Abstract
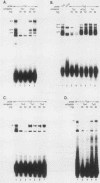
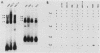
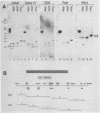
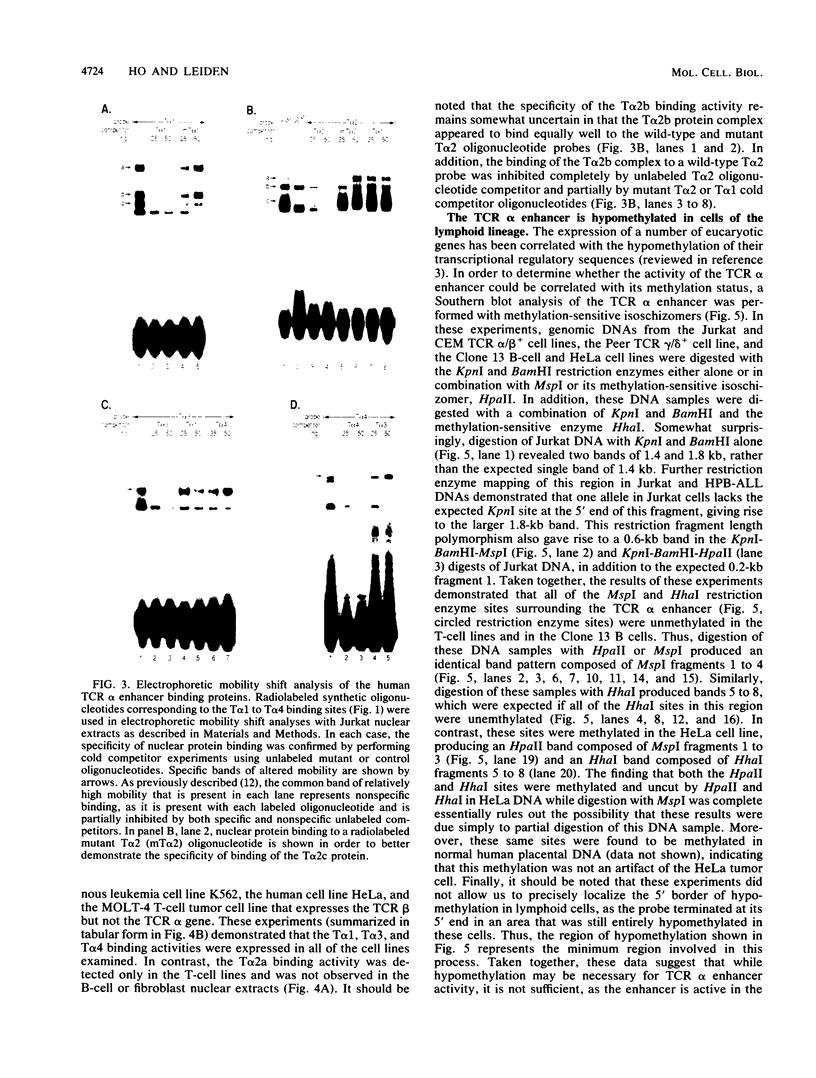
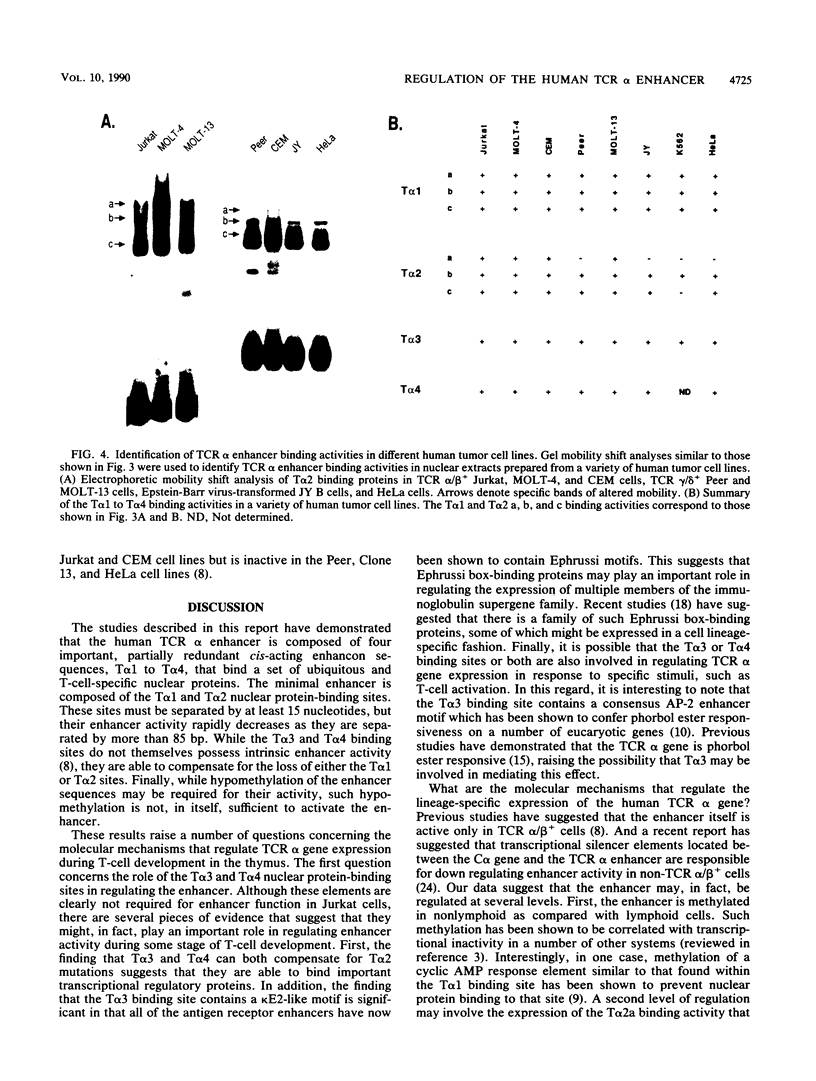
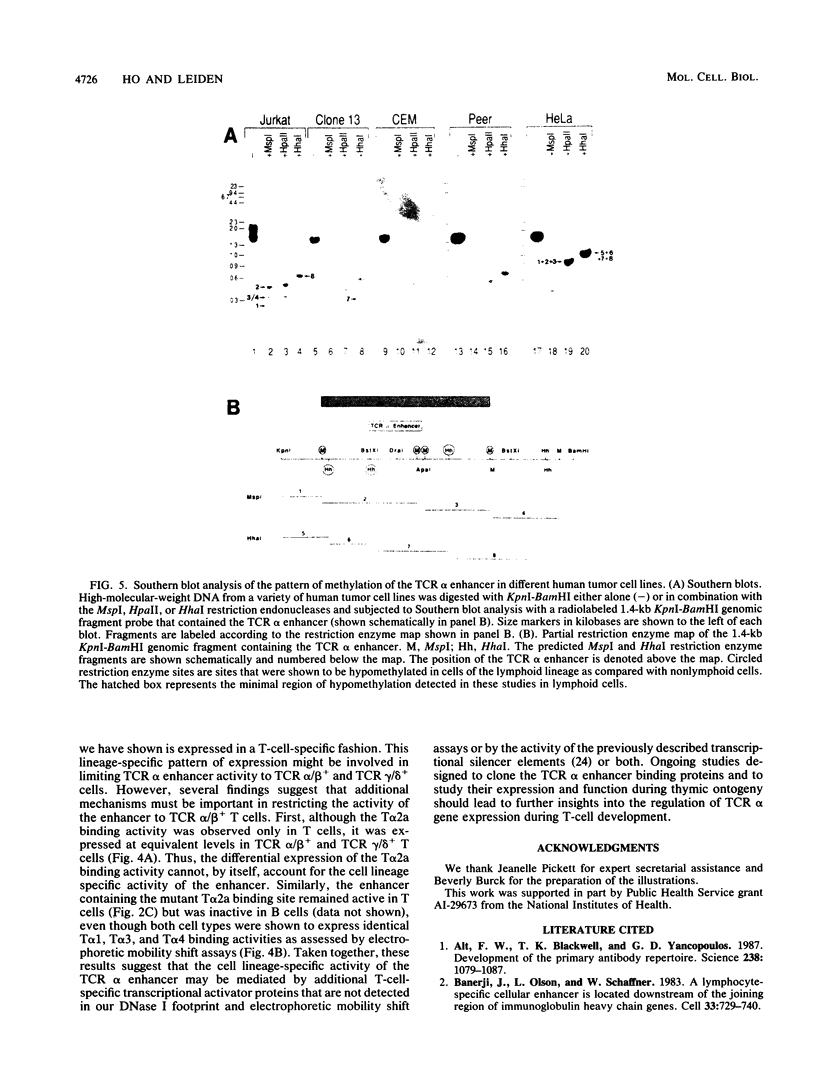
Transcription of human T-cell receptor (TCR) alpha genes is regulated by a T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer that is located 4.5 kilobases 3' of the C alpha gene segment. Previous studies have demonstrated that this enhancer contains at least five nuclear protein-binding sites called T alpha 1 to T alpha 5. In the studies described in this report, we have determined the molecular requirements for human TCR alpha enhancer function. In vitro mutagenesis and deletion analyses demonstrated that full enhancer activity is retained in a 116-base-pair fragment containing the T alpha 1 and T alpha 2 nuclear protein-binding sites and that both of these sites are required for full enhancer function. Functional enhancer activity requires that the T alpha 1 and T alpha 2 binding sites be separated by more than 15 and fewer than 85 base pairs. However, the sequence of this spacer region and the relative phase of the two binding sites on the DNA helix do not affect enhancer function. Deletion and mutation analyses demonstrated that the T alpha 3 and T alpha 4 nuclear protein-binding sites are not necessary or sufficient for TCR alpha enhancer activity. However, a fragment containing these two sites was able to compensate for T alpha 1 and T alpha 2 mutations that otherwise abolished enhancer activity. Electrophoretic mobility shift analyses of the TCR alpha enhancer binding proteins revealed that the T alpha 1, T alpha 3, and T alpha 4 binding proteins are expressed in a variety of T-cell and non-T-cell tumor cell lines. In contrast, one of the two T alpha 2 binding activities was detected only in T-cell nuclear extracts. The activity of the TCR alpha enhancer does not appear to be regulated solely at the level of DNA methylation on that the enhancer sequences were found to be identically hypomethylated in B and T cells as compared with fibroblasts. Taken together, these results suggest that TCR alpha enhancer activity is regulated by the interaction of multiple T-cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins with partially redundant cis-acting enhancer elements that are hypomethylated in cells of the lymphoid lineage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Moore M. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Suh H., Lutzker S., Selsing E., Alt F. W. Recombination between immunoglobulin variable region gene segments is enhanced by transcription. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):585–589. doi: 10.1038/324585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Yang L. H., Morle G., Leiden J. M. A T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer element 3' of C alpha in the human T-cell receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6714–6718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Schaffner W. CpG methylation of the cAMP-responsive enhancer/promoter sequence TGACGTCA abolishes specific factor binding as well as transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):612–619. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski B. A., Yang L. H., Cacheris P., Morle G. D., Leiden J. M. The first intron of the 4F2 heavy-chain gene contains a transcriptional enhancer element that binds multiple nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2588–2597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., de Jong R., Uematsu Y., Dembic Z., Ryser S., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M., Berns A. Transcription of T cell receptor beta-chain genes is controlled by a downstream regulatory element. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B. Transcription of T cell antigen receptor genes is induced by protein kinase C activation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1769–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The T cell receptor. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1073–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.3317824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall S., Peterson C. L., Calame K. A transcriptional enhancer 3' of C beta 2 in the T cell receptor beta locus. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):205–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2968651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. Developmental biology of T cell receptors. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):943–950. doi: 10.1126/science.2658058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. Alpha beta lineage-specific expression of the alpha T cell receptor gene by nearby silencers. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]