallus thymallus (kidney), Switzerland, 2009 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4114 |
F07/357(LeA) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus (liver), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4115 |
F07/357 (LeB) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus (liver), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4116 |
F07/357 (LeC) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus (liver), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4118 |
F07/(MiB) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus (kidney), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4119 |
F07/357 (MiC) |
salmonicida |
- |
Salvelinus (kidney), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
+++ |
- |
| JF4117 |
F07/357 (MiA) |
salmonicida |
salmonicida |
Salvelinus (spleen), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
++++ |
- |
| JF3122 |
As204 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Wrasse UK |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP + aopO-, aopH+ |
++ |
[18] |
| JF3500 |
aAs 4143 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Atlantic cod, Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP + aopO+, aopH- |
++ |
[18] |
| JF3666 |
F06/211 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Bleak (Alburnus alburnus), Switzerland, 2006 |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP- aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[18] |
| JF3124 |
As93 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Plaice, Denmark |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP + aopO+, aopH+ |
- |
[18] |
| JF3520 |
4818 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Atlantic Halibut, Norway, 2003 |
ascV+, aexT-, aopP + aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[18] |
| JF3115 |
ATCC 19261, NCIMB 1109 |
salmonicida |
achromogenes |
Salmo trutta |
ND |
+ |
- |
| JF3116 |
NCIMB 1110 T |
salmonicida |
achromogenes |
Trout, Scotland |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++ |
[17-19] |
| JF2997 |
F-265/87 |
salmonicida |
achromogenes |
Atlantic salmon, Iceland |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++ |
[17,18] |
| JF3123 |
As183 |
salmonicida |
achromogenes [formerly atypical] |
Arctic char, Iceland |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
++ |
[17,18] |
| JF3499 |
aAs4101 |
salmonicida |
achromogenes |
Atlantic Cod, Iceland |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP + aopO+, aopH- |
- |
[18] |
| JF3125 |
As 51 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Rainbow trout, Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP- aopO+, aopH+ |
- |
[18] |
| JF4097 |
- |
salmonicida |
smithia |
Salvelinus alpinus lepeschini, Austria |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[21] |
| JF4460 |
- |
salmonicida |
smithia |
Salvelinus alpinus lepeschini, Austria |
ascV-, aexT+, aopP+, aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[21] |
| JF4439 |
- |
salmonicida |
smithia |
Salvelinus alpinus lepeschini, Austria |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[21] |
| JF3117 |
NCMB13210, ATCC 49393 |
salmonicida |
smithia |
Roach, England |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP-, aopO+, aopH+ |
- |
[17-19] |
| JF3126 |
As 54 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Rainbow trout, Norway |
ascV-, aexT+, aopP-, aopO-, aopH- |
++ |
[18] |
| JF3502 |
aAs 4067 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Spotted wolffish, Norway |
ascV+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+ |
+ |
[18] |
| JF3118 |
ATCC 27013 T |
salmonicida |
masoucida |
Salmon, Japan |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP-, aopO-, aopH+ |
- |
[17-19] |
| JF3119 |
NCMB 2020 |
salmonicida |
masoucida |
same as ATCC 27013 (salmon, Japan) |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF2512 |
CC 30/8038 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Atlantic salmon, Canada, before 1960 |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
- |
[17,18,20] |
| JF2513 |
CC 34/8030 |
salmonicida |
atypical |
Atlantic salmon, Canada, before 1960 |
ascV+, ascU+, aexT+, aopP+, aopO+, aopH+, acrD+ |
- |
[17,18,20] |
| JF3328 |
848 T |
molluscorum |
- |
Type strain |
ND |
- |
[22] |
| JF3071 |
ATCC 51106, bg sobria HG8 |
veronii |
- |
? |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2635 |
429/01 # 1c; official JF2635 |
sobria |
- |
Perca fluviatilis, Switzerland, 2001 |
ascV+, ascU+, acrD+ |
- |
[17] |
| JF3326 |
- |
popoffii |
- |
Urinary tract infection, France |
ND |
- |
[23] |
| JF3120 |
DSM 12609 T |
salmonicida |
pectinolytica |
River water |
ascV-, aexT-, aopP-, aopO-, aopH- |
++++ |
[17,19] |
| JF3240 |
LMG 17542, IK-B-r-15-1 |
popoffii |
- |
Drinking water production plant, Belgium |
ND |
- |
[24] |
| JF2796 |
CECT 4199 |
allosaccharophila |
- |
Type strain |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF3242 |
LMG 17547, AG-9 |
popoffii |
- |
Drinking water treatment plant, Scotland |
ND |
- |
[24] |
| JF2797 |
LMG 17541T, IK-0-a-10-3 |
popoffii |
- |
Drinking water production plant, Belgium |
ND |
- |
[19,24] |
| JF3241 |
LMG 17544, IK-E-a- 14- 1 |
popoffii |
- |
Drinking water production plant, Belgium |
ND |
- |
[24] |
| JF2905 |
Fi 125 |
sobria |
- |
Perch |
ascV+ |
- |
[25] |
| JF2791 |
ATCC 33907 |
media |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr. 2346-98 |
ascV+, ascU+ |
- |
[17,19] |
| JF2899 |
F86/03-2 |
sobria |
- |
Perch |
ascV+ |
- |
[25] |
| JF2806 |
F533E |
popoffii |
- |
Tap water, Switzerland, 2003 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2808 |
F600C |
popoffii |
- |
Tap water, Switzerland, 2003 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2807 |
F548B |
popoffii |
- |
Tap water, Switzerland, 2003 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF 3954 |
868ET |
bivalvium |
- |
Bivalve molluscs; Type strain |
ND |
- |
[26] |
| JF2637 |
Fi 303 |
hydrophila |
- |
Ornamental fish |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF2794 |
ATCC 49657, NENT Nr.2360-98 |
trota (enteropelogenes) |
- |
Human feces, India |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2785 |
CDC 9533-76 |
bestiarum |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr: N2341-98 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF 4032 |
A28)A28B/1-1 |
bestiarum |
- |
Wild perch (Perca fluviatilis), Switzerland, 2007 |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF 4608 |
A28) 28B/1-1 |
bestiarum |
- |
Wild perch, Switzerland, 2009 |
ascV+ |
- |
[22] |
| JF2804 |
F 530 D |
bestiarum |
- |
Tap water |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF3018 |
68 |
bestiarum |
- |
River water |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF3070 |
S 6874 T |
simiae |
- |
Type strain |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2786 |
ATCC 15468 |
caviae |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr. N2344-98 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2789 |
ATCC 7966 |
hydrophila |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr. : N2339-98 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2793 |
CIP 7433; ATCC 43979 |
sobria |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr.2352 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF2929 |
Fi 179a |
sobria |
- |
Perch, Switzerland |
ascV + SacrD+ |
- |
[22] |
| JF2788 |
NCMB 74; ATCC 23309 |
eucrenophila |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr. N2348-98 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF3069 |
ATCC 49904 T |
ichthiosmia |
- |
Type strain Antonella Demarta |
ND |
- |
- |
| JF2790 |
ATCC 49568 |
jandaei |
- |
Type strain NENT Nr. 2355-98 |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF3067 |
CIP 107763 T |
culicicola |
- |
Type strain |
ND |
- |
[19] |
| JF3068 | ATCC 49803 T | enteropelogenes | - | Type strain | ND | - | - |
ND: not determined.
Figure 2.
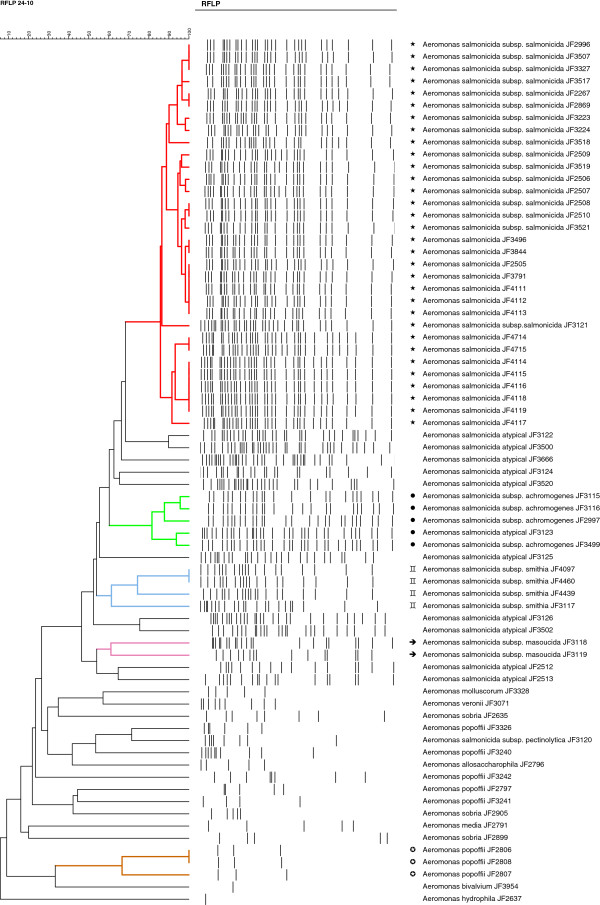
Dendogram generated from the IS630-RFLP patterns of the 87 Aeromonas strains used in this study. The tree was established by using the UPGMA clustering analysis with the BioNumerics software. In red (⋆), the A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida cluster; in green (●), the A. salmonicida subsp. achromogenes cluster; in blue (), the A. salmonicida subsp. smithia cluster; in pink (➜), the A. salmonicida subsp. masoucida cluster; and in brown (✪), A. popoffii strains clustering together.
HCN-IS630-RFLP profiles and stability of IS630 insertions
A high degree of IS630 polymorphism, both in a numerical and positional sense, was observed between the various A. salmonicida subspecies (Figure 1). However, the patterns revealed that IS630 copy numbers and positions are well conserved within the given subspecies (Figure 1). The dendogram in Figure 2 is a RFLP tree that reveals the evolutionary relationship between strains analyzed. Strains of the subspecies salmonicida, smithia, achromogenes and masoucida each grouped together showing a similar banding pattern. The number of IS630-positive bands varied from 27 to 35 in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, 23 to 33 in achromogenes and 19 to 21 in smithia. Within a subspecies, several bands were conserved: 21 in salmonicida, 20 in achromogenes and 13 in smithia subspecies. About 15 distinct patterns were observed in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida without showing geographical association. The IS630 pattern of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strain A449 as calculated from the genome sequence data closely clusters with these 15 patterns. In contrast, each pattern in the achromogenes cluster was different. In A. salmonicida subsp. masoucida 15 to 21 positive bands were detected and only 8 in the subspecies pectinolytica. Even though the copy numbers vary within the subspecies, the patterns form clusters for each subspecies. The most remarkable tight clustering was found for A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. This latter presents IS630 patterns that only show minute differences among strains that were isolated from various continents and over a period of half a century. No pattern was specific of a given geographical region. The results showed also that strains JF3121 and JF3123, formerly classified as A. salmonicida atypical, clustered with A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida (JF3121) and subsp. achromogenes (JF3123) (Figures 1 and 2) showing that they were misclassified previously.
The IS630 pattern of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strain JF 2267 that was subcultured for 4 days at 18°C and 25°C (in stressing conditions) to reach approximately 20 generations remained unchanged (results not shown) indicating a good stability of IS630 under experimental growth conditions.
Copy number of the IS630 element and RFLP among other Aeromonas species
Other Aeromonas species revealed lower copy numbers of IS630: 5 in A. molluscorum, 5 to 8 in clinical A. sobria strains, 9 in A. veronii, 5 in A. allosaccharophila and A. media. Only one copy was found in A. bivalvium and a clinical strain of A. hydrophila. No signal for IS630 was obtained in A. caviae, A. trota, A. simiae, A. eucrenophila, A. ichthiosmia, A. jandaei, A. culicicola, A. enteropelogenes, A. bestiarum and the type strains of A. hydrophila and A. sobria. Among the 8 strains of A. popoffii we found 6 very distinct patterns.
Analysis of IS630 abundance, localization and impact on the genome of Aeromonas species
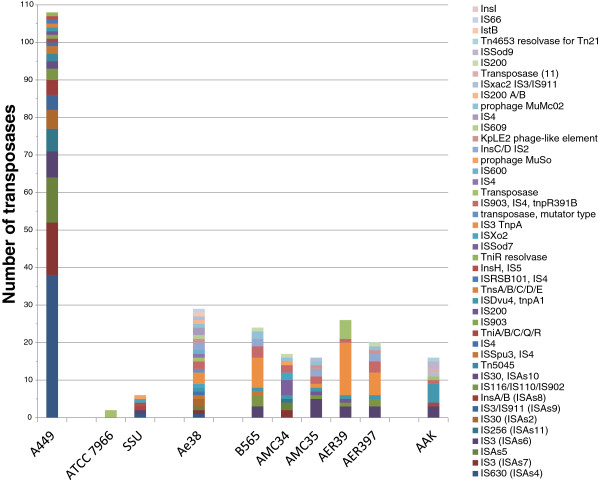
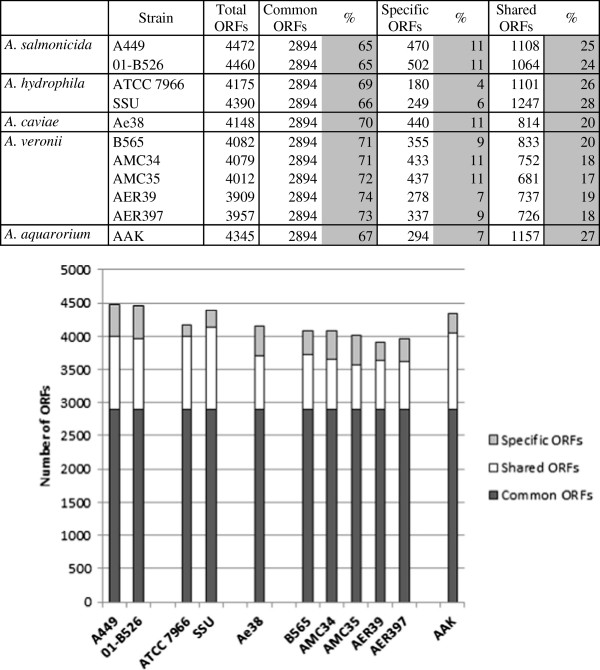
In order to study the origin of IS630 in A. salmonicida, we performed a profound analysis and comparison of published Aeromonas genomes (Additional file 2: Table S2). The genetic environment of IS630 copies in the A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449 genome is shown in detail in Additional file 1: Table S1. About 148 loci or DNA sequences forming 108 complete or partial IS units were found in the chromosome of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449 and on the plasmids pASA4/pASA5 [GenBank: CP000644.1, CP000645.1 and CP000646.1]. IS630 (referred to as ISAs4 in the Genbank genome annotation of A. salmonicida A449 and as ISAs7 in the corresponding manuscript [16]) was found to be present in 38 copies and was the most abundant family representing 35% of transposons in A. salmonicida A449 (Figure 3, Additional file 3: Table S3). The different copies are well-conserved and show 98% nucleotide sequences identity. The other 70 IS elements are ISAs7 (13%), ISAs5 (11%), ISAs6 (6%), ISAs11 (6%), ISAs2 (5%), ISAs9 (4%), ISAs8 (4%), and unclassified ISAs (16%) (Figure 3). 90% of the IS630 copies reside in chromosomal regions that are specific to A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and were not found in other Aeromonas. Interestingly most of these loci correspond to known genes in bacterial genera other than Aeromonas. This is the case for instance for the hypothetical gene ASA_1385 (homology to VOA_002034 of Vibrio sp. RC586) that is directly linked to IS630 in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and is not found in other Aeromonads (Additional file 2: Table S2). In ISAs families other than IS630, 34 (31%) are directly adjacent to IS630 showing that 66% of A. salmonicida A449 transposons are associated to genomic domains of variability. In comparison to other Aeromonas sp., A. salmonicida A449 contains 4 to 54 fold more transposases (Figure 3) which are not responsible for a genome-reductive evolution [27] because the total number of ORFs is stable in comparison to other Aeromonads (Figure 4). However they explain the high abundance of pseudogenes (170) in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida[16] in contrast to A. hydrophila ATCC 7966 which only contains 7 pseudogenes and 2 transposases.
Figure 3.
Number of transposases and IS family affiliation in Aeromonas sp.A. salmonicida A449 [GenBank: CP000644.1, CP000645.1 and CP000646.1], A. hydrophila ATCC 7966 and SSU [GenBank: CP000462.1 and AGWR00000000.1], A. caviae Ae398 [GenBank: CACP00000000.1], A. veronii B565, AMC34, AMC35, AER39 and AER397 [GenBank: CP002607.1, AGWU00000000.1, AGWW00000000.1, AGWT00000000.1 and AGWV00000000.1], and A. aquarorium AAK1 [GenBank: AP012343.1].
Figure 4.
Numerical comparison of common, shared and specific ORFs between several Aeromonas species. The number of ORFs was calculated from Additional file 2: Table S2 without taking into account IS elements, tRNA and rRNA. In dark grey, the number of ORFs that are common among Aeromonas sp. In white, ORFs that are shared with at least one other Aeromonas species. In light grey, ORFs that are unique to the species. A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449 and 01-B526, A. hydrophila ATCC 7966 and SSU, A. caviae Ae398, A. veronii B565, AMC34, AMC35, AER39 and AER397, and A. aquarorium AAK are illustrated in the graph.
Discussion
HCN-IS6110-RFLP has been applied as a standard method to subtype Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains for years [28]. Moreover, RFLP based on IS elements has been employed to type numerous other pathogenic bacteria [14,15,29-31]. The published genome of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449 shows numerous IS elements among which 38 belong to the IS630 family [GenBank: CP000644.1]. We therefore used HCN-IS630-RFLP as a new typing methodology for Aeromonas species.
IS630 was present in different copy numbers and integrated at various sites between the different A. salmonicida subspecies. On the other hand banding patterns were conserved within subspecies (Figure 1). HCN-IS630-RFLP revealed that IS630 is abundant in all subspecies of A. salmonicida allowing a good accuracy for genomic fingerprinting. Our results showed that RFLP profiles can be used to distinguish subspecies of A. salmonicida and to differentiate A. salmonicida from other Aeromonas species. They also indicate a high variability among strains of ‘atypical’ A. salmonicida. All strains of yet unclassified ‘atypical’ A. salmonicida consisted of a high number of IS630 copies and were effectively related to the A. salmonicida cluster. Our method demonstrates that such ‘atypical’ strains represent a heterogeneous group that does not fit into the classification of the five described A. salmonicida subspecies. These strains might represent various subtypes of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida or novel subspecies of A. salmonicida that have adapted to particular ecological niches or respective hosts. On the other hand, all A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida isolated since the 1950s and originating from all over the world have very similar patterns, indicating that they form a single clone showing pathoadaptational stability. Altogether, our results confirm those of a previous study comparing genomic profiles of clinical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida using DNA microarrays [32]. With the origin and intensification of fish farming, genetic rearrangements occurring through IS transposition events could have been responsible for the selection and the emergence of this pathogenic fish specific clone. Such an adaptation process of a pathogenic bacterium towards its host was recently indicated in the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster for Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides[33]. Moreover, no unique pattern was associated to a specific geographical region of the world and we assume that this could be explained by the dissemination of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strains between aquaculture countries via the intensification of the international trade in farmed salmon or by the natural migration of wild salmons.
Besides the epidemiologic and phylogenetic interests of IS630 fingerprinting to subtype A. salmonicida, we studied the characteristics of this predominant IS element to reveal information concerning the pathoadaptation towards its specific host. Mobile genetic elements can exert different effects on bacterial genomes [11,34-36]. Through such genomic effects, IS630 family has had an impact on the modulation of virulence genes in other bacteria [37-43]. In A. salmonicida 90% of the IS630 copies reside in genomic regions that are variable between Aeromonas sp. (Additional file 1: Table S1) and 80% of these sites contain genes that are specific to A. salmonicida and are not encountered in other Aeromonas sp. suggesting that they constitute genomic islands. A part of these coding sequences are phages or hypothetical genes with homologues of characterized sequences in other environmental bacteria: i.e. the ‘Vibrio Seventh Pandemic cluster I’ (VSP-I), genes for the synthesis of polysaccharide capsule, lipopolysaccharide, S-layer, chitinase, cytolytic insecticidal delta-endotoxin, and some effectors (AopO and ApoH) of the type-three secretion system, the major virulence system of the bacterium. Based on these findings we assume that IS630 elements could be used by environmental bacteria to exchange DNA fragments between each other by horizontal transfer. In the genomic islands where IS630 is present, supplementary IS elements can be found, which might serve as hot spots for further insertions. This would allow the transposon and the genomic island to evolve with acquisition of new genes without disruption of existing loci. These observations could explain why the IS630 elements remained stable within the A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida genome.
Other interesting characteristics of IS elements homologous to IS630 in A. salmonicida suggest that they could play a role in the co-adaptation of the bacterium with its host by trans-kingdom horizontal gene transfers through the bacterial T3SS: (i) such IS630 elements are mostly present in Gram-negative bacteria that use a T3SS, (ii) their expression can be specifically induced or increased when bacteria are in direct contact with host cells [44] and (iii) several IS630 are predicted to be T3SS effectors [45]. The Modlab® T3SS effector prediction software gives for A. salmonicida IS630 a positive output at 0.69 which means, that the IS630 itself is a potential T3SS effector. Hence, when the bacteria colonize the host, the IS630 expression could be induced and they could begin to exert their transposase activity by excising the transposon (composite if associated to adjacent additional DNA fragments) from the bacterial genome. Subsequently, the transposase linked to its transposon could be translocated into the host cell by the T3SS, reach the host genome in the nucleus, and finally perform its transposition.
Bacterial IS630 elements constitute with the Tc1/mariner eukaryotic DNA transposon family, a superfamily [46]. It was demonstrated in vitro that eukaryotic members of this family are able to transpose into prokaryotic genomes [46]. We suppose that the opposite could also be possible as IS630 itself could be translocated via type three secretion system from the pathogen to its host. In this perspective, our assumption could explain how the adaptive horizontal transfer of a bacterial mannanase gene (HhMAN1) into the genome of an invasive insect pest of coffee (Hypothenemus hampei) occurred in the immediate genetic vicinity of a Tc1/mariner transposon [47].
Conclusions
In this study we describe HCN-IS630-RFLP as an adequate method for subtyping A. salmonicida strains and to differentiate A. salmonicida from other Aeromonas species. The high degree of conservation of HCN-IS630-RFLP profiles among strains of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida isolated from geographically most distant areas and over the period of half a century shows that practically all copies of IS630 are stably integrated in this pathogen that has a well-defined host range. We therefore conclude that IS630 might have contributed to the pathoadaptation of A. salmonicida to salmonidae and to the emergence of the subtype A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida.
Methods
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
Aeromonas strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Bacteria were grown on trypticase soy agar plates at 18°C for 3 to 6 days until sufficient bacteria were available for DNA extraction.
Southern blot analysis with A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida IS630 probe
Total DNA extraction from each strain was performed with the Peqgold Bacterial DNA extraction Kit (Peqlab Biotechnologie, Erlangen, Germany). One microgram of DNA from each sample was digested overnight with XhoI restriction enzyme (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany), loaded on a 0.7% agarose gel and subjected to electrophoresis for 4 to 5 hours. On each gel a DIG-labeled DNA Marker (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and XhoI digested DNA from A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida JF2267 were loaded for normalization. DNA bands were stained with ethidium bromide for control and transferred onto a nylon membrane (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) with a VacuGene apparatus (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences). The IS630 probe was prepared by PCR using primers Clust_asa1052_S6 (5′- AGGCAGAACTTGGGGTTCTT-3′) and Clust_asa1052_R4 (5′- ACAAAAGCGGGTTGTCACTC-3′) and DNA of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida JF2267 as a template. PCR was performed in 30 μL which contained 0.5 μL of Taq DNA polymerase (5 units/μL) (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany), 300 nM of each primer, 1.75 mM MgCl2, 200 μM concentrations of each dNTP and 1 μl of the Digoxigenin-11-dUTP (1 nmol/μL) (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Each reaction involved a denaturing step at 94°C for 5 min followed by 30 cycles of 10 sec at 94°C, 30 sec at 54°C and 60 sec at 72°C and a final extension step of 7 min at 72°C.
Bioinformatic analysis
The hybridization patterns were scanned and the data were analyzed using the BioNumerics software version 6.6 (Applied Maths, Kortrijk, Belgium). Bands automatically assigned by the computer were checked visually and corrected manually. Cluster analysis of the IS-RFLP patterns was done by the unweighted pair group method with average linkages (UPGMA) using the Dice coefficient and the following parameters: 0.5% Optimization, 0% Band filtering, 0.5% Tolerance and ignore uncertain bands.
Prediction of T3SS effectors was performed with the Modlab® online software (http://gecco.org.chemie.uni-frankfurt.de/T3SS_prediction/T3SS_prediction.html) [45].
Stability of IS630 in cultured A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida
The stability of IS630 under growth conditions in TSB medium was assessed by daily 100x dilution of a culture of strain JF2267 at 18°C and at 25°C during 4 days to reach 20 generations. Every day DNA was extracted from 109 bacteria, digested with XhoI and submitted to southern blot hybridization.
Abbreviations
HCN-IS-RFLP: High copy number insertion element restriction fragment length polymorphism; T3SS: Type-three secretion system; UPGMA: Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Authors’ contributions
NS carried out the experiments, performed BioNumerics analysis and drafted the manuscript. JF participated in the coordination of the study and helped to draft the manuscript. PVB conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, carried out experiments, performed bioinformatic analysis and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Table showing for each A. salmonicida A449 IS630 copy, the size of the XhoI-digested DNA fragment containing the IS, the inter- or intragenic localization, the characteristics of the adjacent genes, and the association to a region of variability or to other IS elements.
Profound analysis and comparison of published Aeromonas genomes used for Figures 3 and 4. Grey: conserved ORFs; light green: ORFs specific of the species; yellow: IS630; pink: other IS elements; red: putative or characterized virulence factors; mauve: ORFs for resistance to antibiotic or heavy metal; dark green: ORFs associated to pili, fimbriae or flagella; blue: ORFs associated to phage; cyan: tRNA and rRNA; orange: ORFs with homology to eukaryotic genes.
Detail of loci corresponding to transposons in Aeromonas sp.
Contributor Information
Nicole Studer, Email: nicolestuder@students.unibe.ch.
Joachim Frey, Email: joachim.frey@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Philippe Vanden Bergh, Email: philippe.vandenbergh@vetsuisse.unibe.ch.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation grant no. 31003A-135808.
References
- Janda JM, Abbott SL. The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:35–73. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00039-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiney M, Olivier G. In: Fish diseases and disorders. Woo PTK, Bruno DW, editor. Walkingford, Oxfordshire, UK: CAB International; 1999. Furunculosis (Aeromonas salmonicidas) pp. 425–425. (viral, bacterial and fungal infections). Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Carnahan A, Joseph SW. In: Bergey’s Manual of systematic bacteriology, second edition, vol. 2 (The Proteobacteria), part B (The gammaproteobacteria) Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM, editor. New York, NY: Springer; 2005. Family I. Aeromonadaceae Colwell, MacDonell and De Ley 1986, 474VP; pp. 556–580. [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund T, Dalsgaard I. Occurrence and significance of atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in non-salmonid and salmonid fish species: a review. Dis Aquat Organ. 1998;32:49–69. doi: 10.3354/dao032049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia JA, Larsen JL, Dalsgaard I, Pedersen K. Pulsed-field gel electrophoriesis analyis of Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. salmonicida. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000;190:163–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson WB, Gudkovs N, Strom MS. Atypical strains of Aeromonas salmonicida contain multiple copies of insertion element ISAsa4 useful as a genetic marker and a target for PCR assay. Dis Aquat Organ. 2006;70:209–217. doi: 10.3354/dao070209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarta A, Tonolla M, Caminada A, Beretta M, Peduzzi R. Epidemiological relationships between Aeromonas strains isolated from symptomatic children and household environments as determined by ribotyping. Eur J Epidemiol. 2000;16:447–453. doi: 10.1023/A:1007675424848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbott SL, Cheung WK, Janda JM. The genus Aeromonas: biochemical characteristics, atypical reactions, and phenotypic identification schemes. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:2348–2357. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2348-2357.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaz-Hidalgo R, Alperi A, Bujan N, Romalde JL, Figueras MJ. Comparison of phenotypical and genetic identification of Aeromonas strains isolated from diseased fish. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2010;33:149–153. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamy B, Kodjo A, Laurent F. Identification of Aeromonas isolates by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;71:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2011.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy CR, Falmer AA, Gey van Pittius NC, Victor TC, van Helden PD, Warren RM. The role of IS6110 in the evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2007;87:393–404. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2007.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne N, Borrell S, Evans J, Magee J, Garcia de Viedma D, Bishop C, Gonzalez-Martin J, Gharbia S, Arnold C. IS6110-based global phylogeny of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11:132–138. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2010.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker BJ, Ewalt DR, MacMillan AP, Foster G, Brew S. Molecular characterization of Brucella strains isolated from marine mammals. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1258–1262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.3.1258-1262.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrea G, Chenal-Francisque V, Leclercq A, Carniel E. Efficient tracing of global isolates of Yersinia pestis by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis using three insertion sequences as probes. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:2084–2092. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02618-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng X, Nicolet J, Poumarat F, Regalla J, Thiaucourt F, Frey J. Insertion element IS1296 in Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides small colony identifies a European clonal line distinct from African and Australian strains. Microbiology. 1995;141:3221–3228. doi: 10.1099/13500872-141-12-3221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith ME, Singh RK, Curtis B, Boyd JM, Bouevitch A, Kimball J, Munholland J, Murphy C, Sarty D, Williams J. The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449: insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:427. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr SE, Pugovkin D, Wahli T, Segner H, Frey J. Attenuated virulence of an Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida type III secretion mutant in a rainbow trout model. Microbiology. 2005;151:2111–2118. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr SE, Frey J. Analysis of type III effector genes in typical and atypical Aeromonas salmonicida. J Fish Dis. 2007;30:711–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpfer M, Kuhnert P, Korczak BM, Peduzzi R, Demarta A. Genetic relationships of Aeromonas strains inferred from 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoB gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006;56:2743–2751. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63650-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier G, Moore AR, Fildes J. Toxicity of Aeromonas salmonicida cells to Atlantic salmon Salmo salar peritoneal macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol. 1992;16:49–61. doi: 10.1016/0145-305X(92)90051-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont E, Hochwartner O, Demarta A, Caminada AP, Frey J. Outbreaks of an ulcerative and haemorrhagic disease in Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus caused by Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. smithia. Dis Aquat Org. 2009;86:81–86. doi: 10.3354/dao02110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minana-Galbis D, Farfan M, Fuste MC, Loren JG. Aeromonas molluscorum sp. nov., isolated from bivalve molluscs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004;54:2073–2078. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua HT, Bollet C, Tercian S, Drancourt M, Raoult D. Aeromonas popoffii urinary tract infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5427–5428. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5427-5428.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huys G, Kampfer P, Altwegg M, Kersters I, Lamb A, Coopman R, Luthy-Hottenstein J, Vancanneyt M, Janssen P, Kersters K. Aeromonas popoffii sp. nov., a mesophilic bacterium isolated from drinking water production plants and reservoirs. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:1165–1171. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-4-1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr SE, Goldschmidt-Clermont E, Kuhnert P, Frey J. Heterogeneity of Aeromonas populations in wild and farmed perch, Perca fluviatilis L. J Fish Dis. 2012;35:607–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2012.01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minana-Galbis D, Farfan M, Fuste MC, Loren JG. Aeromonas bivalvium sp. nov., isolated from bivalve molluscs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007;57:582–587. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64497-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H, Hwang J, Yi H, Ulrich RL, Yu Y, Nierman WC, Kim HS. The early stage of bacterial genome-reductive evolution in the host. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000922. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander DC, Guthrie JL, Pyskir D, Maki A, Kurepina N, Kreiswirth BN, Chedore P, Drews SJ, Jamieson F. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Ontario, Canada: insights from IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive-unit-variable-number tandem-repeat genotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2651–2654. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01946-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergnes M, Ginevra C, Kay E, Normand P, Thioulouse J, Jarraud S, Maurin M, Schneider D. Insertion sequences as highly resolutive genomic markers for sequence type 1 Legionella pneumophila Paris. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:315–324. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01261-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R, Johansson A, Neeson B, Isherwood K, Sjostedt A, Ellis J, Titball RW. Discrimination of human pathogenic subspecies of Francisella tularensis by using restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:50–57. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.1.50-57.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi M, Bodmer M, Frey J, Pilo P. Herd-specific strains of Mycoplasma bovis in outbreaks of mycoplasmal mastitis and pneumonia. Vet Microbiol. 2012;157:363–368. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash JH, Findlay WA, Luebbert CC, Mykytczuk OL, Foote SJ, Taboada EN, Carrillo CD, Boyd JM, Colquhoun DJ, Reith ME. Comparative genomics profiling of clinical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida using DNA microarrays. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A, Shapiro B, Muriuki C, Heller M, Schnee C, Bongcam-Rudloff E, Vilei EM, Frey J, Jores J. The origin of the ‘Mycoplasma mycoides cluster’ coincides with domestication of ruminants. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahillon J, Chandler M. Insertion sequences. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62:725–774. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.3.725-774.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka KH, Dallaire-Dufresne S, Daher RK, Frenette M, Charette SJ. An insertion sequence-dependent plasmid rearrangement in Aeromonas salmonicida causes the loss of the type three secretion system. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-López M, García-Pérez JL. DNA transposons: nature and applications in genomics. Curr Genomics. 2010;11:115–128. doi: 10.2174/138920210790886871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houng HH, Venkatesan MM. Genetic analysis of Shigella sonnei form I antigen: identification of a novel IS630 as an essential element for the form I antigen expression. Microb Pathog. 1998;25:165–173. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1998.0222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P, Oyston PC, Chain P, Chu MC, Duffield M, Fuxelius HH, Garcia E, Halltorp G, Johansson D, Isherwood KE. The complete genome sequence of Francisella tularensis, the causative agent of tularemia. Nat Genet. 2005;37:153–159. doi: 10.1038/ng1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant M, Baxter L, Jarrett P, Shaw E, Ousley M, Winstanley C, Morgan JA. Identification, typing, and insecticidal activity of Xenorhabdus isolates from entomopathogenic nematodes in United Kingdom soil and characterization of the xpt toxin loci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:5895–5907. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00217-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han HJ, Kuwae A, Abe A, Arakawa Y, Kamachi K. Differential expression of type III effector BteA protein due to IS481 insertion in Bordetella pertussis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda T, Okada N, Nakazawa N, Kawakami T, Danbara H. Complete DNA sequence and comparative analysis of the 50-kilobase virulence plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis. Infect Immun. 2001;69:2612–2620. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2612-2620.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney DG, Fierer J. The role of the spv genes in Salmonella pathogenesis. Front Microbiol. 2011;2:129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrinides J, Kirzinger MW, Beasley FC, Guttman DS. E622, a miniature, virulence-associated mobile element. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:509–517. doi: 10.1128/JB.06211-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münch A, Stingl L, Jung K, Heermann R. Photorhabdus luminescens genes induced upon insect infection. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:229. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lower M, Schneider G. Prediction of type III secretion signals in genomes of gram-negative bacteria. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk RH, Izsvák Z, Ivics Z. Resident aliens: the Tc1/mariner superfamily of transposable elements. Trends Genet. 1999;15:326–332. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01777-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acuna R, Padilla BE, Flórez-Ramos CP, Rubio JD, Herrera JC, Benavides P, Lee SJ, Yeats TH, Egan AN, Doyle JJ. Adaptive horizontal transfer of a bacterial gene to an invasive insect pest of coffee. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:4197–4202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121190109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table showing for each A. salmonicida A449 IS630 copy, the size of the XhoI-digested DNA fragment containing the IS, the inter- or intragenic localization, the characteristics of the adjacent genes, and the association to a region of variability or to other IS elements.
Profound analysis and comparison of published Aeromonas genomes used for Figures 3 and 4. Grey: conserved ORFs; light green: ORFs specific of the species; yellow: IS630; pink: other IS elements; red: putative or characterized virulence factors; mauve: ORFs for resistance to antibiotic or heavy metal; dark green: ORFs associated to pili, fimbriae or flagella; blue: ORFs associated to phage; cyan: tRNA and rRNA; orange: ORFs with homology to eukaryotic genes.
Detail of loci corresponding to transposons in Aeromonas sp.