Abstract
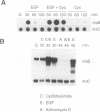
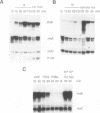
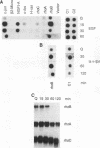
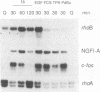
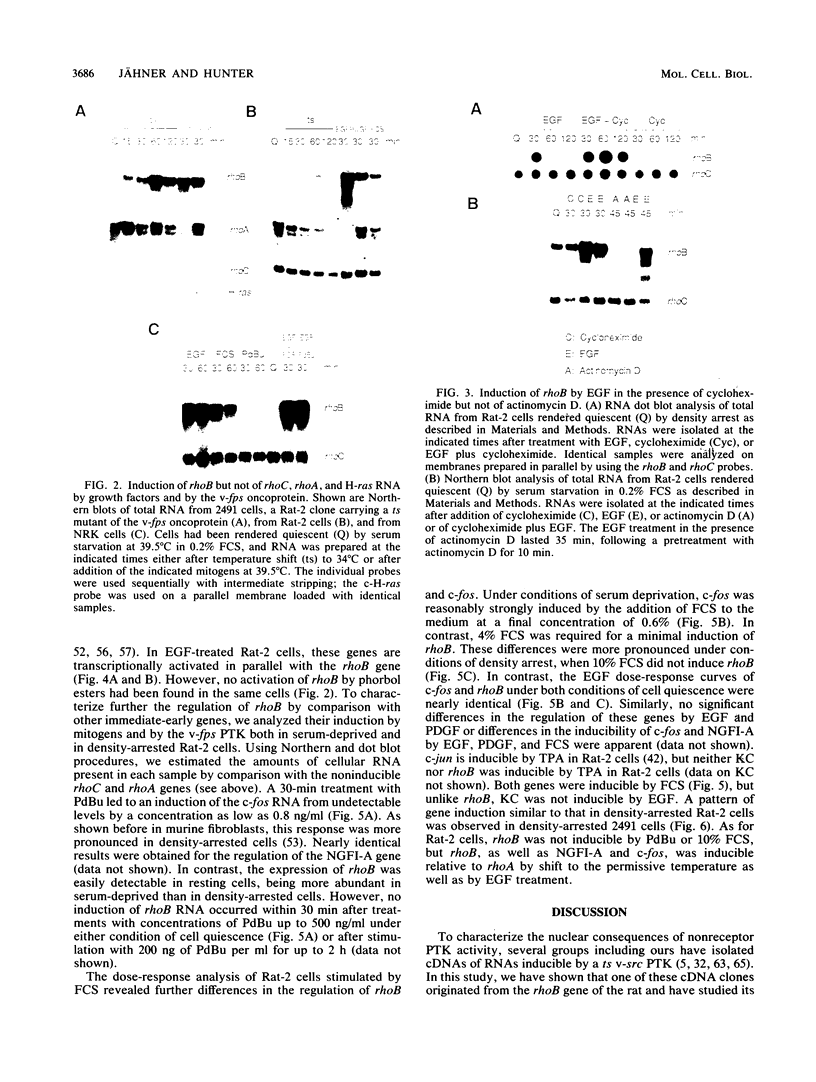
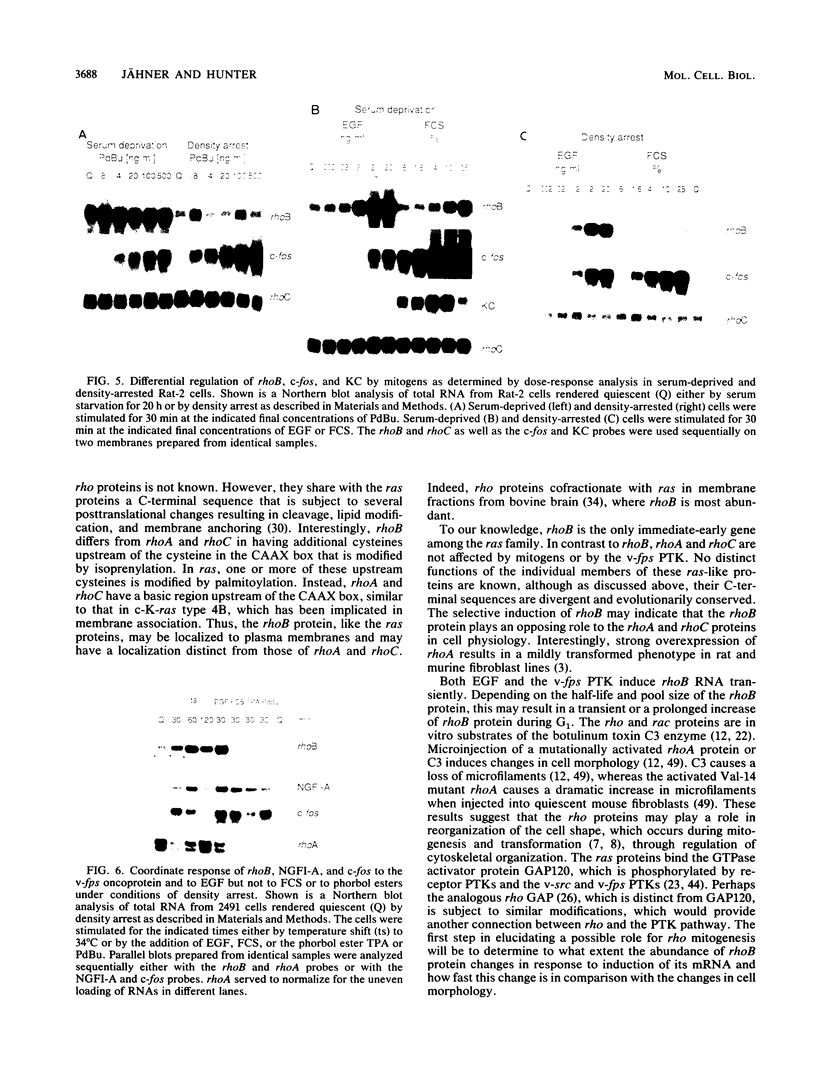
A set of genes is rapidly inducible when quiescent fibroblasts are stimulated by growth factors or by the activation of temperature-sensitive retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases. Most of these so-called immediate-early genes were cloned by differential cDNA hybridization. DNA sequence analysis identified many of them as putative members of the growth factor or of the transcription factor gene family, suggesting a role in signal transmission during the G0-to-G1 transition. In this study, we identified one of the genes that are rapidly inducible by the retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases v-Src and v-Fps of Rous sarcoma virus and Fujinami sarcoma virus, respectively, as the rhoB gene, a member of the ras gene superfamily whose products are GTP-binding proteins, rhoB is transiently activated at the transcriptional level by v-Fps and by epidermal growth factor. Its labile RNA is inducible in the presence of cycloheximide but not of actinomycin D. rhoB is strongly induced by epidermal growth factor and by platelet-derived growth factor both in subconfluent, serum-starved and in density-arrested Rat-2 fibroblasts. Fetal calf serum is a poor inducer, particularly in density-arrested cells, and phorbol esters do not increase rhoB expression at all. These data suggest that rhoB is inducible by protein-tyrosine kinases through a pathway not involving the activation of protein kinase C. Neither the closely related rhoC and rhoA genes nor the distantly related c-H-ras gene is rapidly inducible by mitogens. Thus, rhoB is the first known member of the small GTP-binding proteins among the immediate-early genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham H., Weinberg R. A. Characterization and expression of the human rhoH12 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2058–2066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P. A., Alcorta D., Simmons D. L., Luk K. C., Erikson R. L. Constitutive expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide homologous to biologically active human platelet protein in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Transformation of rat fibroblasts by FSV rapidly increases glucose transporter gene transcription. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1495–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.3029870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockus B. J., Stiles C. D. Regulation of cytoskeletal architecture by platelet-derived growth factor, insulin and epidermal growth factor. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):186–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschek C. B., Jockusch B. M., Friis R. R., Back R., Grundmann E., Bauer H. Early changes in the distribution and organization of microfilament proteins during cell transformation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Litfin M., Karin M., Herrlich P. Activation of the c-fos gene by UV and phorbol ester: different signal transduction pathways converge to the same enhancer element. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changelian P. S., Feng P., King T. C., Milbrandt J. Structure of the NGFI-A gene and detection of upstream sequences responsible for its transcriptional induction by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):377–381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Boquet P., Madaule P., Popoff M. R., Rubin E. J., Gill D. M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Madaule P., Tavitian A. Coding sequence of human rho cDNAs clone 6 and clone 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2717–2717. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. Functional serum response elements upstream of the growth factor-inducible gene zif268. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4889–4895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Ferreira P. C., Gentz R., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. The product of a fos-related gene, fra-1, binds cooperatively to the AP-1 site with Jun: transcription factor AP-1 is comprised of multiple protein complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):173–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. An AP1-binding site in the c-fos gene can mediate induction by epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Self A. J., van Oers C., Hall A. Identification of distinct cytoplasmic targets for ras/R-ras and rho regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Berkowitz L. A., Feramisco J. R., Franza B. R., Jr, Graham R. M., Riabowol K. T., Ryan W. A., Jr Intracellular mediators of c-fos induction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):761–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazel T. G., Nathans D., Lau L. F. A gene inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8444–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Le Beau M. M., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Acharya S., Shows T. B., Rowley J. D., Sukhatme V. P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with "zinc-binding finger" structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Kikuchi A., Mizoguchi A., Takai Y. Intrasynaptosomal distribution of the ras, rho and smg-25A GTP-binding proteins in bovine brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Nov;6(2-3):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Vesque C., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Frank R., Charnay P. The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3456–3467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. H., Levine R. A., Campisi J. c-ras-Ha gene expression is regulated by insulin or insulinlike growth factor and by epidermal growth factor in murine fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3411–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell S. E., Kerr L. D., Matrisian L. M. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of stromelysin mRNA in rat fibroblasts requires induction of proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-jun and activation of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4284–4293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina H., Sato H., Suzuki T., Sato M., Iba H. Isolation and characterization of fra-2, an additional member of the fos gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3619–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Chardin P., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A. Expression of the ras-related ralA, rho12 and rab genes in adult mouse tissues. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oquendo P., Alberta J., Wen D. Z., Graycar J. L., Derynck R., Stiles C. D. The platelet-derived growth factor-inducible KC gene encodes a secretory protein related to platelet alpha-granule proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4133–4137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Guyden J., Kung T. H., Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. A strain of Fujinami sarcoma virus which is temperature-sensitive in protein phosphorylation and cellular transformation. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):767–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90553-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Fisch T. M., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation of c-fos. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):739–748. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Nathans D. Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8464–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Macdonald-Bravo H., Mattéi M. G., Ruppert S., Bravo R. Structure, mapping and expression of a growth factor inducible gene encoding a putative nuclear hormonal binding receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3327–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Transcription activation by serum, PDGF, and TPA through the c-fos DSE: cell type specific requirements for induction. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):3–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Levy D. B., Yannoni Y., Erikson R. L. Identification of a phorbol ester-repressible v-src-inducible gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle M. Y., Sugano S., Hampe A., Vashistha A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein is induced in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells independently of glucose deprivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2675–2680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus induces a novel gene with homology to a mitogenic platelet protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers H. T., Pronk G. J., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Analysis of the rat JE gene promoter identifies an AP-1 binding site essential for basal expression but not for TPA induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):23–34. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai-Morris C. H., Cao X. M., Sukhatme V. P. 5' flanking sequence and genomic structure of Egr-1, a murine mitogen inducible zinc finger encoding gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8835–8846. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G. A., Hunter T. Investigation of the role of P130gag-fps in transformation: generation and use of a temperature-sensitive mutant P130gag-fps. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3849–3854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3849-3854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Zoller M. J., Pawson T. A lysine in the ATP-binding site of P130gag-fps is essential for protein-tyrosine kinase activity. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Cantley L. Phosphoinositide metabolism and the control of cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):327–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeramian P., Chardin P., Madaule P., Tavitian A. Nucleotide sequence of human rho cDNA clone 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1869–1869. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Toschi L., Ryseck R. P., Schuermann M., Müller R., Bravo R. The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):805–813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]