Abstract
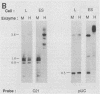
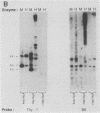
Although DNA can be extensively methylated de novo when introduced into pluripotent cells, the CpG island in the Thy-1 gene does not become methylated either in the mouse embryo or in embryonic stem cells. A 214-base-pair region near the promoter of the Thy-1 gene protects itself as well as heterologous DNA sequences from de novo methylation. We propose that this nucleotide sequence is representative of a class of important signals that limits de novo methylation in the embryo and establishes the pattern of hypomethylated CpG dinucleotides found in somatic tissues.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bestor T. H., Ingram V. M. Two DNA methyltransferases from murine erythroleukemia cells: purification, sequence specificity, and mode of interaction with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5559–5563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestor T., Laudano A., Mattaliano R., Ingram V. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells. The carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Frommer M., Miller O. J., Macleod D. A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated, CpG-rich DNA. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A. H., Nalin C. M., Ward C. A., Poonian M. S., Weissbach A. Primary DNA sequence determines sites of maintenance and de novo methylation by mammalian DNA methyltransferases. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1135–1140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carotti D., Palitti F., Lavia P., Strom R. In vitro methylation of CpG-rich islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9219–9229. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Galbraith L. J., Seidman J. G., White P. C., Parker K. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis of murine 21-hydroxylase genes: mutations affecting gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9601–9605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Scangos G. Expression of transferred thymidine kinase genes is controlled by methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6299–6303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough D. W., Kunkel L. M., Davidson R. L. 5-Azacytidine-induced reactivation of a herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6175023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguére V., Isobe K., Grosveld F. Structure of the murine Thy-1 gene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2017–2024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Lawless G. M., Evans G. A. The mouse Thy-1.2 glycoprotein gene: complete sequence and identification of an unusual promoter. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1482–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Stewart C. L., Harbers K., Löhler J., Simon I., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation and expression of retroviral genomes during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):623–628. doi: 10.1038/298623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolsto A. B., Kollias G., Giguere V., Isobe K. I., Prydz H., Grosveld F. The maintenance of methylation-free islands in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9667–9678. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Grünwald S., Boehm T. L., Drahovsky D. Isolation and characterization of DNA cytosine 5-methyltransferase from human placenta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 2;740(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack Y., Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. Methylation of foreign DNA sequences in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6463–6467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Szyf M. DNA methylation patterns. Formation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Urieli S., Pollack Y., Gruenbaum Y., Glaser G. Studies on the biological role of dna methylation; IV. Mode of methylation of DNA in E. coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1783–1792. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J., Roberts-Ems J., Riggs A. D. Methylation of mouse liver DNA studied by means of the restriction enzymes msp I and hpa II. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):1019–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.424726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Gruenbaum Y., Pollack Y., Razin A., Cedar H. Clonal inheritance of the pattern of DNA methylation in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):61–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyf M., Schimmer B. P., Seidman J. G. Nucleotide-sequence-specific de novo methylation in a somatic murine cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6853–6857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. MspI, an isoschizomer of hpaII which cleaves both unmethylated and methylated hpaII sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Levy D., Perucho M. The somatic replication of DNA methylation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Jolly D. J., Lunnen K. D., Friedmann T., Migeon B. R. Methylation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus on the human X chromosome: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2806–2810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]