Abstract
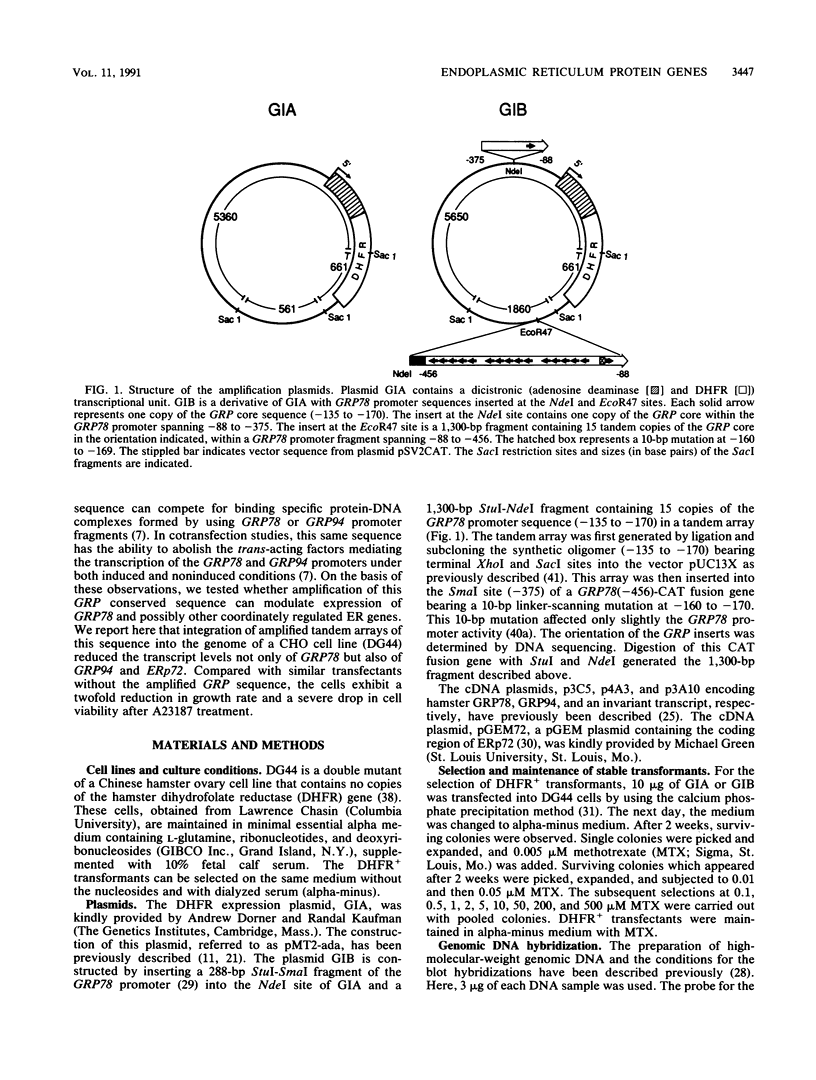
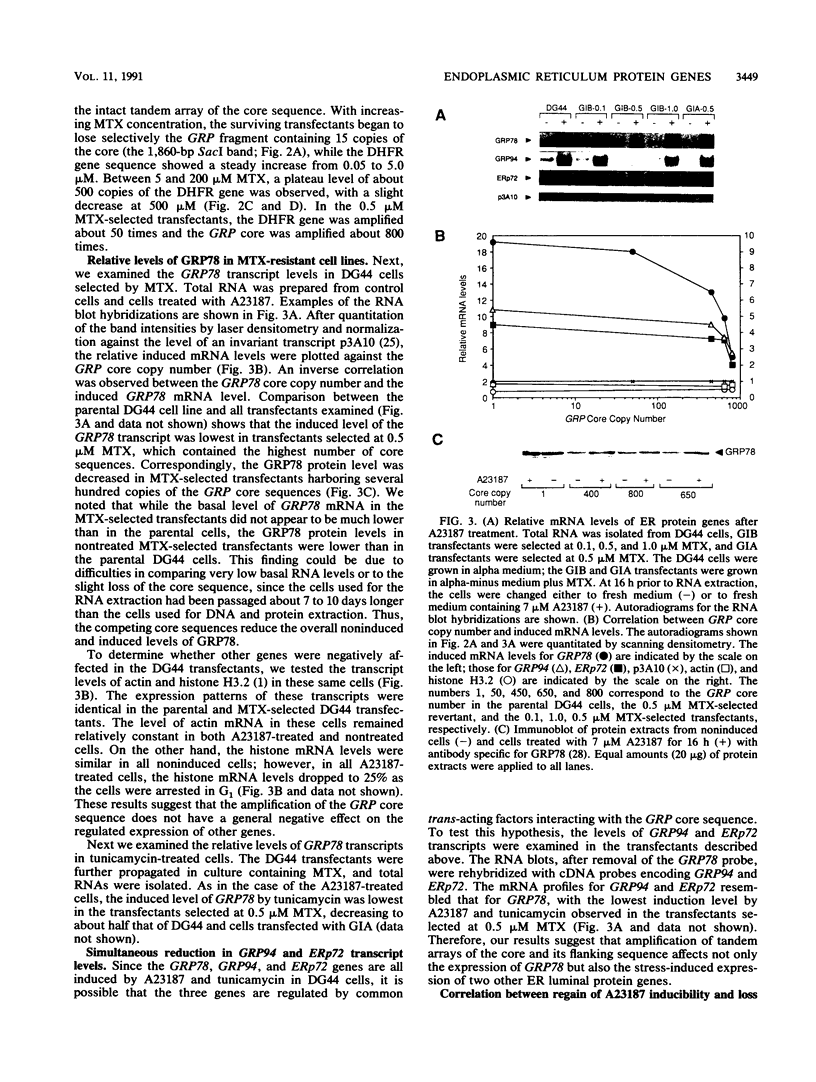
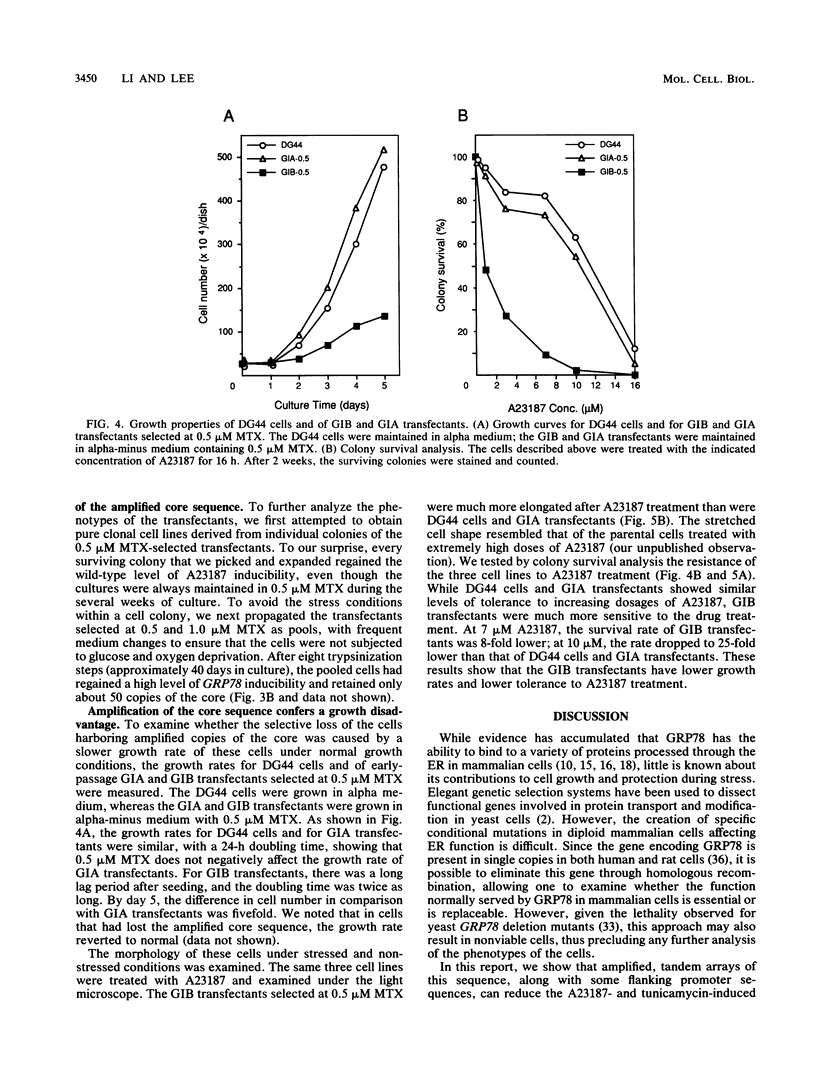
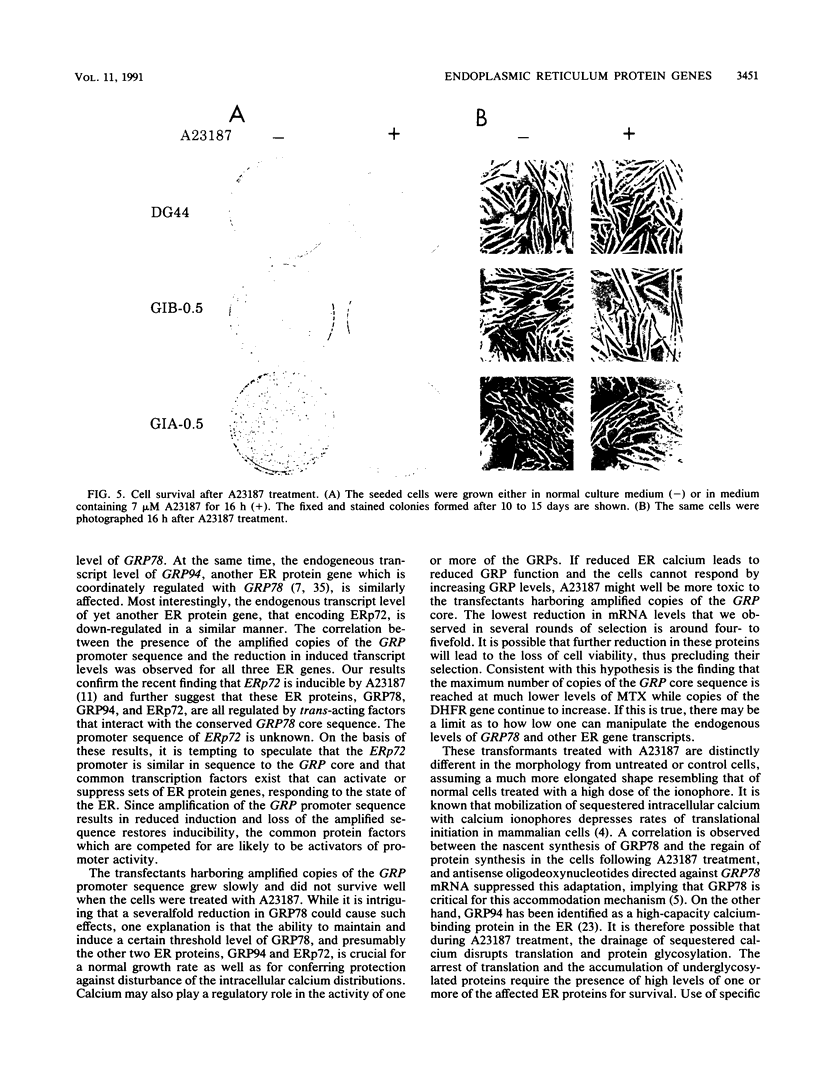
GRP78, a 78-kDa protein localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), has been implicated in protein processing and stress protection. Its promoter contains a 36-bp region which is conserved among GRP genes across species and has the ability to compete for trans-acting factors mediating GRP gene expression. Integration of about 800 tandem copies of this sequence into the genome of a Chinese hamster ovary cell line (DG44) results in transfectants with the following phenotypes: (i) the induction level of GRP78 by the calcium ionophore A23187 and tunicamycin is reduced 4- and 2-fold, respectively, (ii) the induction levels of two other ER luminal protein genes, GRP94 and ERp72, are simultaneously down-regulated, (iii) the growth rate of these cells is half that of transfectants without the amplified sequence, and (iv) cell viability is decreased by 25-fold after A23187 treatment. These results provide new evidence that ERp72 shares common trans-acting regulatory factors with the GRP genes and that a reduction of this set of ER proteins correlates with lower viability after ionophore treatment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M., Kepes F., Schekman R. Sec59 encodes a membrane protein required for core glycosylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1191–1199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A. Calcium-dependent regulation of protein synthesis in intact mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:577–590. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Cade C., Prostko C. R., Gmitter-Yellen D., Brostrom C. O. Accommodation of protein synthesis to chronic deprivation of intracellular sequestered calcium. A putative role for GRP78. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20539–20546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Erwin A. E., Lee A. S. Glucose-regulated protein (GRP94 and GRP78) genes share common regulatory domains and are coordinately regulated by common trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2153–2162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Wooden S. K., Nakaki T., Kim Y. K., Lin A. Y., Kung L., Attenello J. W., Lee A. S. Rat gene encoding the 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein GRP78: its regulatory sequences and the effect of protein glycosylation on its expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):680–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Krane M. G., Kaufman R. J. Reduction of endogenous GRP78 levels improves secretion of a heterologous protein in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4063–4070. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Kaufman R. J. Increased synthesis of secreted proteins induces expression of glucose-regulated proteins in butyrate-treated Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20602–20607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Raney P., Haugejorden S., Green M., Kaufman R. J. The stress response in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Regulation of ERp72 and protein disulfide isomerase expression and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):22029–22034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Lee A. S., Resendez E., Jr, Steinhardt R. A. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores by calcium ionophore A23187 induces the genes for glucose-regulated proteins in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12801–12805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feige J. J., Keller G. A., Scheffler I. E. Temperature-sensitive Chinese hamster cell mutant with a defect in glycoprotein synthesis: accumulation of the EGF receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum and the role of the glucose-regulated protein GRP78. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jul;136(1):33–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L. M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain and binding protein complexes are dissociated in vivo by light chain addition. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):829–837. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L. M., Ting J., Lee A. S. Identity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain-binding protein with the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and the role of posttranslational modifications in its binding function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4250–4256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Oker-Blom C., Summers M. D. Role of glycosylation in the transport of recombinant glycoproteins through the secretory pathway of lepidopteran insect cells. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Apr;42(4):181–191. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. N., Kucey B. L. Competitive inhibition of hsp70 gene expression causes thermosensitivity. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1551–1554. doi: 10.1126/science.3201244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Garcia P. D., Walter P., Kelly R. B. Heavy-chain binding protein recognizes aberrant polypeptides translocated in vitro. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):90–93. doi: 10.1038/333090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Vectors used for expression in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:487–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Lee A. S. Cooperative interactions between the GRP78 enhancer and promoter elements in hamster fibroblasts. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G., Smith M., Macer D., Webster P., Mortara R. Endoplasmic reticulum contains a common, abundant calcium-binding glycoprotein, endoplasmin. J Cell Sci. 1986 Dec;86:217–232. doi: 10.1242/jcs.86.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Delegeane A. M., Baker V., Chow P. C. Transcriptional regulation of two genes specifically induced by glucose starvation in a hamster mutant fibroblast cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Wells S., Kim K. S., Scheffler I. E. Enhanced synthesis of the glucose/calcium-regulated proteins in a hamster cell mutant deficient in transfer of oligosaccharide core to polypeptides. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Dec;129(3):277–282. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Sweet D. J., Pelham H. R. The ERD2 gene determines the specificity of the luminal ER protein retention system. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1359–1363. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90699-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. A., Warren D. W., Gregoire J., Pedersen R. C., Lee A. S. The rat 78,000 dalton glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) as a precursor for the rat steroidogenesis-activator polypeptide (SAP): the SAP coding sequence is homologous with the terminal end of GRP78. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1944–1952. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Chang S. C., Lee A. S. A calcium ionophore-inducible cellular promoter is highly active and has enhancerlike properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella R. A., Srinivasan M., Haugejorden S. M., Green M. ERp72, an abundant luminal endoplasmic reticulum protein, contains three copies of the active site sequences of protein disulfide isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1094–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Attenello J. W., Grafsky A., Chang C. S., Lee A. S. Calcium ionophore A23187 induces expression of glucose-regulated genes and their heterologous fusion genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1212–1219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Wooden S. K., Lee A. S. Identification of highly conserved regulatory domains and protein-binding sites in the promoters of the rat and human genes encoding the stress-inducible 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4579–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Misra L. M., Vogel J. P. KAR2, a karyogamy gene, is the yeast homolog of the mammalian BiP/GRP78 gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. F. The involvement of calcium in transport of secretory proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90798-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff D. J., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Characterization of a cell cycle mutant derived from hamster fibroblast: reversion analysis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):629–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Lee A. S. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Wooden S. K., Kriz R., Kelleher K., Kaufman R. J., Lee A. S. The nucleotide sequence encoding the hamster 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) and its conservation between hamster and rat. Gene. 1987;55(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Kas E., Chasin L. A., Funanage V. L., Myoda T. T., Hamlin J. Effect of gamma rays at the dihydrofolate reductase locus: deletions and inversions. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Nov;12(6):555–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01671941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D., Tooze J., Fuller S. Identification by anti-idiotype antibodies of an intracellular membrane protein that recognizes a mammalian endoplasmic reticulum retention signal. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):495–502. doi: 10.1038/345495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J. P., Misra L. M., Rose M. D. Loss of BiP/GRP78 function blocks translocation of secretory proteins in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1885–1895. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. A consensus sequence polymer inhibits in vivo expression of heat shock genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3200–3206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]