Abstract
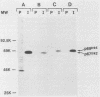
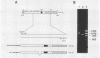
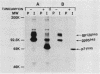
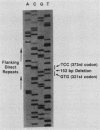
Malignant activation of the human trk proto-oncogene, a member of the tyrosine protein kinase receptor family, has been implicated in the development of certain human cancers, including colon and thyroid papillary carcinomas. trk oncogenes have also been identified in cultured cells transfected with various DNAs. In this study, we report the characterization of three in vitro-generated trk oncogenes, trk2, trk4, and trk5 (R. Oskam, F. Coulier, M. Ernst, D. Martin-Zanca, and M. Barbacid, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:2964-2968, 1988), in an effort to understand the spectrum of mutational events that can activate the human trk gene. Nucleotide sequence analysis of cDNA clones of trk2 and trk4 revealed that these oncogenes were generated by a head-to-tail arrangement of two trk tyrosine protein kinase domains connected by a purine-rich region. These oncogenes code for cytoplasmic molecules of 67,000 (p67trk2) and 69,000 (p69trk4) daltons. In contrast, the product of the trk5 oncogene, gp95trk5, is a cell surface glycoprotein of 95,000 daltons. This oncogene was generated by a 153-base-pair in-frame deletion within sequences coding for the extracellular domain of the trk receptor. This activating deletion encompasses a triplet coding for one of the nine cysteine residues that the trk receptor shares with the product of the highly related trkB tyrosine protein kinase gene. Introduction of a single point mutation (TGT----AGT) in this codon resulted in a novel trk oncogene whose product, gp140S345, differs from the nontransforming trk proto-oncogene receptor in a single amino acid residue, Ser-345 instead of Cys-345. These results illustrate that multiple molecular mechanisms, including point mutation, internal deletion, and kinase domain duplication, can result in the malignant activation of the human trk proto-oncogene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreadis A., Gallego M. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Generation of protein isoform diversity by alternative splicing: mechanistic and biological implications. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:207–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongarzone I., Pierotti M. A., Monzini N., Mondellini P., Manenti G., Donghi R., Pilotti S., Grieco M., Santoro M., Fusco A. High frequency of activation of tyrosine kinase oncogenes in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncogene. 1989 Dec;4(12):1457–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
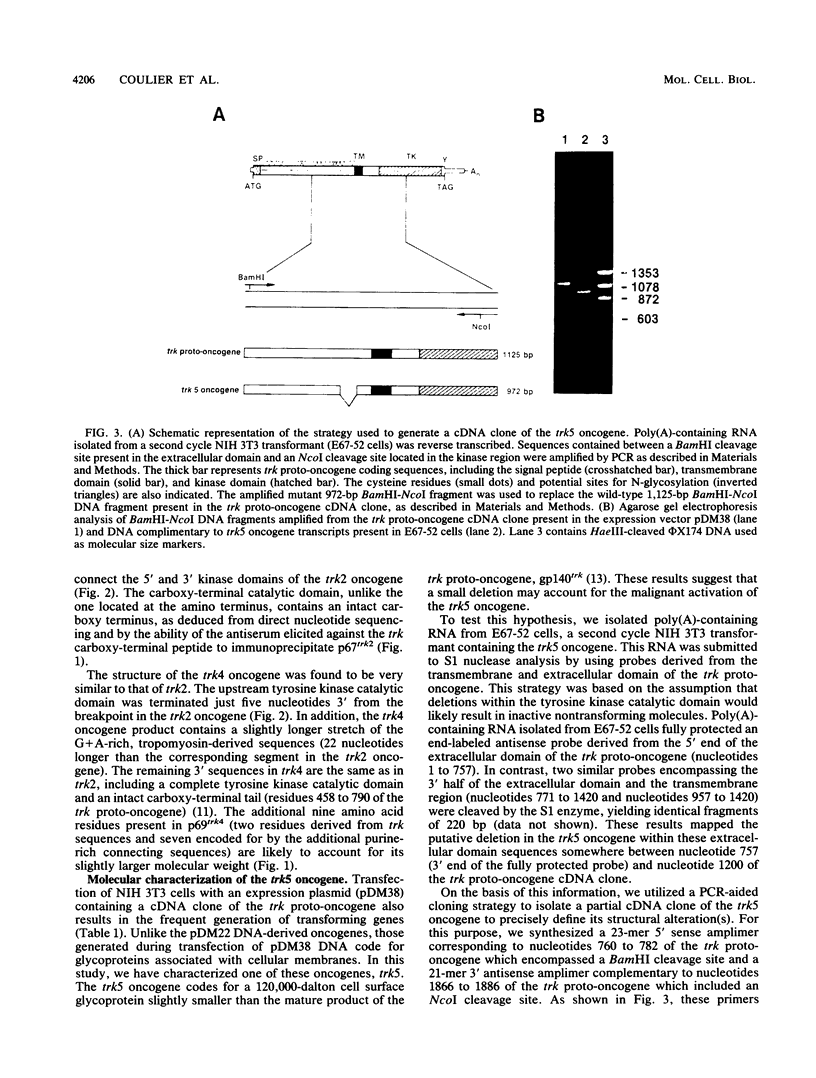
- Coulier F., Martin-Zanca D., Ernst M., Barbacid M. Mechanism of activation of the human trk oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Parada L. F., Coulier F., Barbacid M. trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Redmond S. M., Fu X. C., Saurer S. M., Groner B., Hynes N. E. Activation of the receptor kinase domain of the trk oncogene by recombination with two different cellular sequences. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):147–154. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M., Parada L. F. Expression of the trk proto-oncogene is restricted to the sensory cranial and spinal ganglia of neural crest origin in mouse development. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):683–694. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Oskam R., Mitra G., Copeland T., Barbacid M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):24–33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra G., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Identification and biochemical characterization of p70TRK, product of the human TRK oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6707–6711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskam R., Coulier F., Ernst M., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Frequent generation of oncogenes by in vitro recombination of TRK protooncogene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. The viral and cellular forms of the Abelson (abl) oncogene. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:39–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60708-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
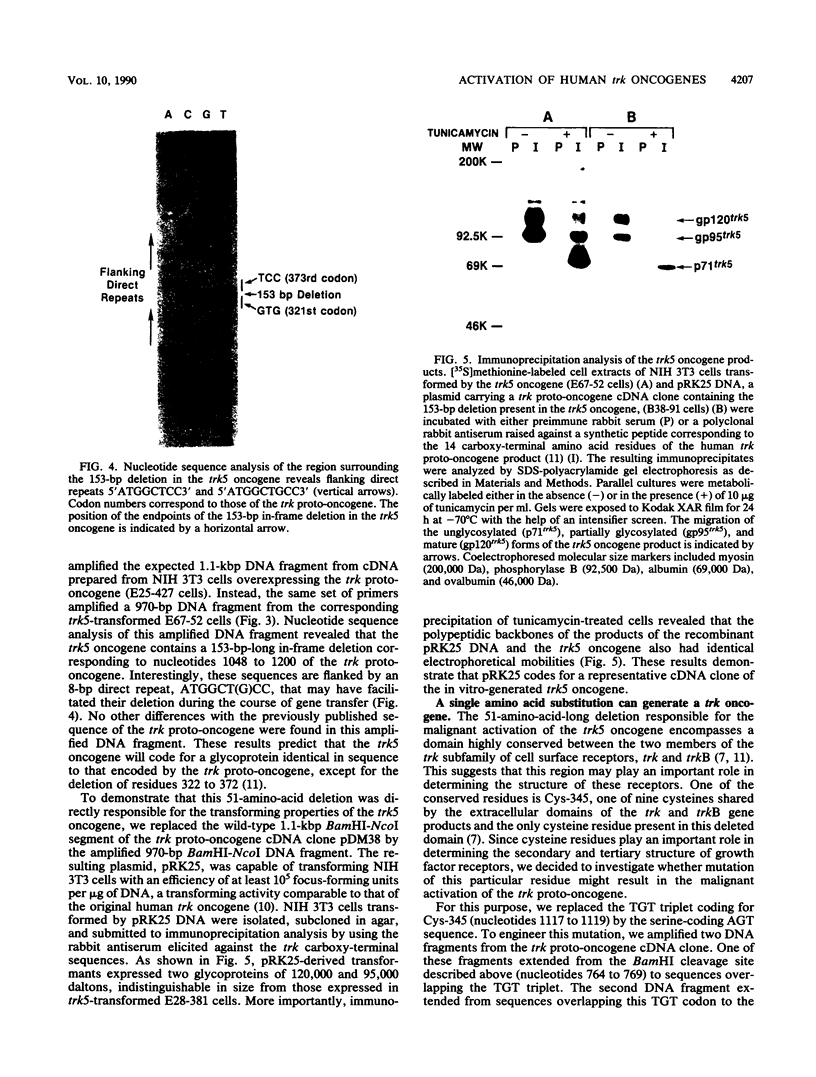
- Roussel M. F., Downing J. R., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. A point mutation in the extracellular domain of the human CSF-1 receptor (c-fms proto-oncogene product) activates its transforming potential. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar S., Barbacid M. Specific patterns of oncogene activation in transplacentally induced tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Retroviruses. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1427–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.3287617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Avian sarcoma viruses. Virus Res. 1988 Feb;9(2-3):159–203. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Müller R. G., Fu X. C., Hynes N. E., Kozma S. Oncogenic activation of the human trk proto-oncogene by recombination with the ribosomal large subunit protein L7a. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):191–196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]