Abstract
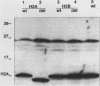
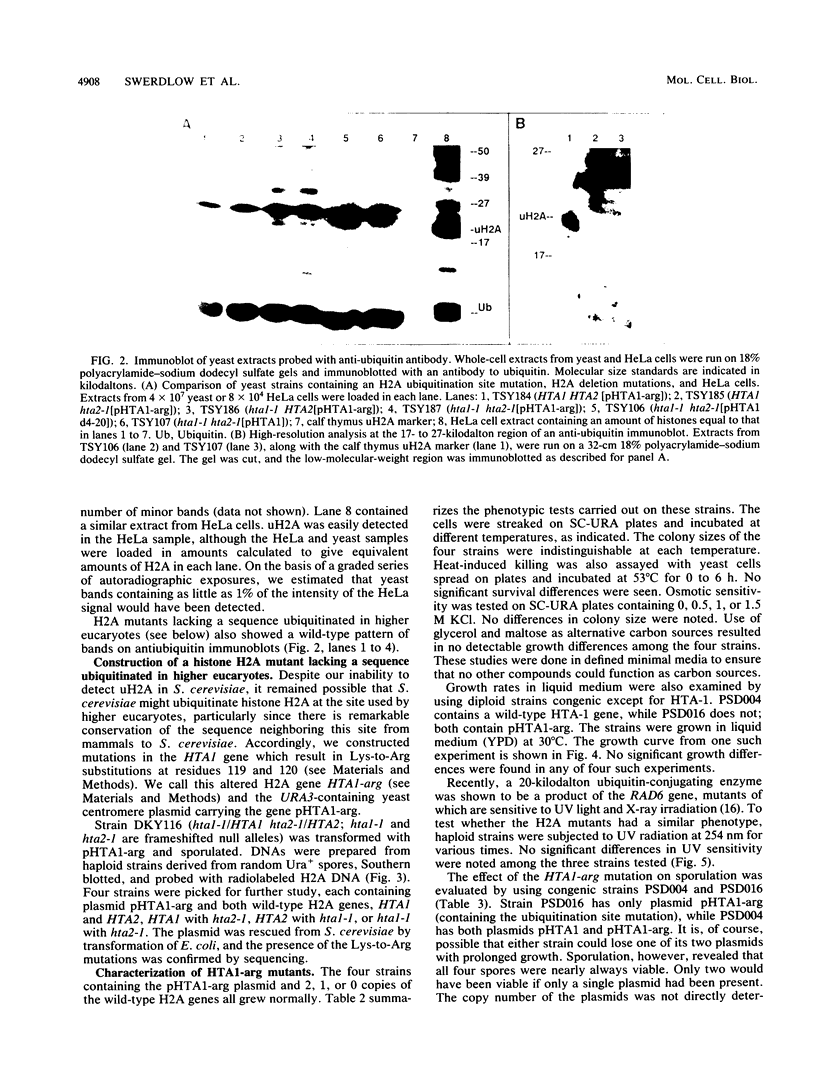
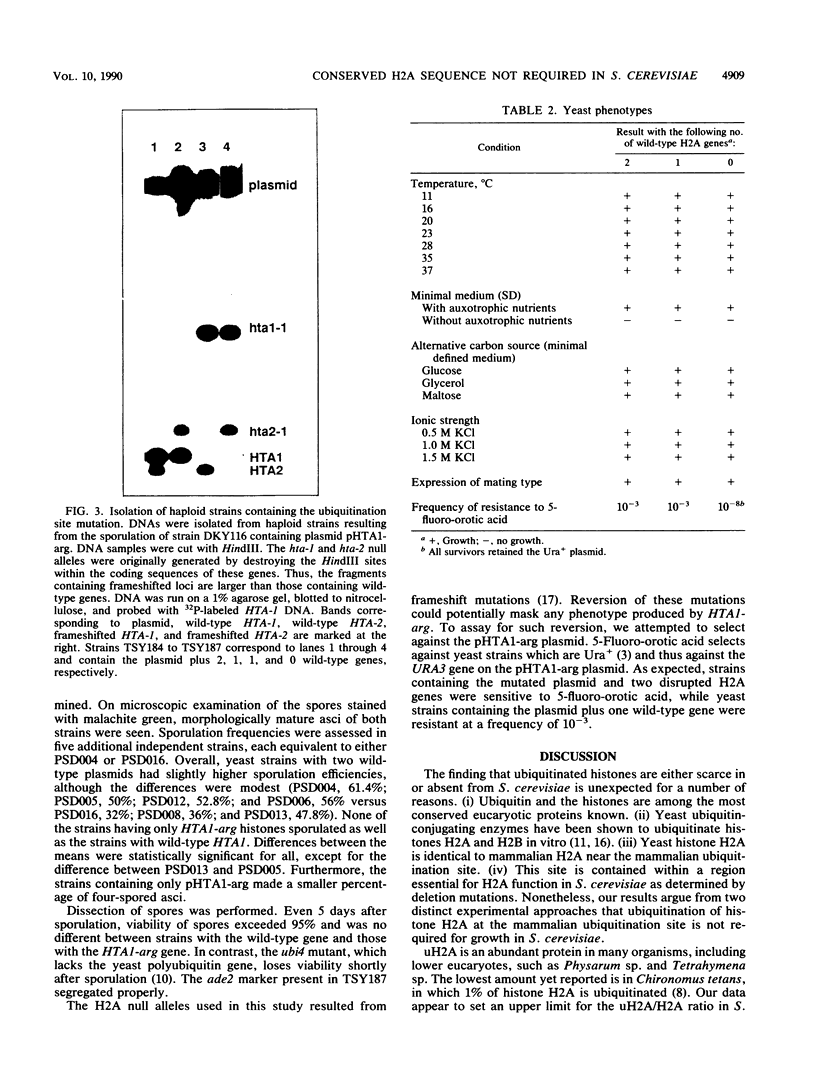
Histones H2A and H2B are modified by ubiquitination of specific lysine residues in higher and lower eucaryotes. To identify functions of ubiquitinated histone H2A, we studied an organism in which genetic analysis of histones is feasible, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Surprisingly, immunoblotting experiments using both anti-ubiquitin and anti-H2A antibodies gave no evidence that S. cerevisiae contains ubiquitinated histone H2A. The immunoblot detected a variety of other ubiquitinated species. A sequence of five residues in S. cerevisiae histone H2A that is identical to the site of H2A ubiquitination in higher eucaryotes was mutated to substitute arginines for lysines. Any ubiquitination at this site would be prevented by these mutations. Yeast organisms carrying this mutation were indistinguishable from the wild type under a variety of conditions. Thus, despite the existence in S. cerevisiae of several gene products, such as RAD6 and CDC34, which are capable of ubiquitinating histone H2A in vitro, ubiquitinated histone H2A is either scarce in or absent from S. cerevisiae. Furthermore, the histone H2A sequence which serves as a ubiquitination site in higher eucaryotes is not essential for yeast growth, sporulation, or resistance to either heat stress or UV radiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsoum J., Levinger L., Varshavsky A. On the chromatin structure of the amplified, transcriptionally active gene for dihydrofolate reductase in mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5274–5282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum J., Varshavsky A. Preferential localization of variant nucleosomes near the 5'-end of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7688–7697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Yeast may not contain histone H1: the only known 'histone H1-like' protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a mitochondrial protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7975–7985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Schuster T., Grunstein M. Organization, primary structure, and evolution of histone H2A and H2B genes of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Mammalian cell cycle mutant defective in intracellular protein degradation and ubiquitin-protein conjugation. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;180:17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C., Goldknopf I. L., Lezzi M., Daneholt B. Low degree of ubiquitination of histone 2A in the dipteran Chironomus tentans. Cell Differ. 1986 Dec;19(4):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(86)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Yochem J., Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A., Byers B. The yeast cell cycle gene CDC34 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1331–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2842867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensold J. O., Swerdlow P. S., Housman D. E. A transient increase in histone H2A ubiquitination is coincident with the onset of erythroleukemic cell differentiation. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1153–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast DNA repair gene RAD6 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):131–134. doi: 10.1038/329131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodrubetz D., Rykowski M. C., Grunstein M. Histone H2A subtypes associate interchangeably in vivo with histone H2B subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7814–7818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. High-resolution fractionation of nucleosomes: minor particles, "whiskers," and separation of mononucleosomes containing and lacking A24 semihistone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3244–3248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Selective arrangement of ubiquitinated and D1 protein-containing nucleosomes within the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. I., Seon B. K., Sandberg A. A. Disappearance of a structural chromatin protein A24 in mitosis: implications for molecular basis of chromatin condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6386–6390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yanagida M. Histone gene organization of fission yeast: a common upstream sequence. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. D., Yasuda H., Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M., Bradbury E. M. Identification of ubiquitinated histones 2A and 2B in Physarum polycephalum. Disappearance of these proteins at metaphase and reappearance at anaphase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5147–5153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. E., Allis C. D., Davie J. R. Ubiquitinated histone H2B is preferentially located in transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):958–963. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. E., Roth S. Y., Cook R. G., Allis C. D., Davie J. R. Changes in the histone H2A variant H2A.Z and polyubiquitinated histone species in developing trout testis. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster T., Han M., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H2A and H2B amino termini have interchangeable functions. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L. Rapid turnover of the histone-ubiquitin conjugate, protein A24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3151–3158. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow P. S., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Enhancement of immunoblot sensitivity by heating of hydrated filters. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne A. W., Sautiere P., Briand G., Crane-Robinson C. The structure of ubiquitinated histone H2B. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1005–1010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunsch A. M., Haas A. L., Lough J. Synthesis and ubiquitination of histones during myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]