Abstract
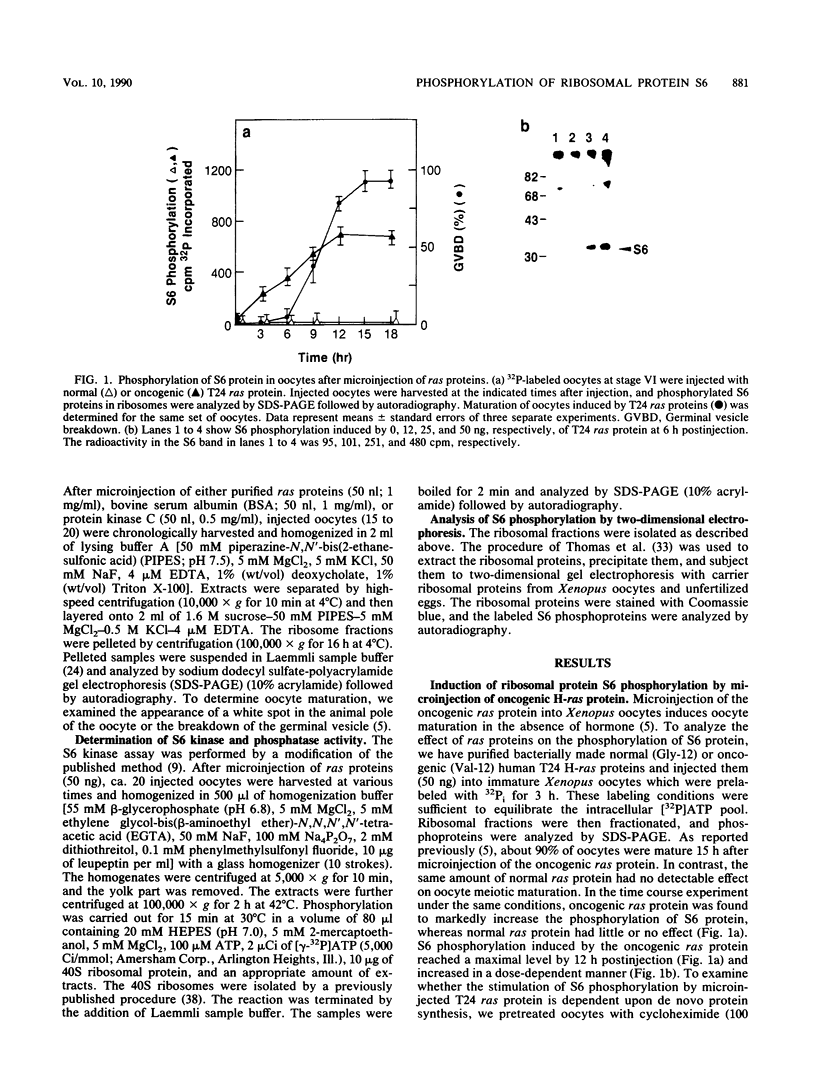
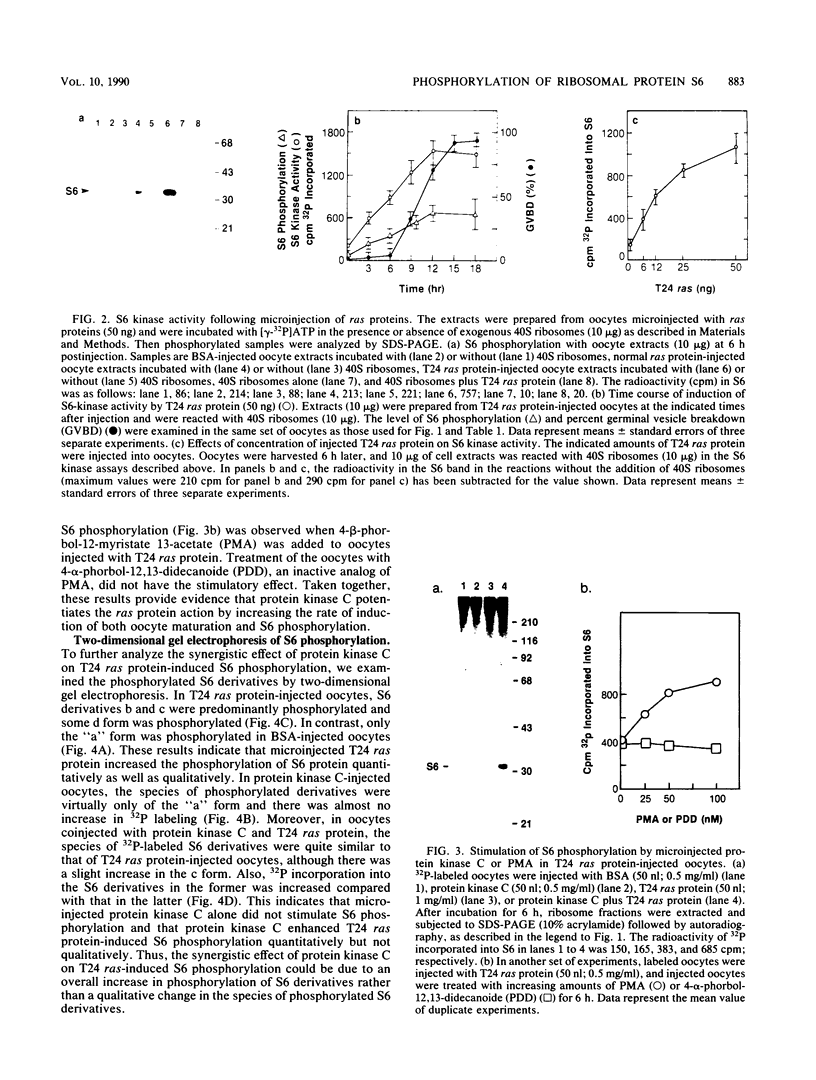
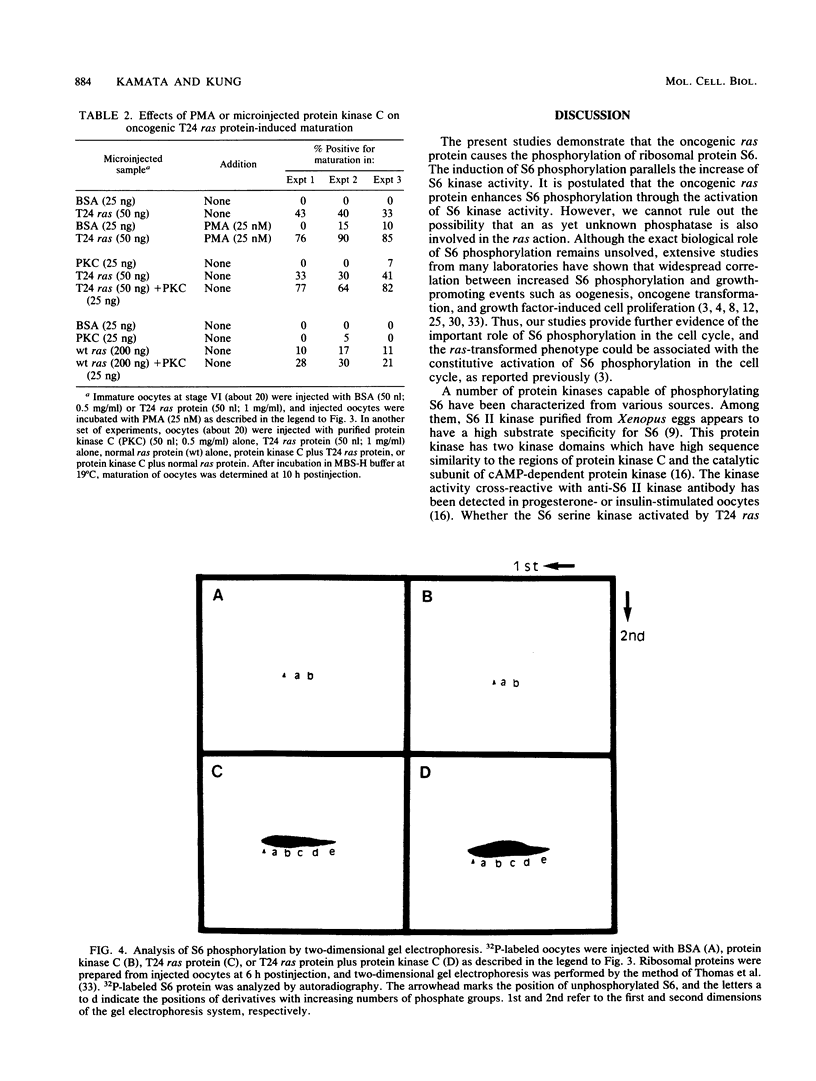
Using Xenopus oocytes as a model system, we investigated the possible involvement of ras proteins in the pathway leading to phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Our results indicate that microinjection of oncogenic T24 H-ras protein (which contains valine at position 12) markedly stimulated S6 phosphorylation on serine residues in oocytes, whereas normal ras protein (which contains glycine at position 12) was without effect. The S6 phosphorylation activity in the cell extract from T24 ras protein-injected oocytes was increased significantly. In addition, injection of protein kinase C potentiated the induction of maturation and S6 phosphorylation by the oncogenic ras protein. A similar potentiation was detected when T24 ras protein-injected oocytes were incubated with active phorbol ester. These findings suggest that ras proteins activate the pathway linked to S6 phosphorylation and that protein kinase C has a synergistic effect on the ras-mediated pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballester R., Furth M. E., Rosen O. M. Phorbol ester- and protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of the cellular Kirsten ras gene product. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2688–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 is elevated in cells transformed by a variety of tumor viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):966–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.966-969.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhard S. J., Traugh J. A. Changes in ribosome function by cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14003–14008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A. K., Kung H. F. Insulin induction of Xenopus laevis oocyte maturation is inhibited by monoclonal antibody against p21 ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1285–1288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Etr M., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Baulieu E. E. Meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes initiated by insulin. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1397–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.472755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Clanton D. J., Satoh T., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y., Kawakita M., Shih T. Y. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody against ras oncogene product p21 which impairs guanine nucleotide exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1999–2002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Feramisco J. R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates guanine nucleotide binding activity and phosphorylation of ras oncogene proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):147–150. doi: 10.1038/310147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Kathuria S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation level of v-Ha-ras protein in membrane fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Kung H. F. Effects of ras-encoded proteins and platelet-derived growth factor on inositol phospholipid turnover in NRK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5799–5803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Sullivan N. F., Wooten M. W. Reduced protein kinase C activity in a ras-resistant cell line derived from Ki-MSV transformed cells. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Fleming T. P., Warren B. S., Blumberg P. M., Aaronson S. A. Involvement of functional protein kinase C in the mitogenic response to the H-ras oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4146–4149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., de la Peña P., Moscat J., Garcia-Barreno P., Anderson P. S., Aaronson S. A. Rapid stimulation of diacylglycerol production in Xenopus oocytes by microinjection of H-ras p21. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):533–536. doi: 10.1126/science.2821623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Baltimore D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 on serine after microinjection of the Abelson murine leukemia virus tyrosine-specific protein kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte A. P., Koster C. H., Snoek G. T., Durston A. J. Protein kinase C mediates neural induction in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):618–620. doi: 10.1038/334618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikumar P., Ulsh L. S., Clanton D. J., Huang K. P., Shih T. Y. Novel phosphorylation of c-ras p21 by protein kinases. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(3):213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Erikson R. L., Maller J. L. Microinjection of pp60v-src into Xenopus oocytes increases phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and accelerates the rate of progesterone-induced meiotic maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1631–1634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith B. J., Maller J. L. Induction of meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Apr;169(2):514–523. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. Elevated levels of diacylglycerol and decreased phorbol ester sensitivity in ras-transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):359–361. doi: 10.1038/325359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Tsai M. H., Stacey D. W. Cellular ras activity and phospholipid metabolism. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Purification of eukaryotic initiation factor 1 (EIF1) from Artemia salina embryos. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:197–206. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






