Abstract
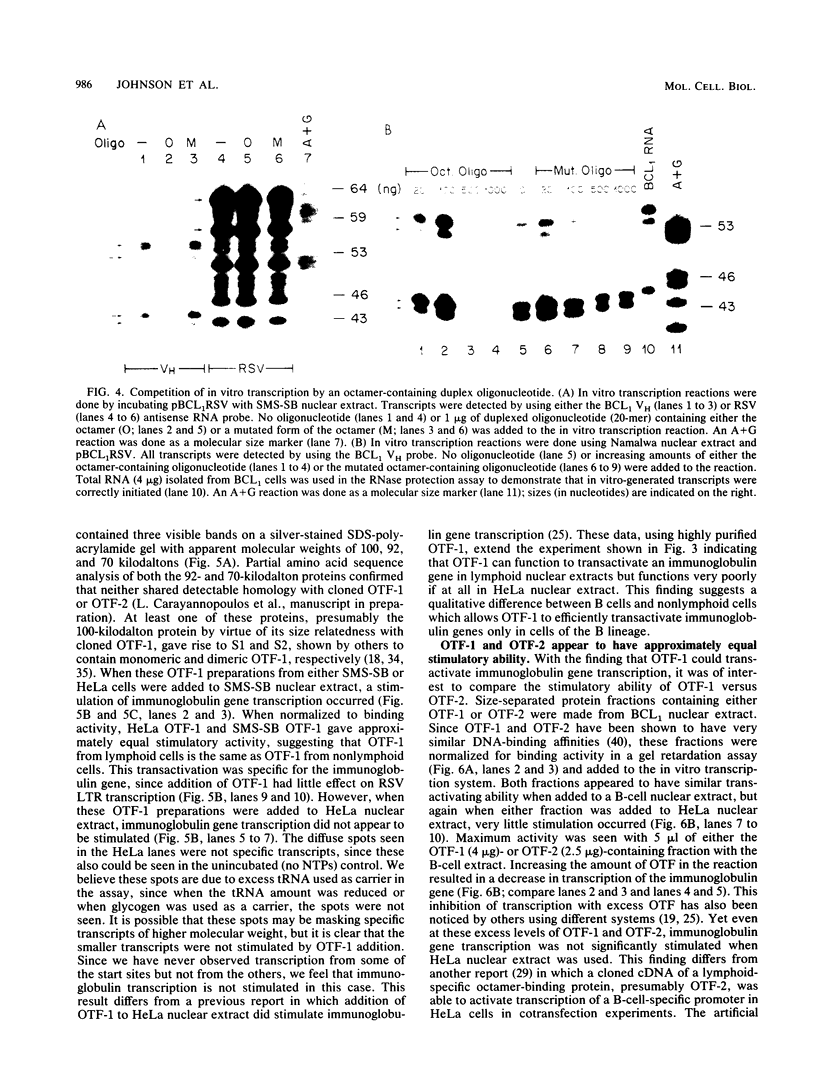
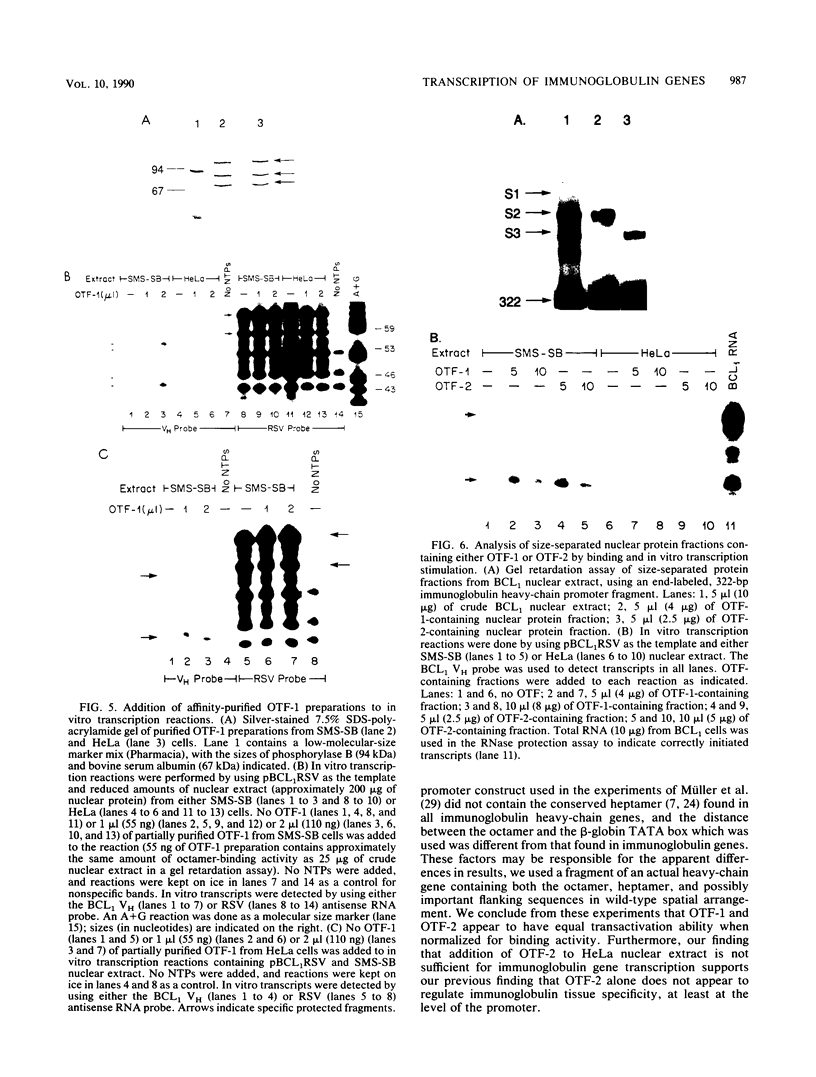
All immunoglobulin genes contain a conserved octanucleotide promoter element, ATGCAAAT, which has been shown to be required for their normal B-cell-specific transcription. Proteins that bind this octamer have been purified, and cDNAs encoding octamer-binding proteins have been cloned. Some of these proteins (referred to as OTF-2) are lymphoid specific, whereas at least one other, and possibly more (referred to as OTF-1), is found ubiquitously in all cell types. The exact role of these different proteins in directing the tissue-specific expression of immunoglobulin genes is unclear. We have identified two human pre-B-cell lines that contain extremely low levels of OTF-2 yet still express high levels of steady-state immunoglobulin heavy-chain mRNA in vivo and efficiently transcribe an immunoglobulin gene in vitro. Addition of a highly enriched preparation of OTF-1 made from one of these pre-B cells or from HeLa cells specifically stimulated in vitro transcription of an immunoglobulin gene. Furthermore, OFT-1 appeared to have approximately the same transactivation ability as OTF-2 when normalized for binding activity. These results suggest that OTF-1, without OTF-2, is sufficient for transcription of immunoglobulin genes and that OTF-2 alone is not responsible for the B-cell-specific regulation of immunoglobulin gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Doyen N., Rougeon F. The conserved decanucleotide from the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter induces a very high transcriptional activity in B-cells when introduced into an heterologous promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton S., Calame K. Multiple DNA sequence elements are necessary for the function of an immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke J. H., Landolfi N. F., Tucker P. W., Capra J. D. Identification of murine nuclear proteins that bind to the conserved octamer sequence of the immunoglobulin promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3560–3564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R., Hozier J., LeBien T., Minowada J., Gajl-Peczalska K., Kubonishi I., Kersey J. Characterization of a leukemic cell line of the pre-B phenotype. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):174–180. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker S., Nielsen V., Matthias P., Picard D. Both immunoglobulin promoter and enhancer sequences are targets for suppression in myeloma-fibroblast hybrid cells. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3093–3098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schreiber E., Müller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2001–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Latchman D. S. Differential regulation of octamer-containing cellular genes by the herpes simplex virus virion protein Vmw65 is mediated by sequence differences in the octamer element. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4239–4244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. R., Liu C. P., Newell N., Ward R. B., Tucker P. W., Strober S., Blattner F. Simultaneous expression of immunoglobulin mu and delta heavy chains by a cloned B-cell lymphoma: a single copy of the VH gene is shared by two adjacent CH genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2996–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. A human protein specific for the immunoglobulin octamer DNA motif contains a functional homeobox domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Yin X. M., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. A conserved heptamer upstream of the IgH promoter region octamer can be the site of a coordinate protein-DNA interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5503–5514. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1227–1237. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima-Sugano J., Roeder R. G. Cell-type-specific transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8511–8515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R., Haigh A. Direct combinatorial interaction between a herpes simplex virus regulatory protein and a cellular octamer-binding factor mediates specific induction of virus immediate-early gene expression. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4231–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J. Purification and characterization of nuclear factor III (origin recognition protein C), a sequence-specific DNA binding protein required for efficient initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):931–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G. Functional cooperativity between protein molecules bound at two distinct sequence elements of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):573–576. doi: 10.1038/337573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Anti-OTF-1 antibodies inhibit NFIII stimulation of in vitro adenovirus DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1845–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. In vitro transcription of immunoglobulin genes in a B-cell extract: effects of enhancer and promoter sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1989–1994. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Dev V. G., Shannon W. A., Jr Characterization of a novel human pre-B leukemia cell line. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.3399892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Herr W. The POU domain is a bipartite DNA-binding structure. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):601–604. doi: 10.1038/336601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Nakai S., Honjo T. Cloning of human immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with mouse mu gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5983–5991. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J., Smith R. G., Ozanne B. Characterization of a leukemia-derived transforming growth factor. Leukemia. 1987 Nov;1(11):737–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Yu H., Eckhardt L. A. Genes activated in the presence of an immunoglobulin enhancer or promoter are negatively regulated by a T-lymphoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1932–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]