Abstract
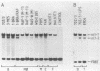
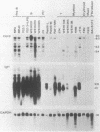
The immunoglobulin genes have B-cell-specific promoter and enhancer elements. The regulation of these elements is thought to be mediated to a large degree by the trans-activating factor oct-2, which binds the octamer element (ATTTGCAT). We have further examined the role of this octamer element in directing the lymphoid-specific expression of the immunoglobulin H enhancer. No direct relationship was found between the levels of expression of the Cmu gene and oct-2. Indeed, variable amounts of oct-2 were detected in all of the hemopoietic lineage cells tested in this study.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Harris A. W., Pinkert C. A., Corcoran L. M., Alexander W. S., Cory S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Rosenberg N., Enea V., Siden E., Baltimore D. Multiple immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcripts in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed lymphoid cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):386–400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki K., Maeda H., Wang J., Kitamura D., Watanabe T. Purification of a nuclear trans-acting factor involved in the regulated transcription of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):723–730. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox P. M., Temperley S. M., Kumar H., Goding C. R. A distinct octamer-binding protein present in malignant melanoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11047–11056. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Doyen N., Rougeon F. The conserved decanucleotide from the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter induces a very high transcriptional activity in B-cells when introduced into an heterologous promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Mocikat R., Zachau H. G. Sequences closely related to an immunoglobulin gene promoter/enhancer element occur also upstream of other eukaryotic and of prokaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8819–8827. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Robins A. J., Wells J. R. Independently evolving chicken histone H2B genes: identification of a ubiquitous H2B-specific 5' element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7851–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Adams J. M. Transcripts of the immunoglobulin C mu gene vary in structure and splicing during lymphoid development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7400–7404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. Expression of the immunoglobulin C mu gene in mouse T and B lymphoid and myeloid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinken S. P., Alexander W. S., Adams J. M. Hemopoietic lineage switch: v-raf oncogene converts Emu-myc transgenic B cells into macrophages. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):857–867. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Webb E., Housiaux P., Adams J. M. Expression of multiple homeobox genes within diverse mammalian haemopoietic lineages. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens T., Miller J. F. Interaction in vivo between hapten-specific suppressor T cells and an in vitro cultured helper T cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1687–1692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. L. Complex protein binding within the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4194–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Orth K., Calame K. L. Binding in vitro of multiple cellular proteins to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4168–4178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. Homoeo boxes, POU proteins and the limits to promiscuity. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):522–524. doi: 10.1038/336522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. How do different transcription factors binding the same DNA sequence sort out their jobs? Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.3399892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain B-lymphocyte enhancer efficiently stimulates transcription in non-lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):553–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Localization of a repressive sequence contributing to B-cell specificity in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):988–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]