Abstract
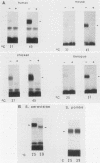
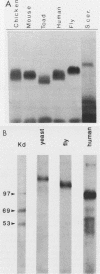
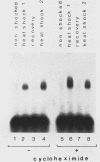
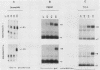
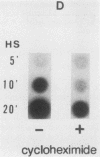
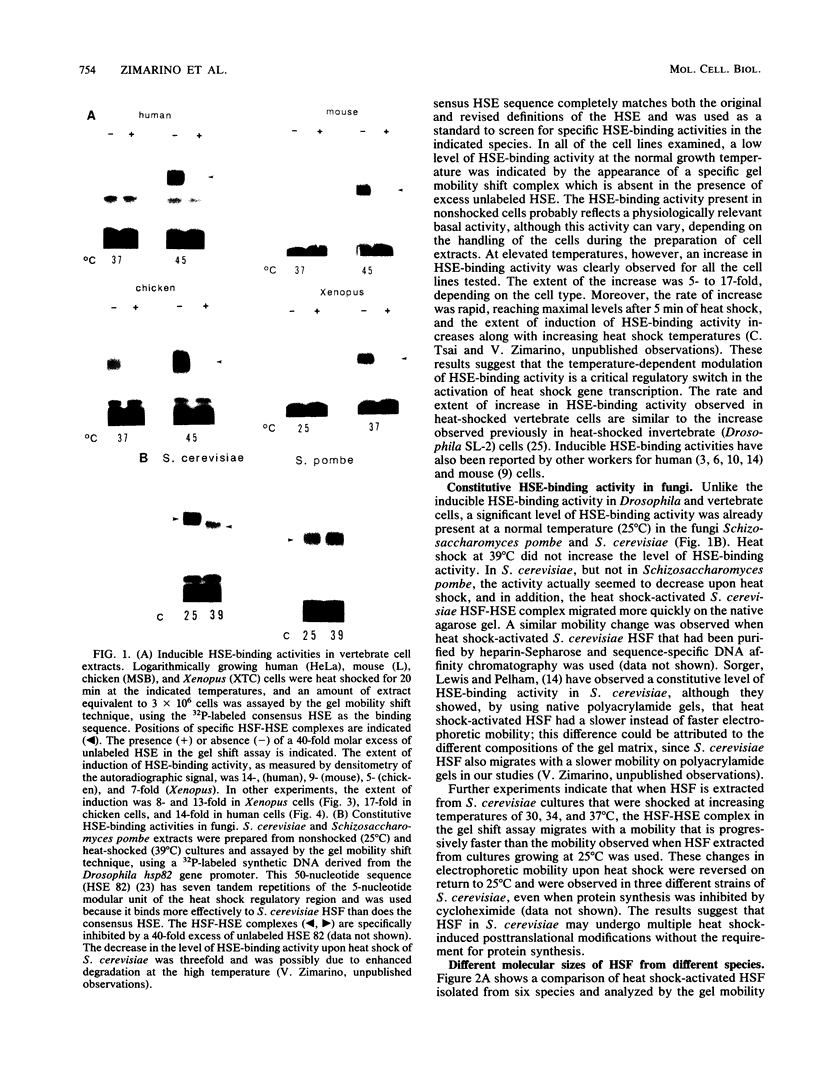
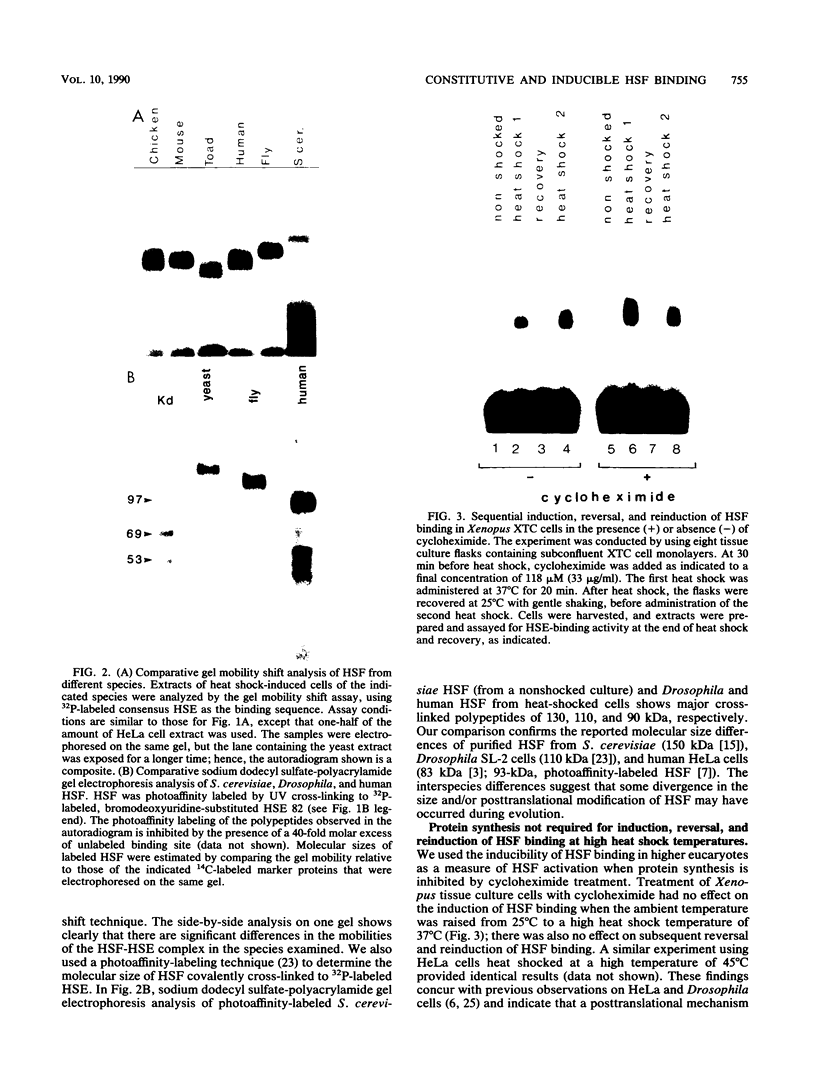
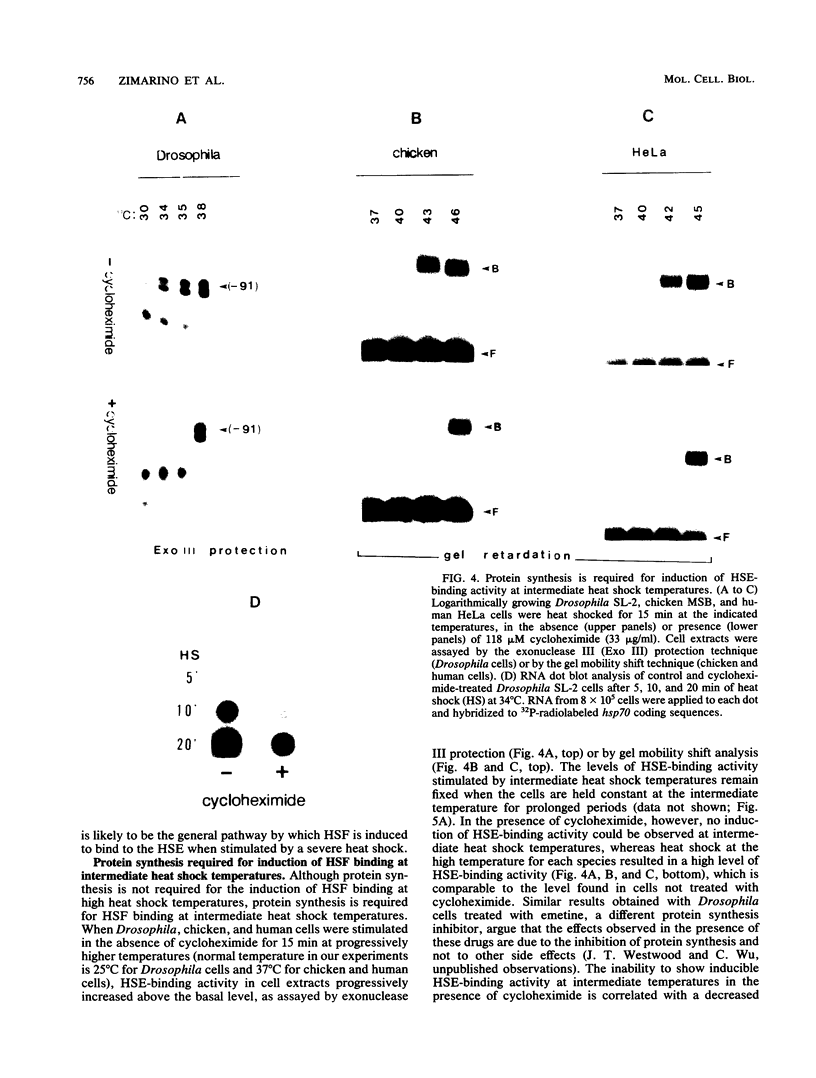
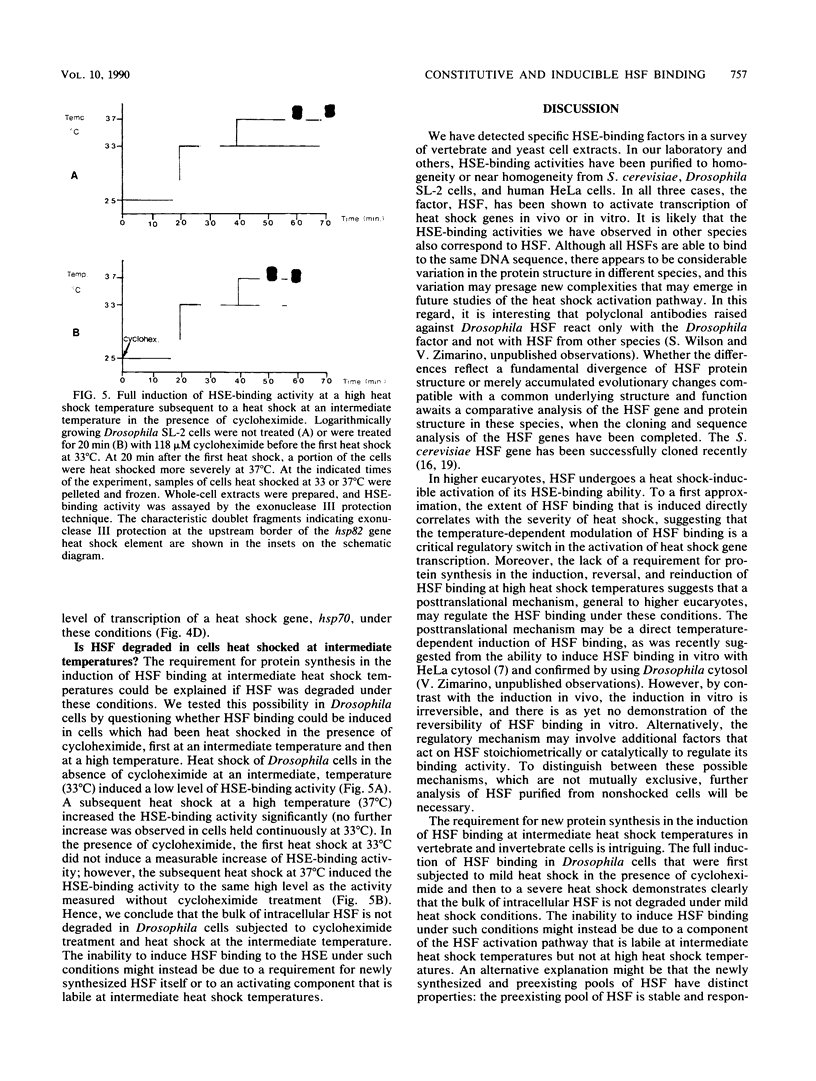
Eucaryotic organisms respond to elevated environmental temperatures by rapidly activating the expression of heat shock genes. The transcriptional activation of heat shock genes is mediated by a conserved upstream regulatory sequence, the heat shock element (HSE). Using an HSE-binding assay, we show that a cellular factor present in a range of vertebrate species binds specifically to the HSE. This factor is presumably the transcriptional activator of heat shock genes, heat shock factor (HSF). In vertebrates, the binding of HSF to the HSE was induced when cells were subjected to heat shock at high temperatures, even in the absence of protein synthesis. Under mild heat shock conditions, HSF binding was induced to a lesser extent, but this induction required protein synthesis, suggesting that synthesis of HSF itself, or an activating factor, is necessary for response to heat shock at intermediate temperatures. The inducibility of HSF binding in higher eucaryotes is contrasted with constitutive HSF binding activity in fungi. It appears that despite conservation of the HSE in evolution, the means by which HSF is activated to bind DNA in higher and lower eucaryotes may have diverged.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. The heat shock response. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(3):239–280. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Luo Y., Fenna M., Baler R., Weinmann R., Voellmy R. Purified human factor activates heat shock promoter in a HeLa cell-free transcription system. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19734–19739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5040–5042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Schuetz T. J., Larin Z. Heat-inducible human factor that binds to a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J. S., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Activation in vitro of sequence-specific DNA binding by a human regulatory factor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):372–375. doi: 10.1038/335372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezger V., Bensaude O., Morange M. Unusual levels of heat shock element-binding activity in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3888–3896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Coordinate changes in heat shock element-binding activity and HSP70 gene transcription rates in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4736–4744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi C., Finkelstein D. B., Garrard W. T. Sharp boundaries demarcate the chromatin structure of a yeast heat-shock gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2191–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Shuey D. J., Kibbe W. A., Parker C. S. The Saccharomyces and Drosophila heat shock transcription factors are identical in size and DNA binding properties. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]