Abstract
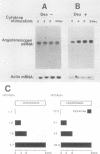
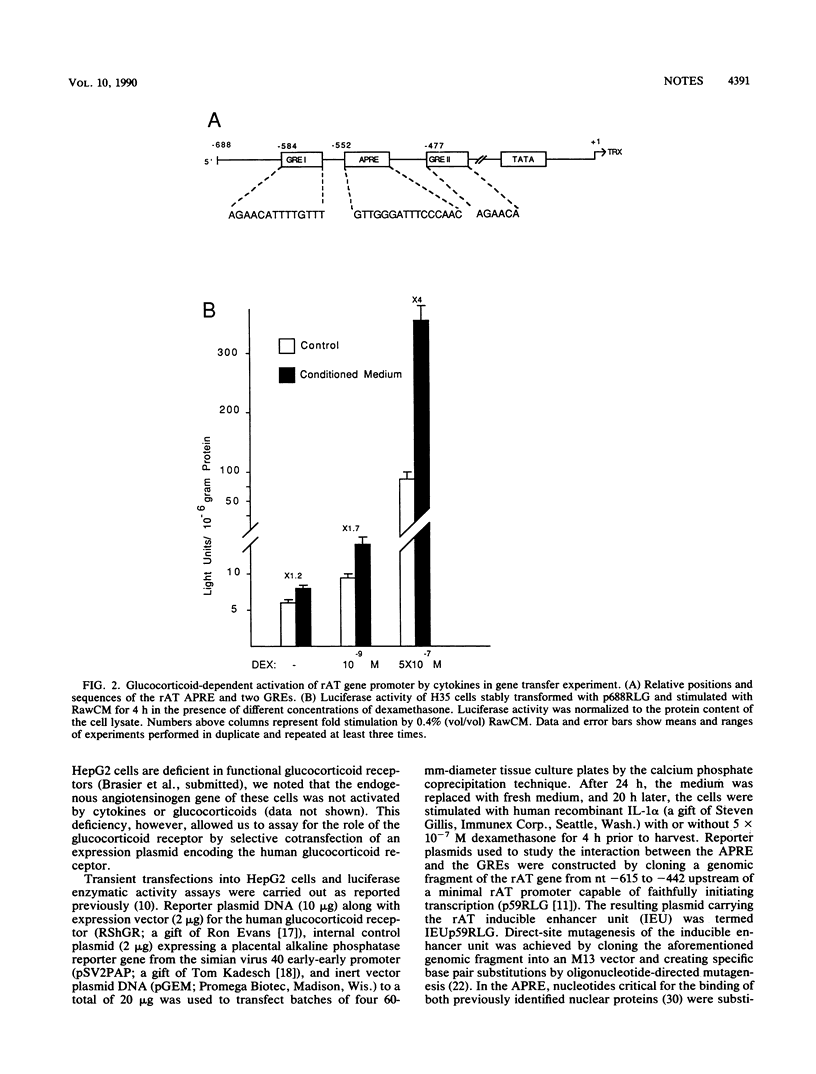
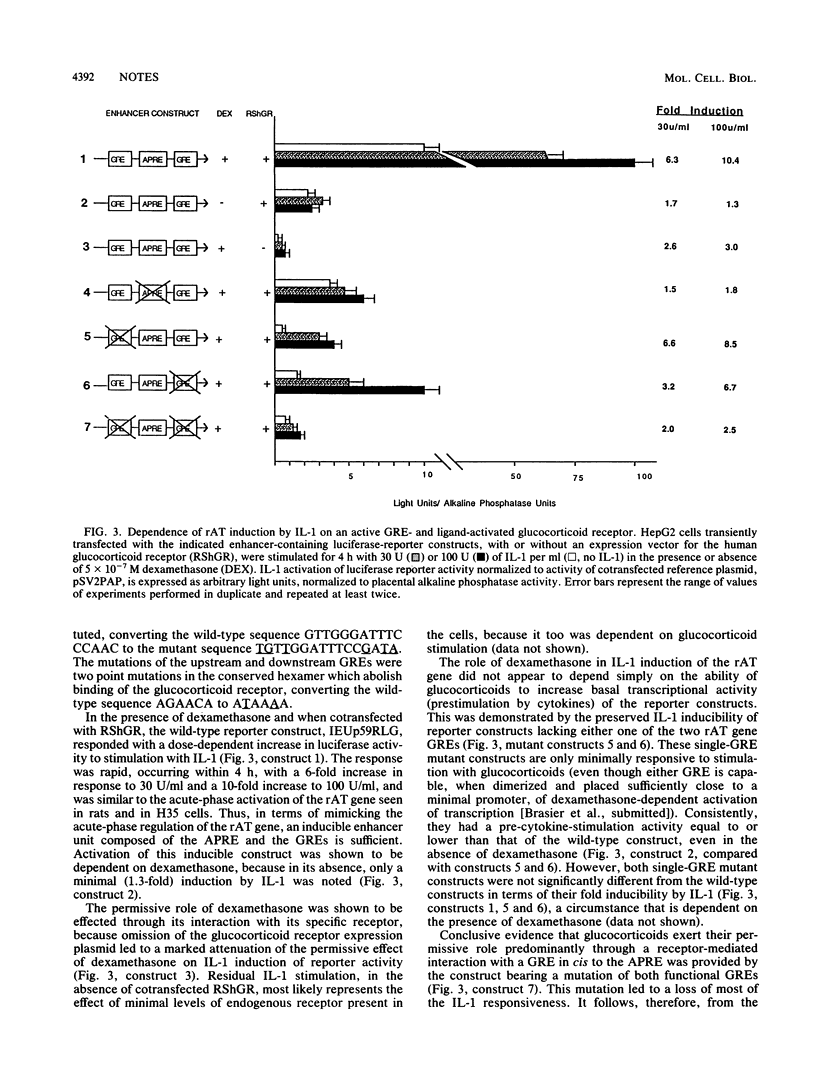
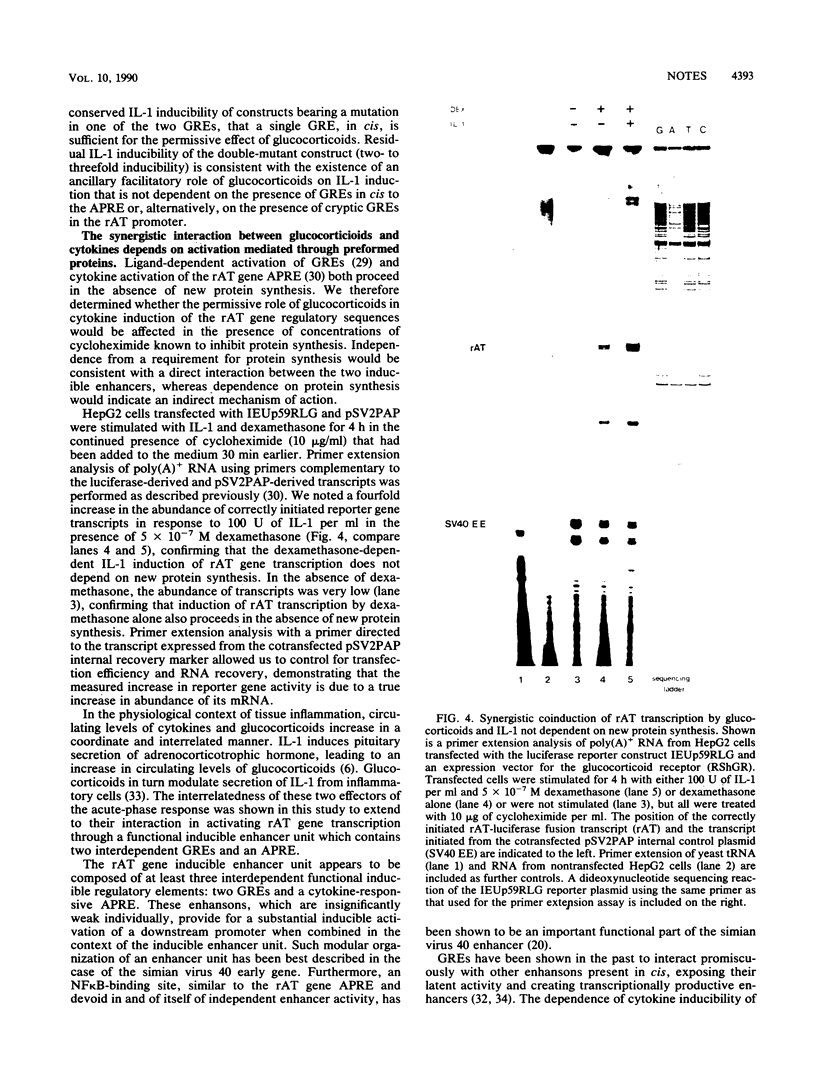
The acute-phase activation of the rat angiotensinogen (rAT) gene in liver cells is a transcriptional event mediated through an interleukin-1-inducible, NF kappa B-binding, cis-acting element (the acute-phase response element [APRE]). Using a cell culture model for the acute-phase response, we showed that the increase in angiotensionogen mRNA in H35 rat hepatoma cells requires costimulation with glucocorticoids and cytokines. Stably transfected rAT promoter-luciferase reporter genes were also activated by cytokines only in the presence of glucocorticoids. This permissive role of glucocorticoids is dependent on the expression of functional glucocorticoid receptors, because in HepG2 cells naturally deficient in such receptors, rAT gene-luciferase reporter constructs responded to interleukin-1 only when cotransfected with an expression vector for the glucocorticoid receptor. Point mutations in the two rAT gene glucocorticoid response elements located adjacent to the APRE led to loss of interleukin-1 inducibility. Induction of luciferase activity in transfected cells occurred even in the presence of cycloheximide, demonstrating that this synergistic response did not depend on new protein synthesis. Thus, a direct interaction between the interleukin-1-inducible NF kappa B-binding APRE and glucocorticoid response elements, located in cis, underlies the acute-phase activation of the rAT gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Hoffman J. A., Bogerd H. P., Dixon E. P., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. Activation of the interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene: regulatory role for DNA-protein interactions flanking the kappa B enhancer. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Firestone G. L., Burgess T. L., Gross K. W., Yamamoto K. R., Held W. A. Dexamethasone regulation of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and other acute phase reactants in rat liver and hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):563–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H. Hepatic acute phase reaction in vivo and in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02626167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Prowse K. R., Marinković S., Won K. A., Jahreis G. P. Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:280-95, discussion 295-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch H. E., Schreiber G. Transcriptional regulation of plasma protein synthesis during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8077–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhnik J., Savoie F., Corvol P. Differential effects of inflammation models on rat T-kininogen and rat angiotensinogen. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;37(6):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Philippe J., Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Novel expression of the angiotensinogen gene in a rat pancreatic islet cell line. Transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16148–16154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Ron D., Habener J. F. Multiple cis-acting DNA regulatory elements mediate hepatic angiotensinogen gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;3(6):1022–1034. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-6-1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E., Perlman A. J. Multiple hormones regulate angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acid levels in a rat hepatoma cell line. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):513–519. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Zervos P., Raducha M., Harris H., Kadesch T. Expression of a human placental alkaline phosphatase gene in transfected cells: use as a reporter for studies of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6342–6346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Induction of rat liver angiotensinogen mRNA following acute inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):826–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91966-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno M., Fromental C., Staub A., Ruffenach F., Davidson I., Chambon P. The SV40 TC-II(kappa B) and the related H-2Kb enhansons exhibit different cell type specific and inducible proto-enhancer activities, but the SV40 core sequence and the AP-2 binding site have no enhanson properties. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4205–4214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification of an inducible factor that binds to a positive regulatory element of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Guyre P. M., Holbrook N. J. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984 Winter;5(1):25–44. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Nakayama K., Tanaka T., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution of rat angiotensinogen mRNA and structural analysis of its heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. M., Grenett H. E., Fuller G. M. The coordinated regulation of fibrinogen gene transcription by hepatocyte-stimulating factor and dexamethasone. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1067–1072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Baumann H. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor, beta 2 interferon, and interleukin-1 enhance expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via a distal upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Tomkins G. M., Bishop M., Varmus H. E. Dexamethasone-mediated induction of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: a system for studying glucocorticoid action. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Stanley F., Shapiro L. E. Control of growth hormone synthesis in cultured GH1 cells by 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine and glucocorticoid agonists and antagonists: studies on the independent and synergistic regulation of the growth hormone response. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):715–721. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Unanue E. R. Corticosteroids inhibit murine macrophage Ia expression and interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1803–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Schmid W., Schütz G. Synergistic action of the glucocorticoid receptor with transcription factors. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3389–3395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. L., Abeles F. B., Beall F. A., Dinterman R. E., Wannemacher R. W., Jr Influence of the adrenal glucocorticoids on the stimulation of synthesis of hepatic ribonucleic acid and plasma acute-phase globulins by leucocytic endogenous mediator. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):25–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1560025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]