Abstract
GAL4I, GAL4II, and GAL4III are three forms of the yeast transcriptional activator protein that are readily distinguished on the basis of electrophoretic mobility during sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Phosphorylation accounts for the reduced mobility of the slowest-migrating form, GAL4III, which is found to be closely associated with high-level GAL/MEL gene expression (L. Mylin, P. Bhat, and J. Hopper, Genes Dev. 3:1157-1165, 1989). Here we show that GAL4II, like GAL4III, can be converted to GAL4I by phosphatase treatment, suggesting that in vivo GAL4II is derived from GAL4I by phosphorylation. We found that cells which overproduced GAL4 under conditions in which it drove moderate to low levels of GAL/MEL gene expression showed only forms GAL4I and GAL4II. To distinguish which forms of GAL4 (GAL4I, GAL4II, or both) might be responsible for transcription activation in the absence of GAL4III, we performed immunoblot analysis on UASgal-binding-competent GAL4 proteins from four gal4 missense mutants selected for their inability to activate transcription (M. Johnston and J. Dover, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2401-2405, 1987; Genetics 120;63-74, 1988). The three mutants with no detectable GAL1 expression did not appear to form GAL4II or GAL4III, but revertants in which GAL4-dependent transcription was restored did display GAL4II- or GAL4III-like electrophoretic species. Detection of GAL4II in a UASgal-binding mutant suggests that neither UASgal binding nor GAL/MEL gene activation is required for the formation of GAL4II. Overall, our results imply that GAL4I may be inactive in transcriptional activation, whereas GAL4II appears to be active. In light of this work, we hypothesize that phosphorylation of GAL4I makes it competent to activate transcription.
Full text
PDF

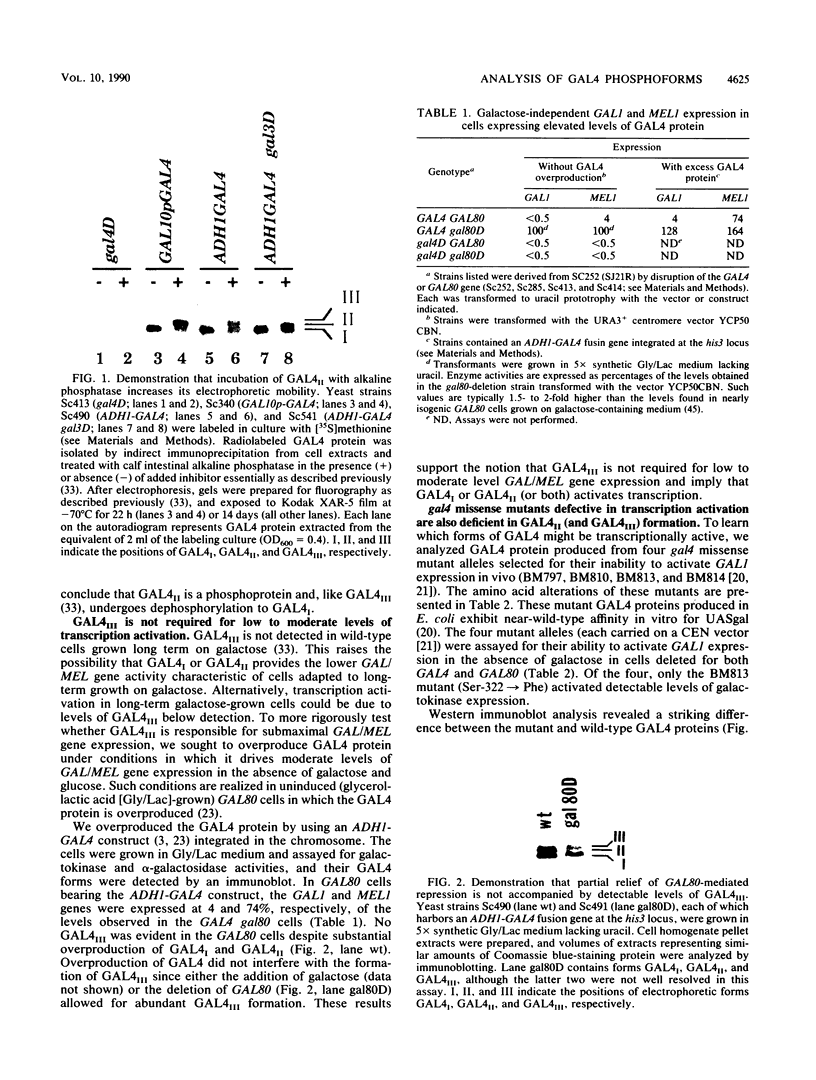




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerer G. Expression of genes in yeast using the ADCI promoter. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:192–201. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Yeast regulatory gene GAL3: carbon regulation; UASGal elements in common with GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, GAL80, and MEL1; encoded protein strikingly similar to yeast and Escherichia coli galactokinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3439–3447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E., Jaehning J. A. Transcription of multiple copies of the yeast GAL7 gene is limited by specific factors in addition to GAL4. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):127–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00330433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P. J., Oh D., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the GAL3 signal transduction pathway activating GAL4 protein-dependent transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):281–291. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume K. G., Beutler E. Galactokinase from human erythrocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:47–53. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Cannon L. E., Halvorson H. O. In vitro synthesis of repressible yeast acid phosphatase: identification of multiple mRNAs and products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. A GAL family of upstream activating sequences in yeast: roles in both induction and repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):603–608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M. Regulation of sugar utilization in Saccharomyces species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4873–4877. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4873-4877.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Lees M. B., Derr J. E. A linear Lowry--Folin assay for both water-soluble and sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized proteins. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Broach J. R., Rowe L. B. Regulation of the galactose pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: induction of uridyl transferase mRNA and dependency on GAL4 gene function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2878–2882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi M., Segawa T., Nogi Y., Suzuki Y., Fukasawa T. Autogenous regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae regulatory gene GAL80. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00331589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Dover J. Mutational analysis of the GAL4-encoded transcriptional activator protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):63–74. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Dover J. Mutations that inactivate a yeast transcriptional regulatory protein cluster in an evolutionarily conserved DNA binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Zavortink M. J., Debouck C., Hopper J. E. Functional domains of the yeast regulatory protein GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6553–6557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. L., Campbell J. L. Cloning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA replication genes: isolation of the CDC8 gene and two genes that compensate for the cdc8-1 mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Hopper J. E. The relationship of regulatory proteins and DNase I hypersensitive sites in the yeast GAL1-10 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8409–8423. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Chasman D. I., Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. Interaction of GAL4 and GAL80 gene regulatory proteins in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3446–3451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Converting a eukaryotic transcriptional inhibitor into an activator. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):443–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Bhat J. P., Hopper J. E. Regulated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of GAL4, a transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1157–1165. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Hofmann K. J., Schultz L. D., Hopper J. E. Regulated GAL4 expression cassette providing controllable and high-level output from high-copy galactose promoters in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:297–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85026-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., Silver P. Context affects nuclear protein localization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh D., Hopper J. E. Transcription of a yeast phosphoglucomutase isozyme gene is galactose inducible and glucose repressible. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1415–1422. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthun M. R., Jaehning J. A. Purification and characterization of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Hamilton R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulation of basal and induced levels of the MEL1 transcript in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1238–1245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Glycogen synthase and glycogen synthase kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;20:45–105. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152820-1.50006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Hofmann K. J., Mylin L. M., Montgomery D. L., Ellis R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulated overproduction of the GAL4 gene product greatly increases expression from galactose-inducible promoters on multi-copy expression vectors in yeast. Gene. 1987;61(2):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Majors J. E. In vivo DNA-binding properties of a yeast transcription activator protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3260–3267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Fukasawa T. Controlled transcription of the yeast regulatory gene GAL80. Gene. 1985;39(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Chiang A., Sadler I. Mutations that alter both localization and production of a yeast nuclear protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):707–717. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hamilton R. W., Cano C. L., Hopper J. E. Disruption of regulatory gene GAL80 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on carbon-controlled regulation of the galactose/melibiose pathway genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1521–1527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the GAL3 gene in the expression of the galactose/melibiose regulon of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):229–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Johnston M. Molecular cloning of the GAL80 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of a gal80 deletion. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







