Abstract
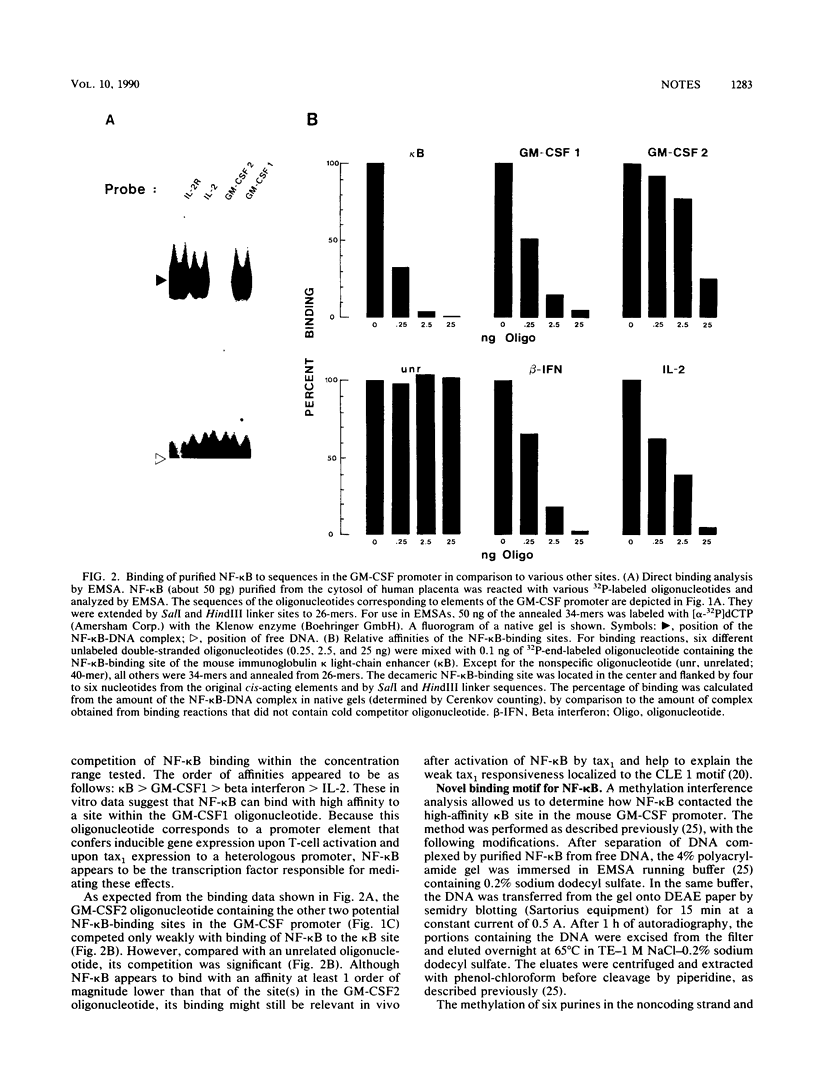
The expression of the gene encoding the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is induced upon activation of T cells with phytohemagglutinin and active phorbolester and upon expression of tax1, a transactivating protein of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I. The same agents induce transcription from the interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain and interleukin-2 genes, depending on promoter elements that bind the inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B (or an NF-kappa B-like factor). We therefore tested the possibility that the GM-CSF gene is also regulated by a cognate motif for the NF-kappa B transcription factor. A recent functional analysis by Miyatake et al. (S. Miyatake, M. Seiki, M. Yoshida, and K. Arai, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:5581-5587, 1988) described a short promoter region in the GM-CSF gene that conferred strong inducibility by T-cell-activating signals and tax1, but no NF-kappa B-binding motifs were identified. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assays, we showed binding of purified human NF-kappa B and of the NF-kappa B activated in Jurkat T cells to an oligonucleotide comprising the GM-CSF promoter element responsible for mediating responsiveness to T-cell-activating signals and tax1. As shown by a methylation interference analysis and oligonucleotide competition experiments, purified NF-kappa B binds at positions -82 to -91 (GGGAACTACC) of the GM-CSF promoter sequence with an affinity similar to that with which it binds to the biologically functional kappa B motif in the beta interferon promoter (GGGAAATTCC). Two kappa B-like motifs at positions -98 to -108 of the GM-CSF promoter were also recognized but with much lower affinities. Our data provide strong evidence that the expression of the GM-CSF gene following T-cell activation is controlled by binding of the NF-kappa B transcription factor to a high-affinity binding site in the GM-CSF promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Phorbol-ester-induced activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor involves dissociation of an apparently cytoplasmic NF-kappa B/inhibitor complex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):789–798. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Kaushansky K., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Interleukin 1 stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):464–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Slamon D. J., Nimer S. D., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Regulation of expression of human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8669–8673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W. HIV-1, HTLV-1 and normal T-cell growth: transcriptional strategies and surprises. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos B., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins: role in the regulation of human interleukin-2 gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):457–460. doi: 10.1126/science.2497518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Malefijt R. D., Heike T., Fujisawa J., Takebe Y., Nishida J., Shlomai J., Yokota T., Yoshida M. Activation of T cell-derived lymphokine genes in T cells and fibroblasts: effects of human T cell leukemia virus type I p40x protein and bovine papilloma virus encoded E2 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6547–6566. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Yoshida M., Arai K. T-cell activation signals and human T-cell leukemia virus type I-encoded p40x protein activate the mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene through a common DNA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5581–5587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munker R., Gasson J., Ogawa M., Koeffler H. P. Recombinant human TNF induces production of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):79–82. doi: 10.1038/323079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimer S. D., Morita E. A., Martis M. J., Wachsman W., Gasson J. C. Characterization of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter region by genetic analysis: correlation with DNase I footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1979–1984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon M. F., Gamble J. R., Vadas M. A. Nuclear proteins interacting with the promoter region of the human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Regulation of cytokine gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:439–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]