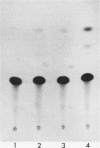
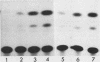
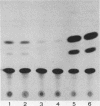
Abstract
Treatment of Daudi or HeLa cells with human interferon (IFN) alpha 8 before induction with either poly(I)-poly(C) or Sendai virus resulted in an 8- to 100-fold increase in IFN production. The extent of priming in Daudi cells paralleled the increase in the intracellular content of IFN-beta mRNA. IFN-alpha mRNA remained undetectable in poly(I)-poly(C)-treated Daudi cells either before or after priming. An IFN-resistant clone of Daudi cells was found to produce 4- to 20-fold more IFN after priming, indicating that priming was unrelated to the phenotype of IFN sensitivity. IFN treatment of either Daudi or HeLa cells transfected with the human IFN-beta promoter (-282 to -37) linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene resulted in an increase in CAT activity after induction with poly(I)-poly(C) or Sendai virus. A synthetic double-stranded oligonucleotide corresponding to an authentic 30-base-pair (bp) region of the human IFN-beta promoter between positions -91 and -62 was found to confer virus inducibility upon the reporter CAT gene in HeLa cells. IFN treatment of HeLa cells transfected with this 30-bp region of the IFN-beta promoter in either the correct or reversed orientation also increased CAT activity upon subsequent induction. IFN treatment alone had no detectable effect on the activity of either the 30-bp region or the complete human IFN promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brack C., Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Molecular analysis of the human interferon-alpha gene family. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter H., Hauser H. Cooperative interaction of multiple DNA elements in the human interferon-beta promoter. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Modjtahedi N., Brison O., Tovey M. G. Interferon modulation of c-myc expression in cloned Daudi cells: relationship to the phenotype of interferon resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G., Eid P. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. III. Interferon-induced proteins in relation to the phenotype of interferon resistance. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):787–795. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. I. Characterization. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2641–2647. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G., Uzé G. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. IV. Characterization of clones with altered binding of human interferon alpha subspecies. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):663–669. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Two different virus-inducible elements are required for human beta-interferon gene regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kohno S. Studies on interferon priming: cellular response to viral and nonviral inducers and requirement of protein synthesis. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi P., Perricaudet M. The E4 transcriptional unit of Ad2: far upstream sequences are required for its transactivation by E1A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7877–7888. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Costas M., Staeheli P., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Organization of the murine Mx gene and characterization of its interferon- and virus-inducible promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3065–3079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Maroteaux L., Cohen B., Mory I. Priming affects the transcription rate of human interferon-beta 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14242–14247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Structure of a chromosomal gene for human interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Dierks P., Ragg H., Weissmann C. A 46-nucleotide promoter segment from an IFN-alpha gene renders an unrelated promoter inducible by virus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Gosser L. B., Lockart R. Z., Jr Priming: a nonantiviral function of interferon. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):792–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.792-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Derynck R., Fiers W. Evidence for a unique human fibroblast interferon (IFN-beta 1) chromosomal gene, devoid of intervening sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):461–471. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Dron M., Gresser I. Interferon enhances the expression of epstein-Barr virus early antigen in Daudi cells. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):31–38. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Dron M., Mogensen K. E., Lebleu B., Mechti N., Begonlours-Guymarho J. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. II. On the mechanisms of resistance. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2649–2653. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M. G., Clauss I. M., Nols C. B., Content J., Huez G. A. New inducers revealed by the promoter sequence analysis of two interferon-activated human genes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Cohen L., Hiscott J. Multiple protein-DNA interactions within the human interferon-beta regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1139–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]