Abstract
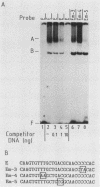
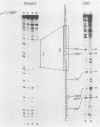
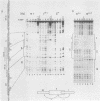
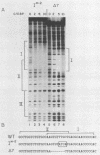
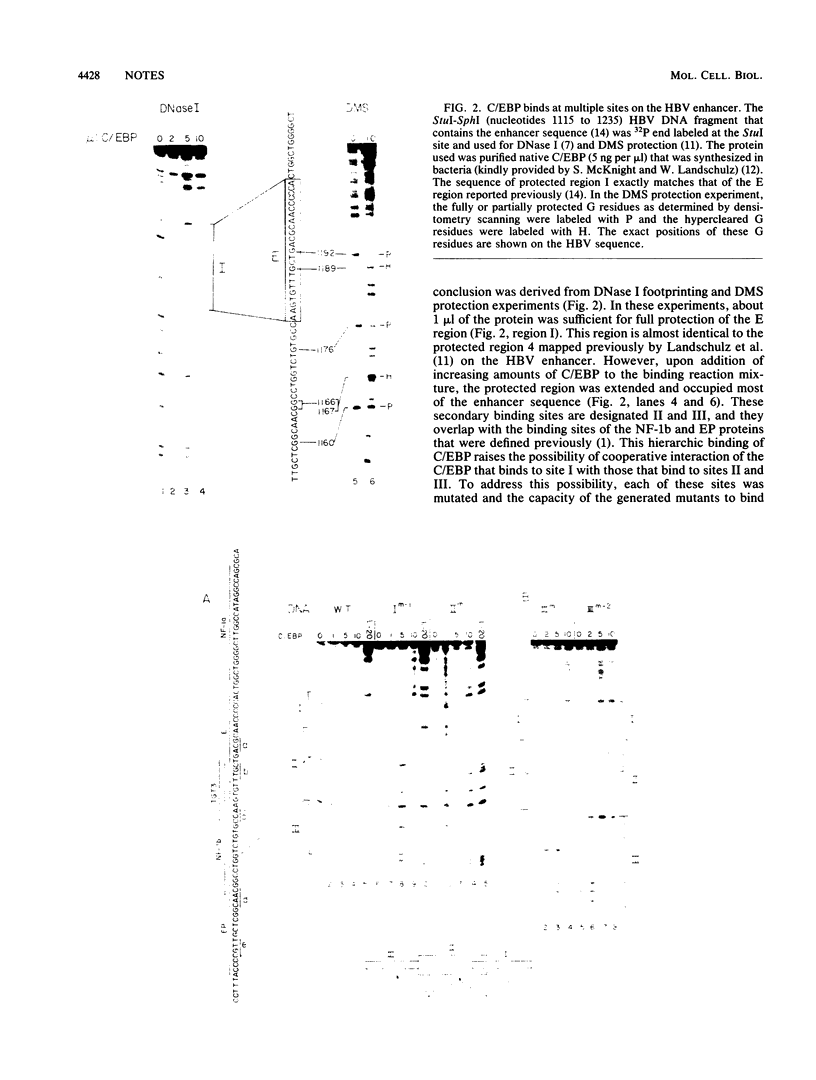
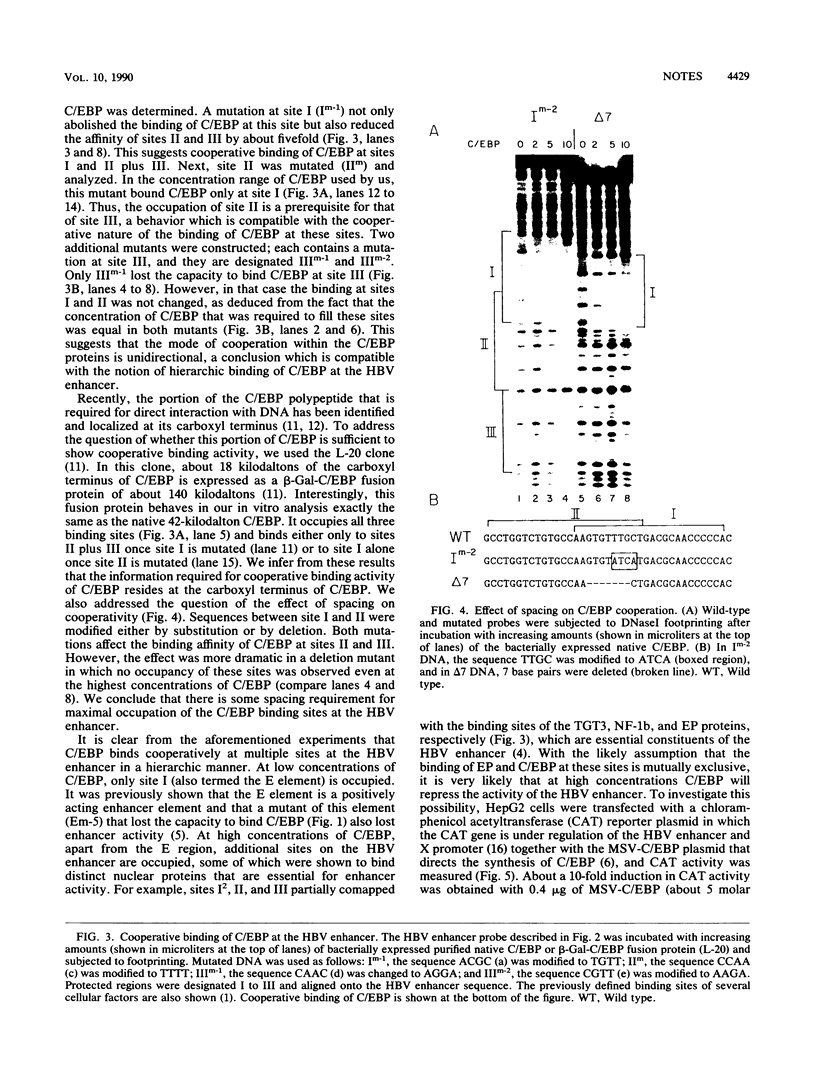
We used the enhancer-binding protein C/EBP as a model to study the nature and the complexity of interaction of an enhancer-binding protein with its target DNA. We found that bacterially expressed C/EBP binds the hepatitis B virus enhancer at multiple sites in a hierarchic and cooperative manner. At low concentrations, only the E element is occupied, but at higher concentrations, additional sites are filled including a site that binds EP, a crucial enhancer-activating protein. This pattern of C/EBP binding may explain the concentration-dependent effect of C/EBP on enhancer activity.
Full text
PDF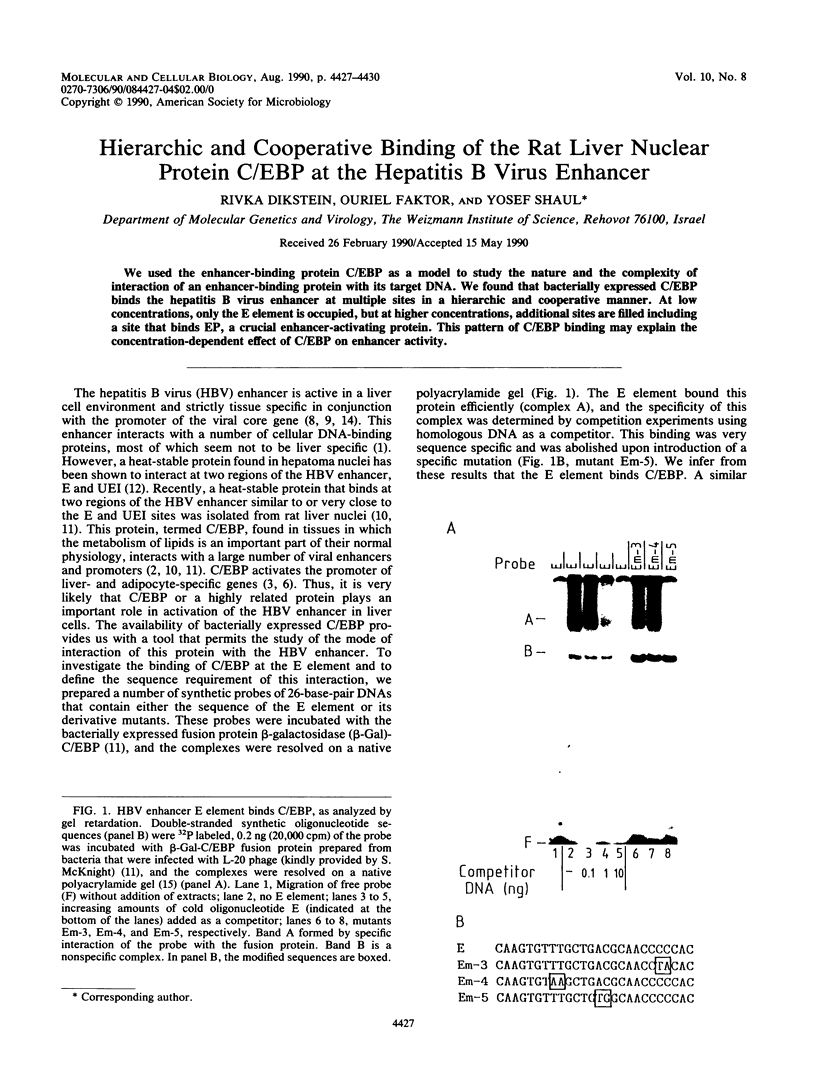

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. Functional organization of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., Budlovsky S., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. A single element within the hepatitis B virus enhancer binds multiple proteins and responds to multiple stimuli. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1861–1863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1861-1863.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A. The human hepatitis B virus enhancer requires trans-acting cellular factor(s) for activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treinin M., Laub O. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):545–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]