Abstract
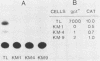
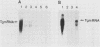
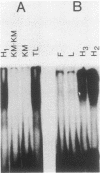
Thyroglobulin gene expression was repressed in a rat thyroid cell line transformed with Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Expression of a dominant selectable marker driven by the thyroglobulin promoter was also inhibited. Somatic cell hybridization of transformed and differentiated thyroid cells resulted in extinction of thyroglobulin gene expression. When transformed cells carrying a dominant selectable marker driven by the thyroglobulin promoter were fused to differentiated cells and expression of this marker was selected, we obtained stable hybrid cell lines expressing both the endogenous and the exogenous thyroglobulin promoters. Although the expression of v-ras remained unchanged compared with expression in the parental transformed cells, transformation was suppressed in the hybrid cell lines. The other thyroid differentiation markers, iodide uptake and thyroid-stimulating hormone-dependent growth, were inhibited in all the hybrids tested. We show that activity of the thyroglobulin promoter correlates with the presence of a thyroid nuclear factor that binds the promoter at position -60 from the transcription start site. Loss of this factor accompanies the extinction of thyroglobulin gene expression in hybrids selected for expression of a non-thyroid-specific promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avvedimento E. V., Obici S., Sanchez M., Gallo A., Musti A., Gottesman M. E. Reactivation of thyroglobulin gene expression in transformed thyroid cells by 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1135–1142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avvedimento V. E., Musti A., Fusco A., Bonapace M. J., Di Lauro R. Neoplastic transformation inactivates specific trans-acting factor(s) required for the expression of the thyroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1744–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Maniatis T. Rapid reprogramming of globin gene expression in transient heterokaryons. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90885-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlingieri M. T., Musti A. M., Avvedimento V. E., Di Lauro R., Di Fiore P. P., Fusco A. The block of thyroglobulin synthesis, which occurs upon transformation of rat thyroid epithelial cells, is at the transcriptional level and it is associated with methylation of the 5' flanking region of the gene. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Aug;183(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolotti R., Weiss M. C. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids. II. Aldolase. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Apr;79(2):211–224. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040790206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin A. C., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-regulation of 16 liver-specific genes in hepatoma-fibroblast hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colletta G., Pinto A., Di Fiore P. P., Fusco A., Ferrentino M., Avvedimento V. E., Tsuchida N., Vecchio G. Dissociation between transformed and differentiated phenotype in rat thyroid epithelial cells after transformation with a temperature-sensitive mutant of the Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2099–2109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W., Sager R. Suppression of tumorigenicity in hybrids of normal and oncogene-transformed CHEF cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L. Gene expression in somatic cell hybrids. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:195–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lauro R., Obici S., Condliffe D., Ursini V. M., Musti A., Moscatelli C., Avvedimento V. E. The sequence of 967 amino acids at the carboxyl-end of rat thyroglobulin. Location and surroundings of two thyroxine-forming sites. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougère C., Weiss M. C. Phenotypic exclusion in mouse melanoma-rat hepatoma hybrid cells: pigment and albumin production are not reexpressed simultaneously. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):843–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusco A., Pinto A., Tramontano D., Tajana G., Vecchio G., Tsuchida N. Block in the expression of differentiation markers of rat thyroid epithelial cells by transformation with Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):618–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser A. G., Der C. J., Marshall C. J., Stanbridge E. J. Suppression of tumorigenicity with continued expression of the c-Ha-ras oncogene in EJ bladder carcinoma-human fibroblast hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5209–5213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. When the products of oncogenes and anti-oncogenes meet. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90975-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Wu D., Castrillo J. L., Dana S., Strobl J., Thompson E. B., Karin M. Extinction of growth hormone expression in somatic cell hybrids involves repression of the specific trans-activator GHF-1. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musti A. M., Ursini V. M., Avvedimento E. V., Zimarino V., Di Lauro R. A cell type specific factor recognizes the rat thyroglobulin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8149–8166. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C., Levilliers J., Ott M. O., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression of the rat albumin gene: genetic control of its extinction in microcell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2561–2565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R. Genetic suppression of tumor formation. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:43–68. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Allen N. E., Hobbs J. N., Jr, Rao R. N., Schmidt R. J. Expression of prokaryotic genes for hygromycin B and G418 resistance as dominant-selection markers in mouse L cells. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon P. J., Srivatsan E. S., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of human chromosome 11 via microcell transfer controls tumorigenic expression of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3461–3466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenschein C., Richardson U. I., Tashjian A. H., Jr Loss of growth hormone production following hybridization of a functional rat pituitary cell strain with a mouse fibroblast line. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Dec;69(2):336–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursini M. V., Gallo A., Olivetta E., Musti A. M. Protein binding domains of the rat thyroglobulin promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):481–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Chaplain M. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: reappearance of tyrosine aminotransferase inducibility after the loss of chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. E., Saxon P. J., Pasquale S. R., Jones G. R., Geiser A. G., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of a normal human chromosome 11 into a Wilms' tumor cell line controls its tumorigenic expression. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):175–180. doi: 10.1126/science.3031816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Porton B., Shen L. Y., Eckhardt L. A. Role of the octamer motif in hybrid cell extinction of immunoglobulin gene expression: extinction is dominant in a two enhancer system. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]