Abstract
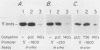
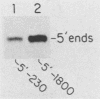
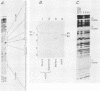
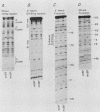
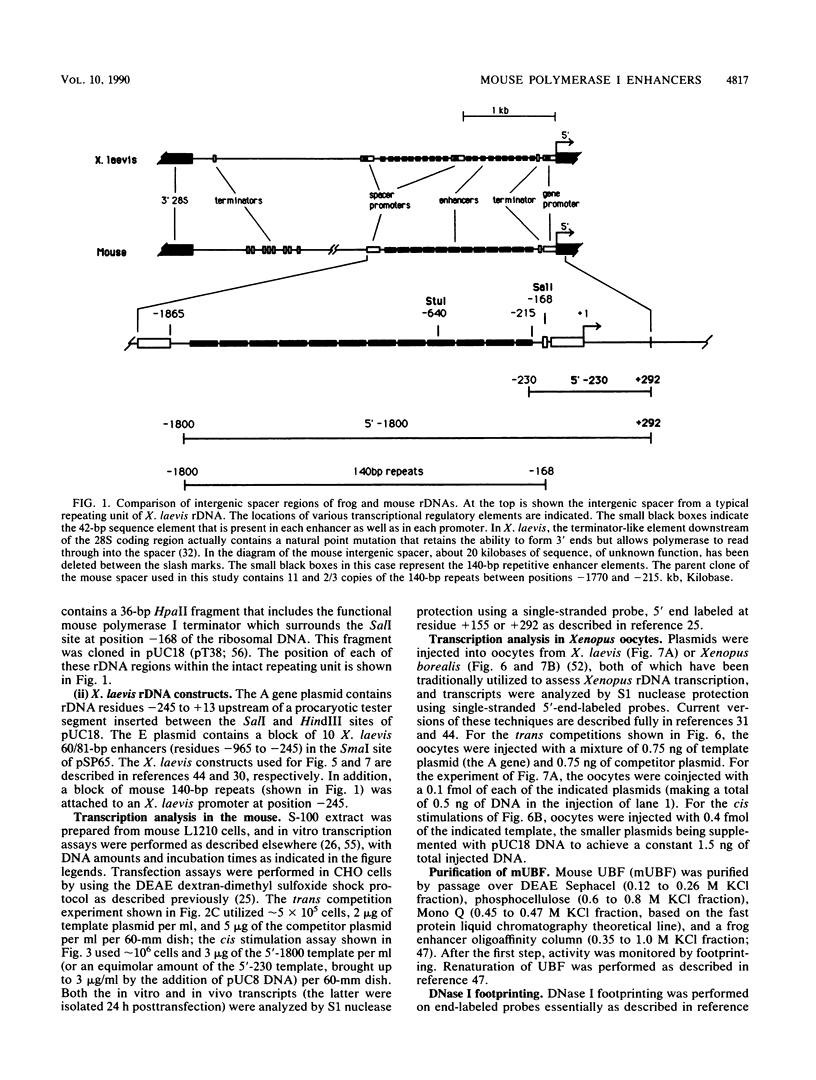
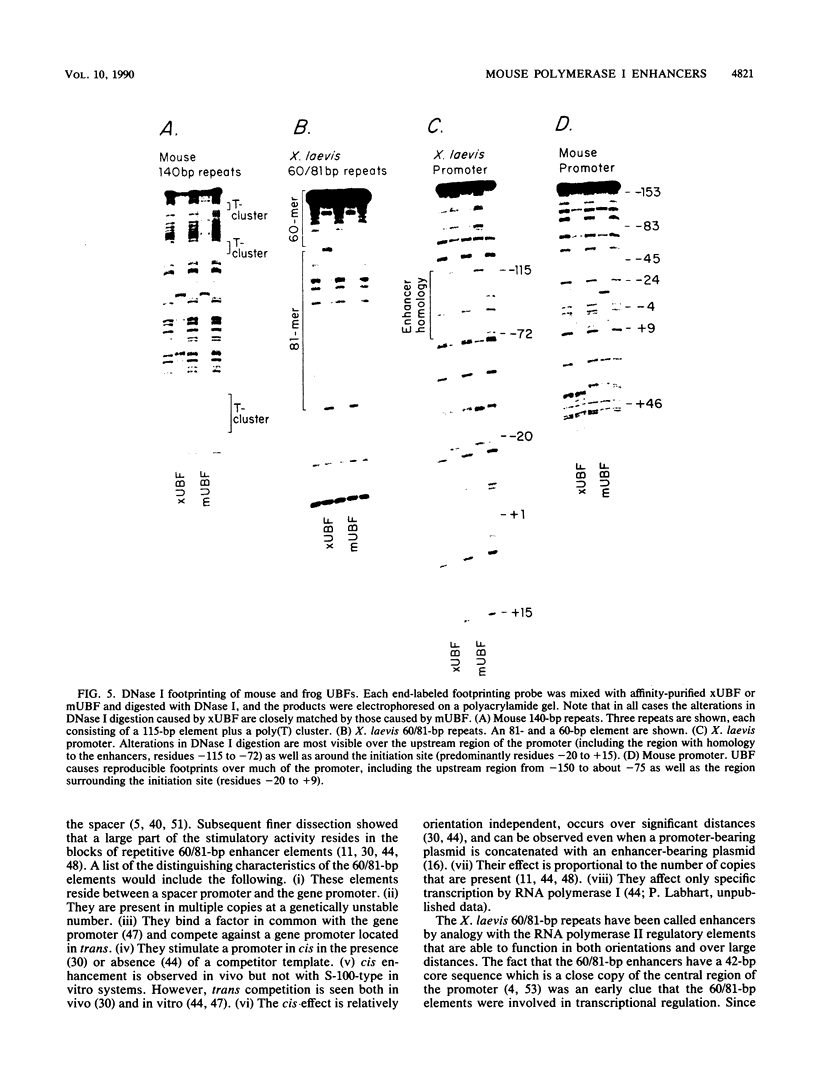
The intergenic spacer of the mouse ribosomal genes contains repetitive 140-base-pair (bp) elements which we show are enhancers for RNA polymerase I transcription analogous to the 60/81-bp repetitive enhancers (enhancers containing a 60-bp and an 81-bp element) previously characterized from Xenopus laevis. In rodent cell transfection assays, the 140-bp repeats stimulated an adjacent mouse polymerase I promoter when located in cis and competed with it when located in trans. Remarkably, in frog oocyte injection assays, the 140-bp repeats enhanced a frog ribosomal gene promoter as strongly as did the homologous 60/81-bp repeats. Mouse 140-bp repeats also competed against frog promoters in trans. The 140-bp repeats bound UBF, a DNA-binding protein we have purified from mouse extracts that is the mouse homolog of polymerase I transcription factors previously isolated from frogs and humans. The DNA-binding properties of UBF are conserved from the mouse to the frog. The same regulatory elements (terminators, gene and spacer promoters, and enhancers) have now been identified in both a mammalian and an amphibian spacer, and they are found in the same relative order. Therefore, this arrangement of elements probably is widespread in nature and has important functional consequences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker R. F., Harberd N. P., Jarvis M. G., Flavell R. B. Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90434-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Spacer sequences regulate transcription of ribosomal gene plasmids injected into Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Additional RNA polymerase I initiation site within the nontranscribed spacer region of the rat rRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2388–2396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Transcriptional role for the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2766–2773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikaraishi D. M., Buchanan L., Danna K. J., Harrington C. A. Genomic organization of rat rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6437–6452. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Wilkinson J. K., Sollner-Webb B. Mouse and frog violate the paradigm of species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7498–7502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription in Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):813–827. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Chao W., Jacob S. T. An enhancer element in the far upstream spacer region of rat ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11616–11622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Jacob S. T. A cis-acting sequence within the rat ribosomal DNA enhancer region can modulate RNA polymerase II-directed transcription of the metallothionein I gene in vitro. DNA. 1989 Jun;8(5):311–320. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumenco V. M., Wejksnora P. J. Characterization of the region around the start point of transcription of ribosomal RNA in the Chinese hamster. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. A transcription factor, TFIS, interacts with both the promoter and enhancer of the Xenopus rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1768–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M., Dröge P. Transactivation of the Xenopus rRNA gene promoter by its enhancer. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):657–659. doi: 10.1038/341657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Jacob S. T. A 37-base pair element in the far upstream spacer region can enhance transcription of rat rDNA in vitro and can bind to the core promoter-binding factor(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Di Nocera P. P. Multiple repeated units in Drosophila melanogaster ribosomal DNA spacer stimulate rRNA precursor transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Sollner-Webb B. The promoter-proximal rDNA terminator augments initiation by preventing disruption of the stable transcription complex caused by polymerase read-in. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):212–223. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. A novel promoter in the mouse rDNA spacer is active in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3487–3492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Mitchelson K., de Winter R. The promotion of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:207–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtif V. L., Rae P. M. In vivo transcription of rDNA spacers in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Mougey E. B., Sollner-Webb B. The Xenopus ribosomal DNA 60- and 81-base-pair repeats are position-dependent enhancers that function at the establishment of the preinitiation complex: analysis in vivo and in an enhancer-responsive in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5093–5104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Half helical turn spacing changes convert a frog into a mouse rDNA promoter: a distant upstream domain determines the helix face of the initiation site. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):52–62. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Eaton S., Calame K. Purified mu EBP-E binds to immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4972–4980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. Sequence elements essential for function of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4282–4288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Smith S. D., Reeder R. H., Rothblum L. rUBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor from rats, produces DNase I footprints identical to those produced by xUBF, its homolog from frogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3810–3812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Mechanisms of nucleolar dominance in animals and plants. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):2013–2016. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G. The mechanism of nucleolar dominance in Xenopus hybrids. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90524-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., McKnight S. L. Accurate transcription of cloned Xenopus rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: demonstration by S1 nuclease mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3391–3405. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Henderson S. L., Dougherty K. M., Wejksnora P. J., Sollner-Webb B. An RNA polymerase I promoter located in the CHO and mouse ribosomal DNA spacers: functional analysis and factor and sequence requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1513–1525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. K., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of Xenopus ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14375–14383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Purification and characterization of a high-mobility-group-like DNA-binding protein that stimulates rRNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3406–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]