Abstract
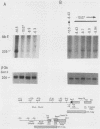
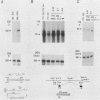
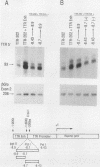
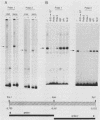
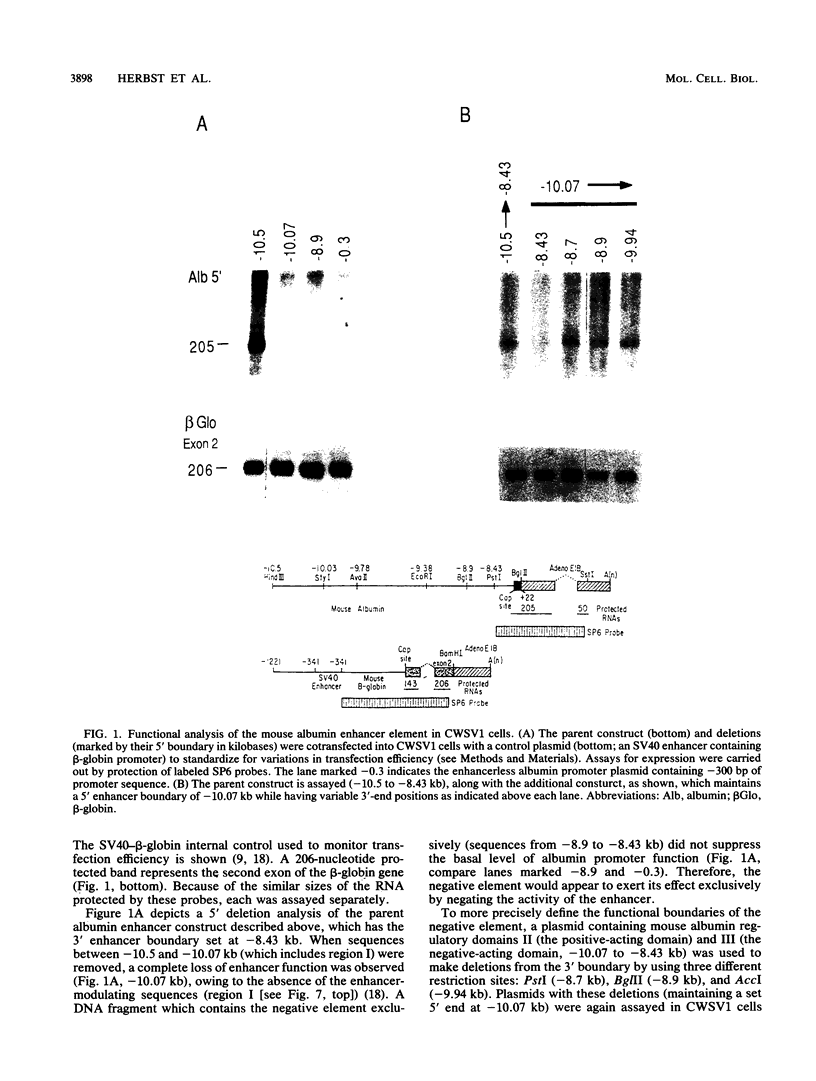
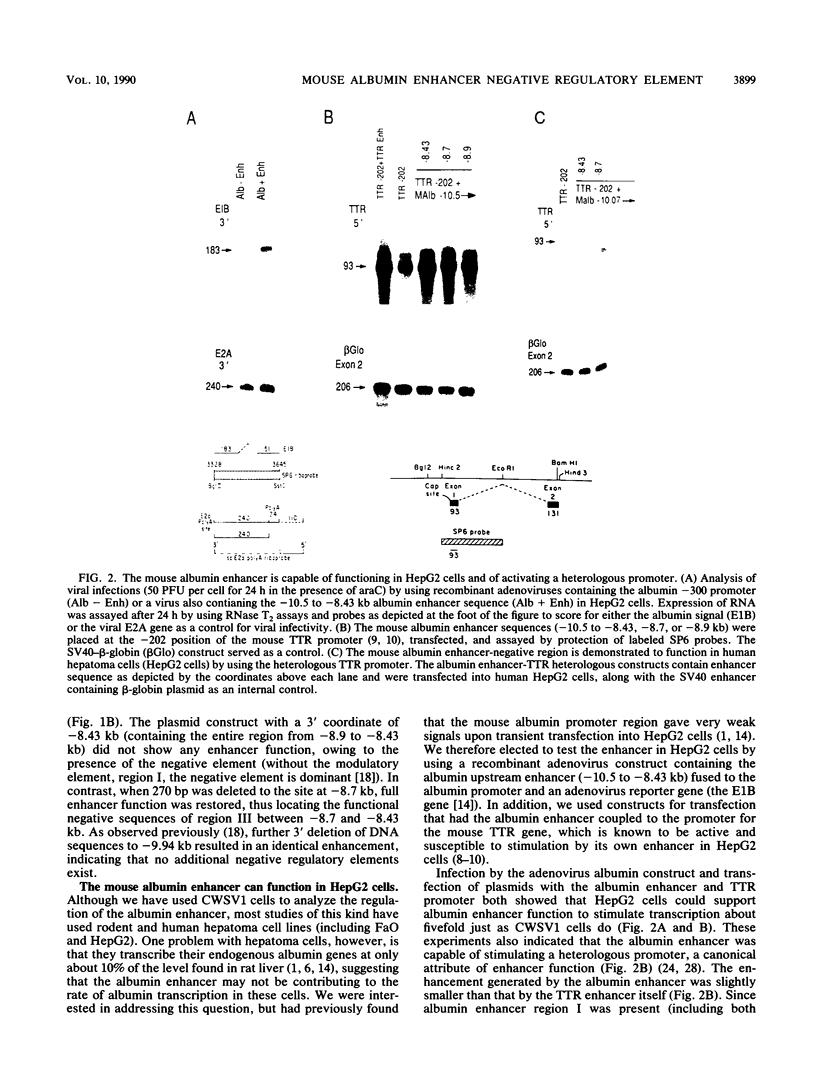
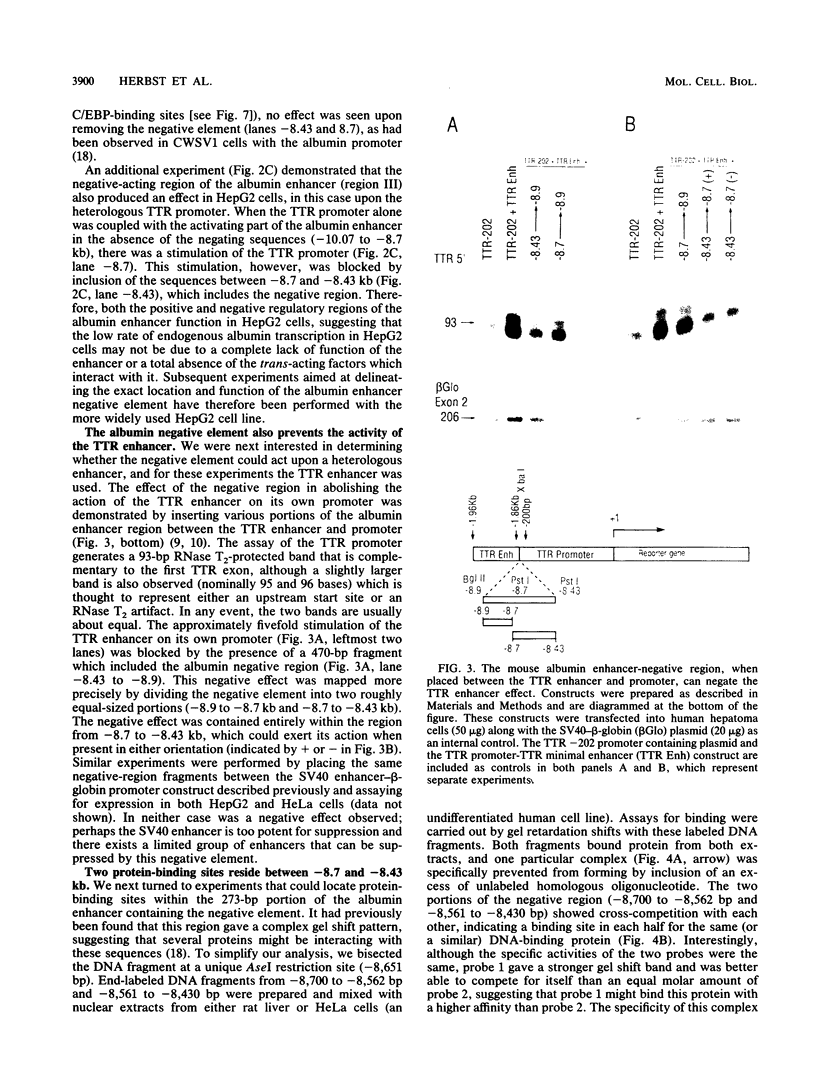
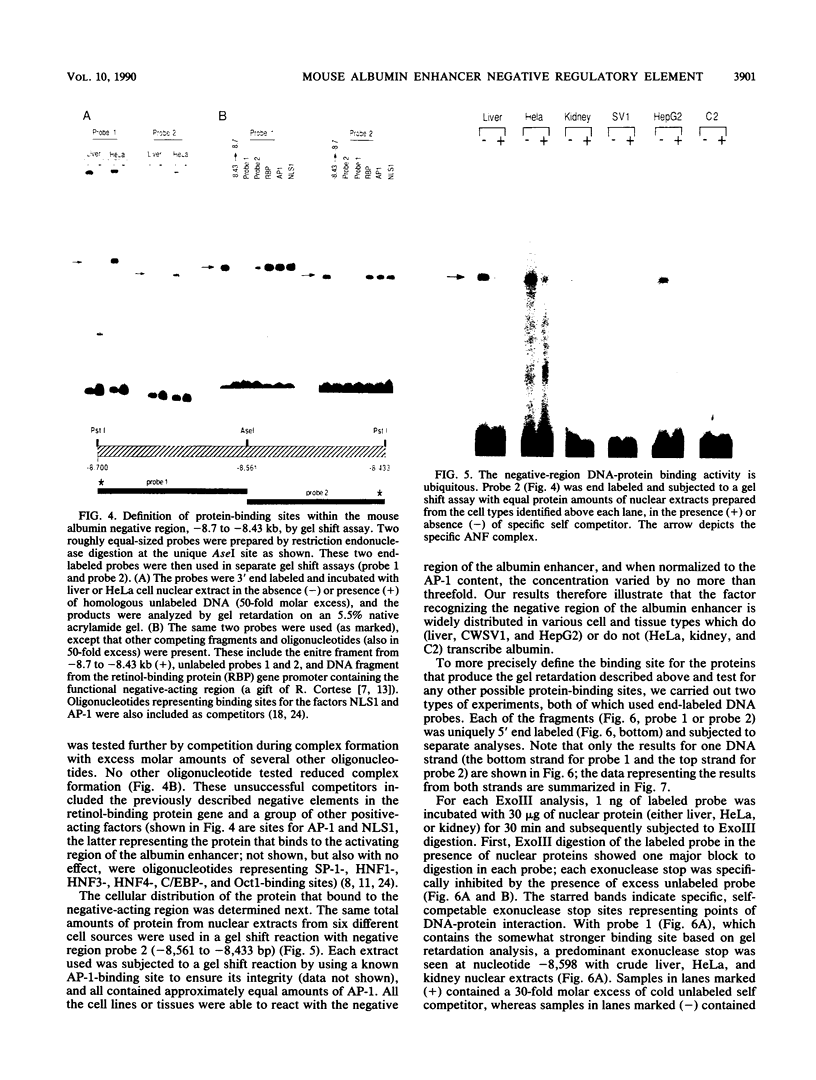
The far-upstream mouse albumin enhancer (-10.5 to -8.43 kilobases) has both positive and negative regulatory domains which contribute to the rate and tissue specificity of albumin gene transcription. (R. S. Herbst, N. Friedman, J. E. Darnell, Jr., and L. E. Babiss, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1553-1557). In this work, the negative regulatory region has been functionally localized to sequences -8.7 to -8.43 kilobases upstream of the albumin gene cap site. In the absence of the albumin-modulating region (in which there are binding sites for the transcription factor C/EBP), the negative region can suppress a neighboring positive-acting element, thereby interfering with albumin enhancer function. The negative region is also capable of negating the positive action of the heterologous transthyretin enhancer in an orientation-independent fashion. Within this negative-acting region we can detect two DNA-binding sites, both of which are recognized by a protein present in all cell types tested. This DNA-binding activity is not competed for by any of a series of known DNA-binding sites, and hence this new protein is a candidate for a role in suppressing the albumin gene in nonhepatic cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiss L. E., Herbst R. S., Bennett A. L., Darnell J. E., Jr Factors that interact with the rat albumin promoter are present both in hepatocytes and other cell types. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):256–267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M. Postnatal repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene is enhancer independent. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):537–546. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. F., Harrelson A. L., Darnell J. E., Jr Dependence of liver-specific transcription on tissue organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2623–2632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control of the mouse prealbumin (transthyretin) gene: both promoter sequences and a distinct enhancer are cell specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4697–4708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The cell-specific enhancer of the mouse transthyretin (prealbumin) gene binds a common factor at one site and a liver-specific factor(s) at two other sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Onofrio C., Colantuoni V., Cortese R. Structure and cell-specific expression of a cloned human retinol binding protein gene: the 5'-flanking region contains hepatoma specific transcriptional signals. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1981–1989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Babiss L. E., Clayton D. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Cellular promoters incorporated into the adenovirus genome: cell specificity of albumin and immunoglobulin expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3791–3797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Takimoto M., Bishop J. M. A FOS protein is present in a complex that binds a negative regulator of MYC. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):293–303. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Riggs K. J., Gillespie W., Calame K. A transcriptional repressor of c-myc. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):718–721. doi: 10.1038/339718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. K., Bergman Y., Zaret K. S. The mouse albumin promoter and a distal upstream site are simultaneously DNase I hypersensitive in liver chromatin and bind similar liver-abundant factors in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):528–541. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Rothman-Denes L. B. Cell type-specific negative regulatory element in the control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C., Levilliers J., Ott M. O., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression of the rat albumin gene: genetic control of its extinction in microcell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2561–2565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuermann R. H., Chen U. A developmental-specific factor binds to suppressor sites flanking the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1255–1266. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Isom H. C. Regulation of albumin gene expression in a series of rat hepatocyte cell lines immortalized by simian virus 40 and maintained in chemically defined medium. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3740–3748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]