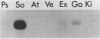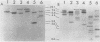Abstract
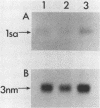
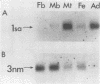
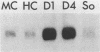
We have isolated a cDNA clone for the human slow-twitch muscle isoform myosin light-chain 1slow-a (MLC1sa) from a skeletal muscle library and for the human nonmuscle isoform myosin light-chain 3nonmuscle (MLC3nm) from a fibroblast library. The nucleotide sequence of both isoforms was determined, and isoform-specific probes were constructed. In addition, MLC1sa was subsequently isolated from the fibroblast library. MLC1sa and MLC3nm were found to be very closely related to each other and distant from all other myosin light-chain isoforms so far described. We concluded that MLC1sa arose by duplication of MLC3nm rather than from any other isoform. A comparison was made between all human myosin light chains described to date and a model proposed for the evolution of this multigene family. A comparison between human and chicken myosin light-chain isoforms showed that human isoforms are more similar to their chicken counterparts than to human MLC1sa. The expression of MLC1sa and MLC3nm was studied in humans, rabbits, mice, and rats. MLC1sa was detected at the onset of both human and murine myogenesis in vitro. With development, MLC1sa may be replaced by the other slow-twitch muscle isoform, 1sb, in slow-twitch skeletal muscle, but the proportion of MLC1sa to 1sb expression varies between different species. MLC1sa was detected in nonmuscle cells in humans, mice, and rats. MLC3nm was the major nonmuscle alkaline myosin light chain in all species tested, but its pattern of expression in nonmuscle tissues was not identical to that of beta- or gamma-actin. We have shown that in the human, as in the chicken, one exon is spliced out of the MLC3nm transcript in smooth muscle to give an alternative product. We concluded that all alkali myosin light-chain isoforms may be functionally different.
Full text
PDF




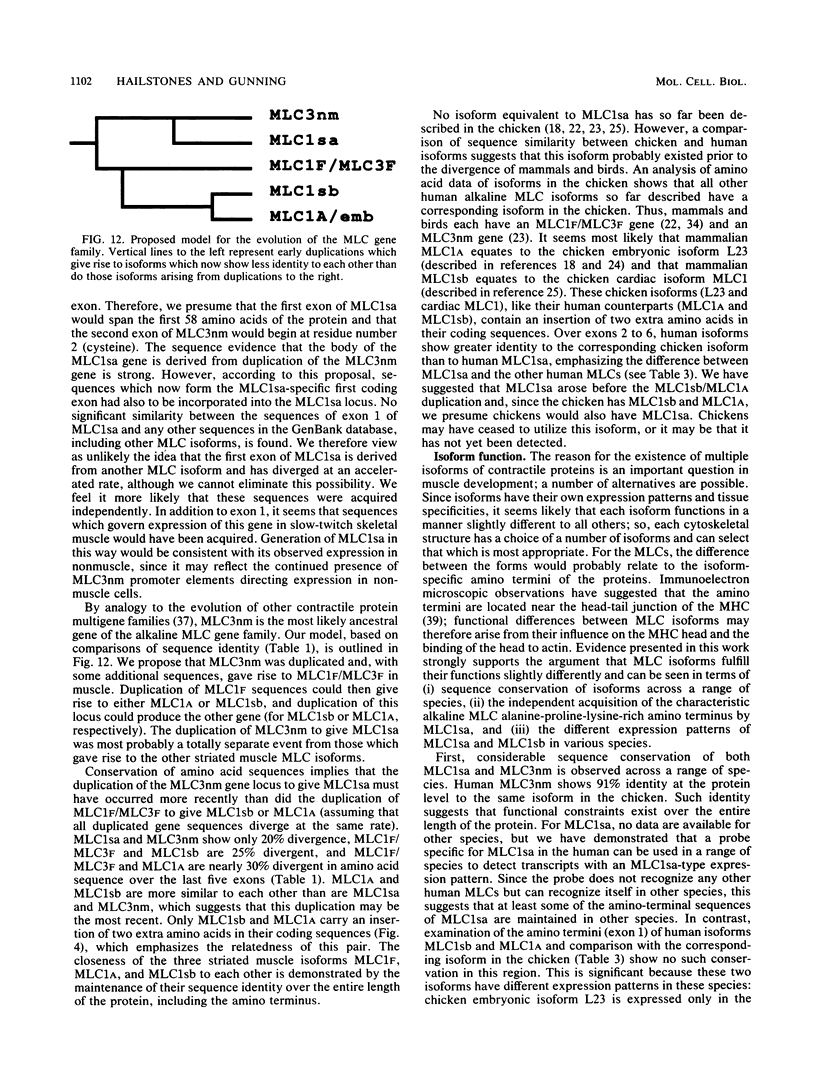
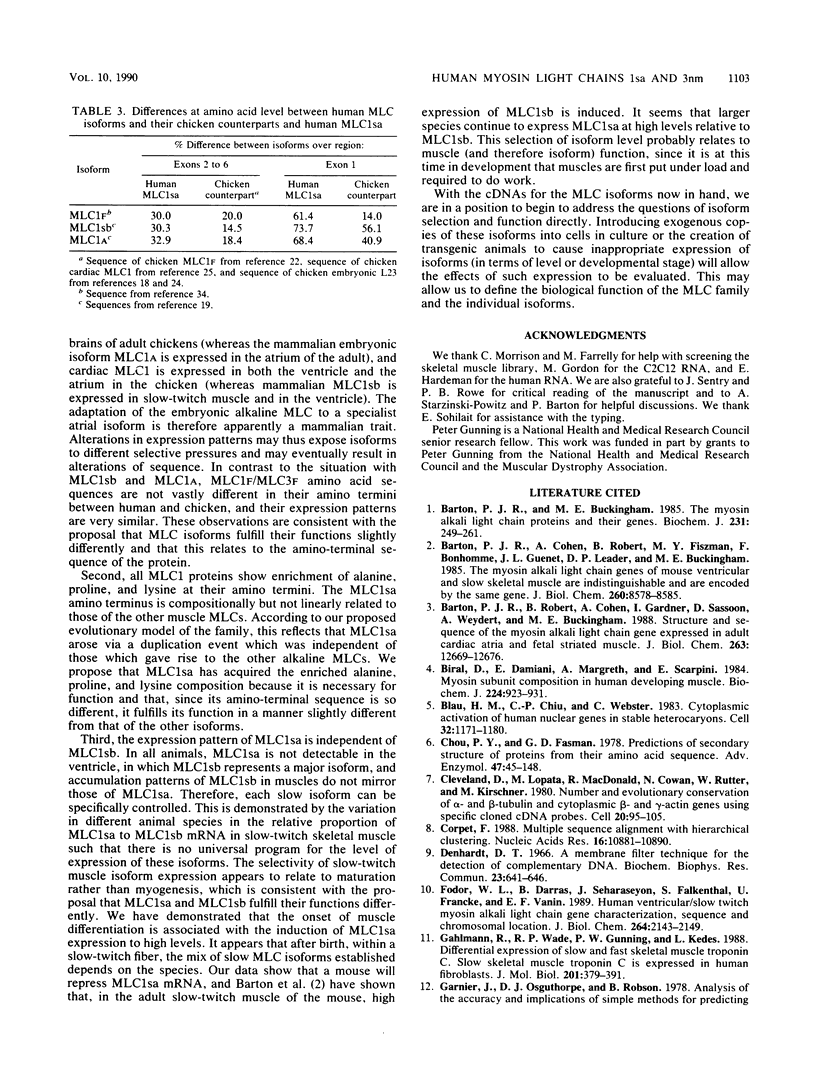

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton P. J., Buckingham M. E. The myosin alkali light chain proteins and their genes. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):249–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2310249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Cohen A., Robert B., Fiszman M. Y., Bonhomme F., Guénet J. L., Leader D. P., Buckingham M. E. The myosin alkali light chains of mouse ventricular and slow skeletal muscle are indistinguishable and are encoded by the same gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8578–8584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Robert B., Cohen A., Garner I., Sassoon D., Weydert A., Buckingham M. E. Structure and sequence of the myosin alkali light chain gene expressed in adult cardiac atria and fetal striated muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12669–12676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biral D., Damiani E., Margreth A., Scarpini E. Myosin subunit composition in human developing muscle. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):923–931. doi: 10.1042/bj2240923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10881–10890. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor W. L., Darras B., Seharaseyon J., Falkenthal S., Francke U., Vanin E. F. Human ventricular/slow twitch myosin alkali light chain gene characterization, sequence, and chromosomal location. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2143–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Wade R., Gunning P., Kedes L. Differential expression of slow and fast skeletal muscle troponin C. Slow skeletal muscle troponin C is expressed in human fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S., Benfield P. A., Hobbs A. W. Distribution and properties of myosin isozymes in developing avian and mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):471–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Hardeman E., Wade R., Ponte P., Bains W., Blau H. M., Kedes L. Differential patterns of transcript accumulation during human myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4100–4114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. D., Trayer I. P., Brewer S., Levine B. A. The widespread distribution of alpha-N-trimethylalanine as the N-terminal amino acid of light chains from vertebrate striated muscle myosins. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima M., Nabeshima Y., Obinata T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A common myosin light chain is expressed in chicken embryonic skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles and in brain continuously from embryo to adult. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14408–14414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurabayashi M., Komuro I., Tsuchimochi H., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of human atrial and ventricular myosin alkali light chain cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13930–13936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Nabeshima Y., Kawashima M., Nakamura S., Nonomura Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Isolation of the chick myosin alkali light chain gene expressed in embryonic gizzard muscle and transitional expression of the light chain gene family in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Nabeshima Y., Nonomura Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Nonmuscle and smooth muscle myosin light chain mRNAs are generated from a single gene by the tissue-specific alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10608–10612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Nabeshima Y., Kobayashi H., Nabeshima Y., Nonomura Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Single chicken cardiac myosin alkali light-chain gene generates two different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Strehler E. E., Garfinkel L. I., Gubits R. M., Ruiz-Opazo N., Nadal-Ginard B. Fast skeletal muscle myosin light chains 1 and 3 are produced from a single gene by a combined process of differential RNA transcription and splicing. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13595–13604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Stull J. T., Cooke R. The effect of myosin phosphorylation on the contractile properties of skinned rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7951–7954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J. M. Interactive molecular biology computing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1813–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Daubas P., Akimenko M. A., Cohen A., Garner I., Guenet J. L., Buckingham M. A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salviati G., Betto R., Danieli Betto D., Zeviani M. Myofibrillar-protein isoforms and sarcoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-transport activity of single human muscle fibres. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):215–225. doi: 10.1042/bj2240215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel U., Bober E., Winter B., Lenz S., Lohse P., Arnold H. H. The complete nucleotide sequences of cDNA clones coding for human myosin light chains 1 and 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4989–4989. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Grant J. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Cloning and characterization of mammalian myosin regulatory light chain (RLC) cDNA: the RLC gene is expressed in smooth, sarcomeric, and nonmuscle tissues. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1505–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R., Feldman D., Gunning P., Kedes L. Sequence and expression of human myosin alkali light chain isoforms. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;87(2):119–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00219255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller G. S., Lowey S. Myosin subunit interactions. Localization of the alkali light chains. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14368–14373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G. Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]