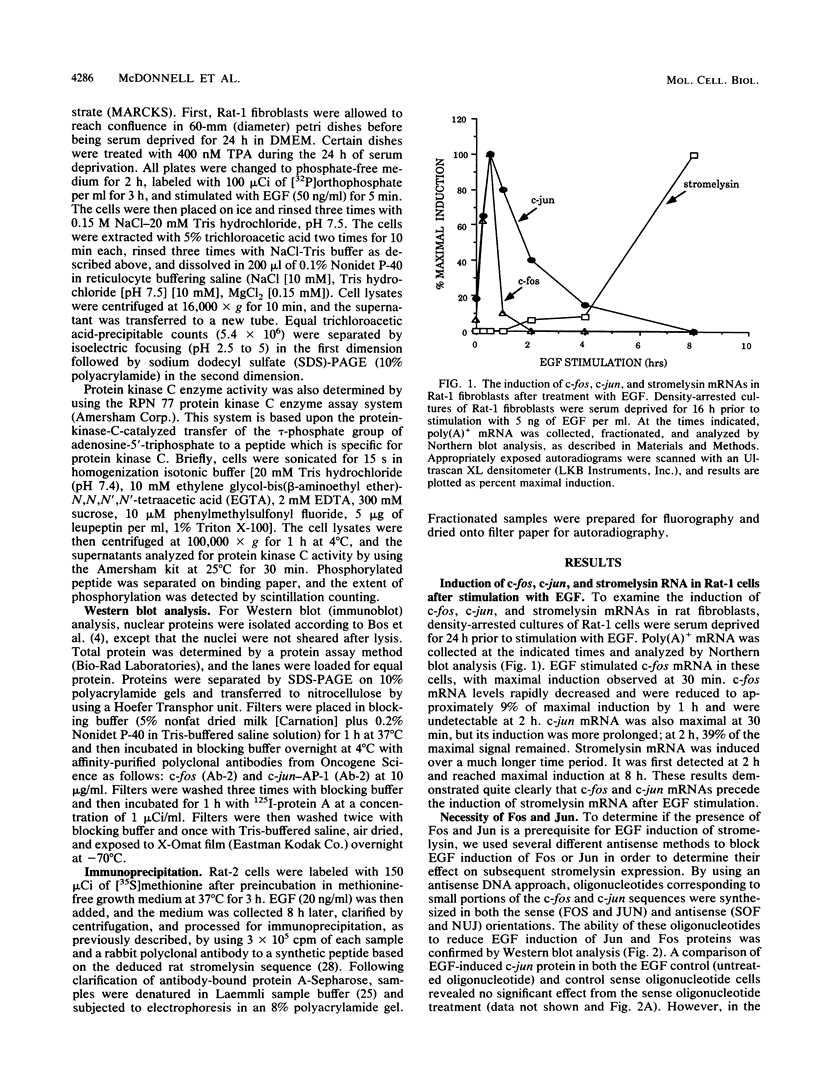
Abstract
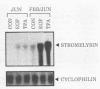
Stromelysin (transin) is a secreted metalloprotease that is transcriptionally induced by a variety of growth factors and oncogenes. We examined the necessity of specific secondary (protein kinase C) and tertiary (c-fos and c-jun protein products) messengers in the transactivation of stromelysin gene expression by epidermal growth factor (EGF). Rat-1 fibroblasts exposed to antisense c-fos DNA or RNA demonstrated that c-fos expression was necessary for complete EGF induction of stromelysin expression. Similar results demonstrating the necessity of c-jun protein in the EGF induction of stromelysin were obtained. We also demonstrated that protein kinase C activation is required for the EGF induction of stromelysin, since phorbol ester desensitization of C kinase proteins abolished the ability of EGF to induce stromelysin mRNA, protein, and promoter activity. In reconstitution experiments, neither c-fos, c-jun, nor C kinase activation alone induced significant stromelysin expression. Overexpression of c-fos and c-jun was able to induce stromelysin to a level similar to that of the growth factor, and stimulation of protein kinase C activity augmented this induction. The data suggest that the EGF induction of stromelysin in rat fibroblasts procedes through a pathway involving c-fos, c-jun, and protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Bohmann D., Tsuchie H., Tjian R., Vogt P. K. v-jun encodes a nuclear protein with enhancer binding properties of AP-1. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracke M. E., Van Cauwenberge R. M., Mareel M. M., Castronovo V., Foidart J. M. Flavonoids: tools for the study of tumor invasion in vitro. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;213:441–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Adler R. R., Rappolee D. A., Pedersen R. A., Werb Z. Genes for extracellular-matrix-degrading metalloproteinases and their inhibitor, TIMP, are expressed during early mammalian development. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):848–859. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Korc M. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding in rat pancreatic acini by palmitoyl carnitine: evidence for Ca2+ and protein kinase C independent regulation. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 1;47(7):1805–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Binding of phorbol esters to high-affinity sites on murine fibroblastic cells elicits a mitogenic response. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):42–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Mitchell R. L., Meijlink F., Kruijer W., Schubert D., Verma I. M. Proto-oncogene fos is expressed during development, differentiation, and growth. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:733–745. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Ruley H. E. Transcription from the stromelysin promoter is induced by interleukin-1 and repressed by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16300–16304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki H., Horiuchi T., Yamashita K., Hakii H., Suganuma M., Nishino H., Iwashima A., Hirata Y., Sugimura T. Inhibition of tumor promotion by flavonoids. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;213:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb R. H., Liotta L. A. Proteolytic enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Oct;12(4):294–307. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasley L. E., Johnson G. L. Regulation of protein kinase C by nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and phorbol esters in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Gopal T. V., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Holt J. T., Matrisian L. M. Growth factors regulate transin gene expression by c-fos-dependent and c-fos-independent pathways. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.2462278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Olashaw N. E., Matrisian L. M. Transforming growth factor beta 1 and cAMP inhibit transcription of epidermal growth factor- and oncogene-induced transin RNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16999–17005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Krieg P., Fürstenberger G., Briand J. P., Leroy P., Breathnach R. The mRNA coding for the secreted protease transin is expressed more abundantly in malignant than in benign tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9413–9417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. G., Pledger W. J., Cheung H. S. Molecular mechanism of basic calcium phosphate crystal-induced mitogenesis. Role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14071–14077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscat J., Molloy C. J., Fleming T. P., Aaronson S. A. Epidermal growth factor activates phosphoinositide turnover and protein kinase C in BALB/MK keratinocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Sep;2(9):799–805. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-9-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski L. E., Finch J., Krieg P., Matrisian L., Patskan G., O'Connell J. F., Phillips J., Slaga T. J., Breathnach R., Bowden G. T. Expression pattern of a gene for a secreted metalloproteinase during late stages of tumor progression. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(1):13–19. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Graff J. M., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Blackshear P. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding the "80- to 87-kDa" myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate: a major cellular substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Enami S., Curran T., Verma I. M. FBR murine osteosarcoma virus. II. Nucleotide sequence of the provirus reveals that the genome contains sequences acquired from two cellular genes. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]