Abstract
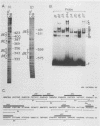
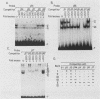
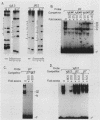
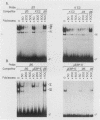
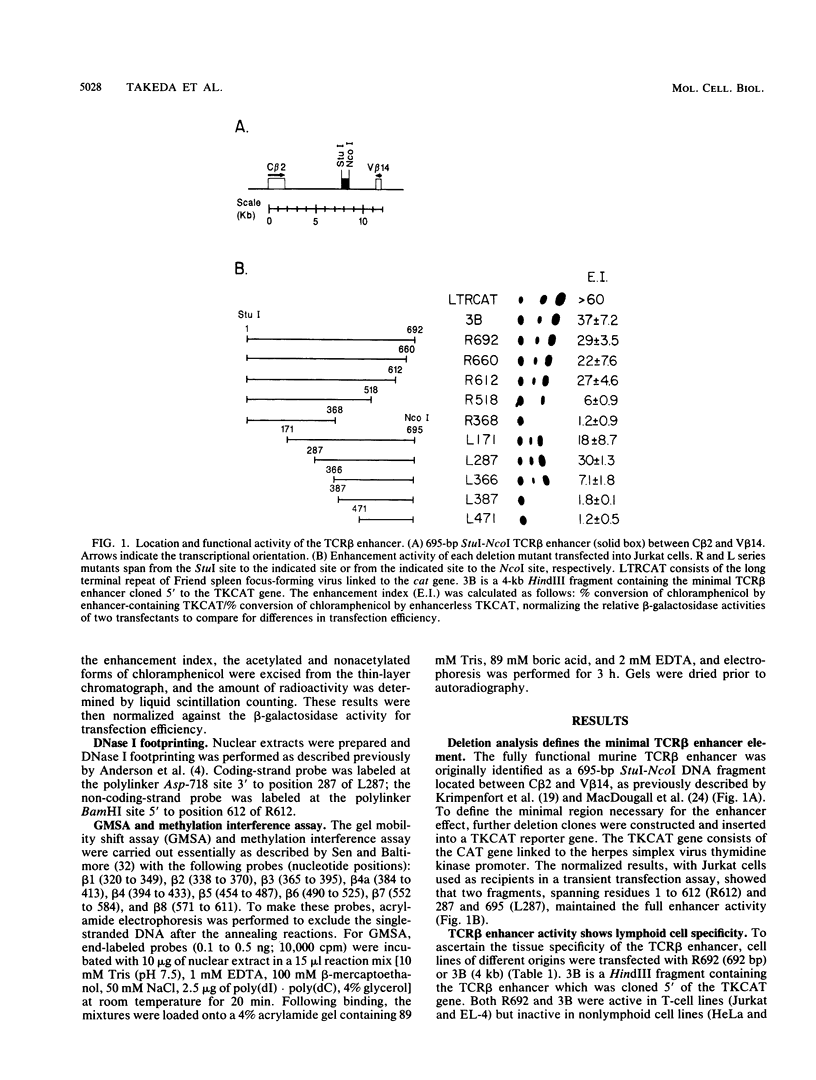
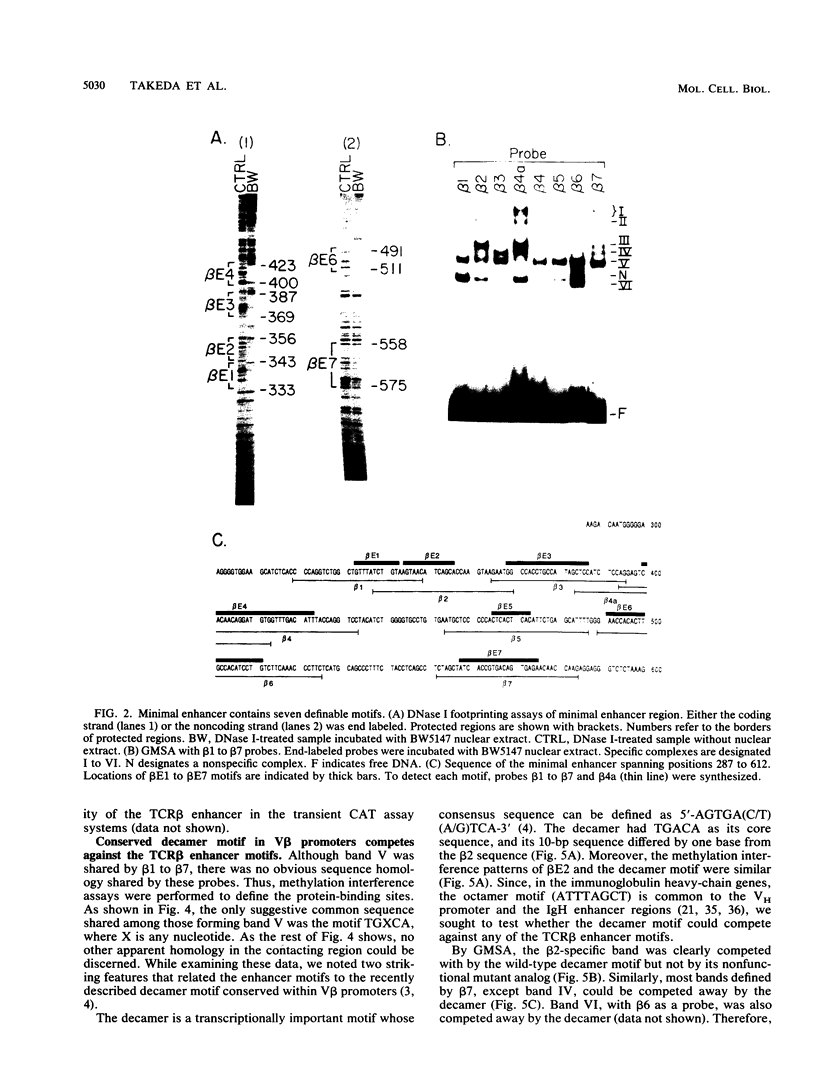
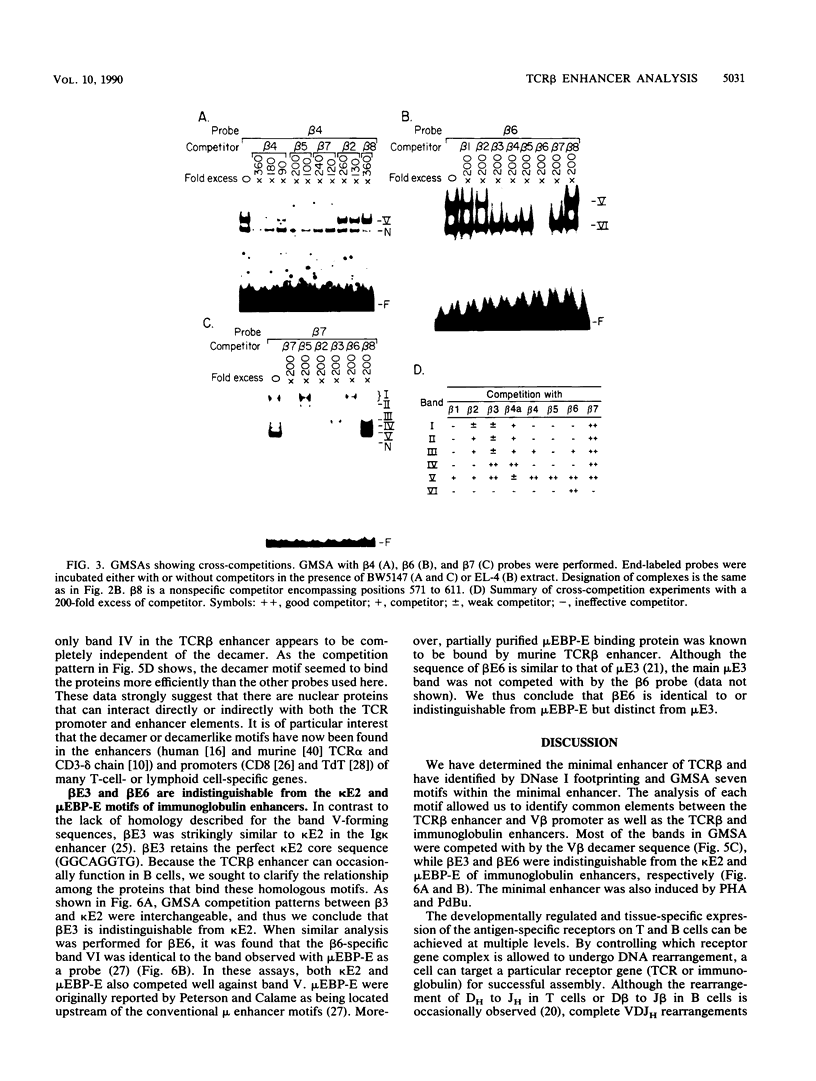
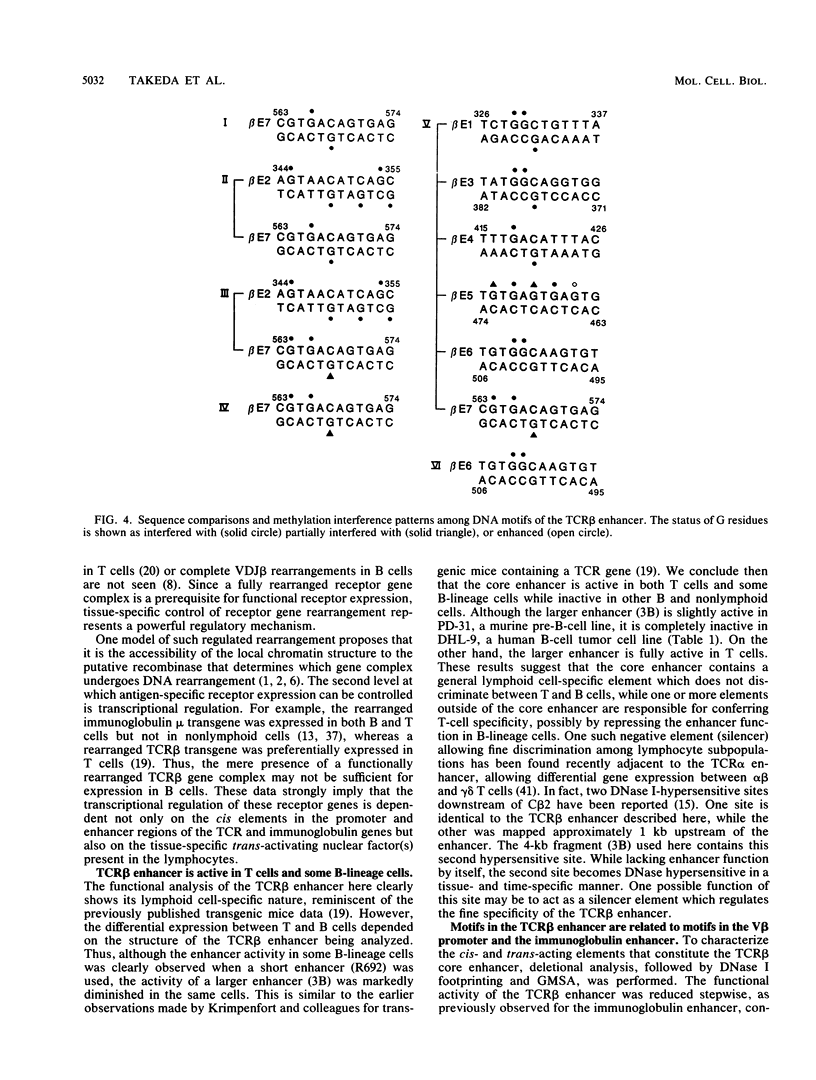
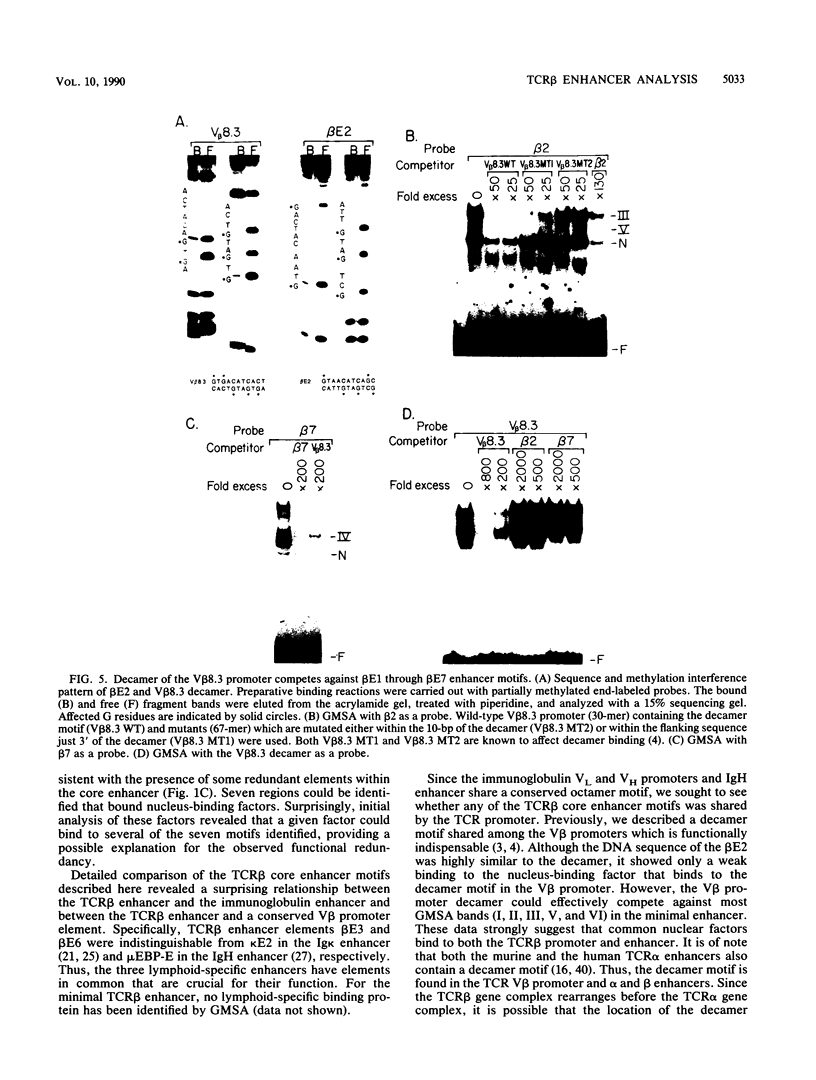
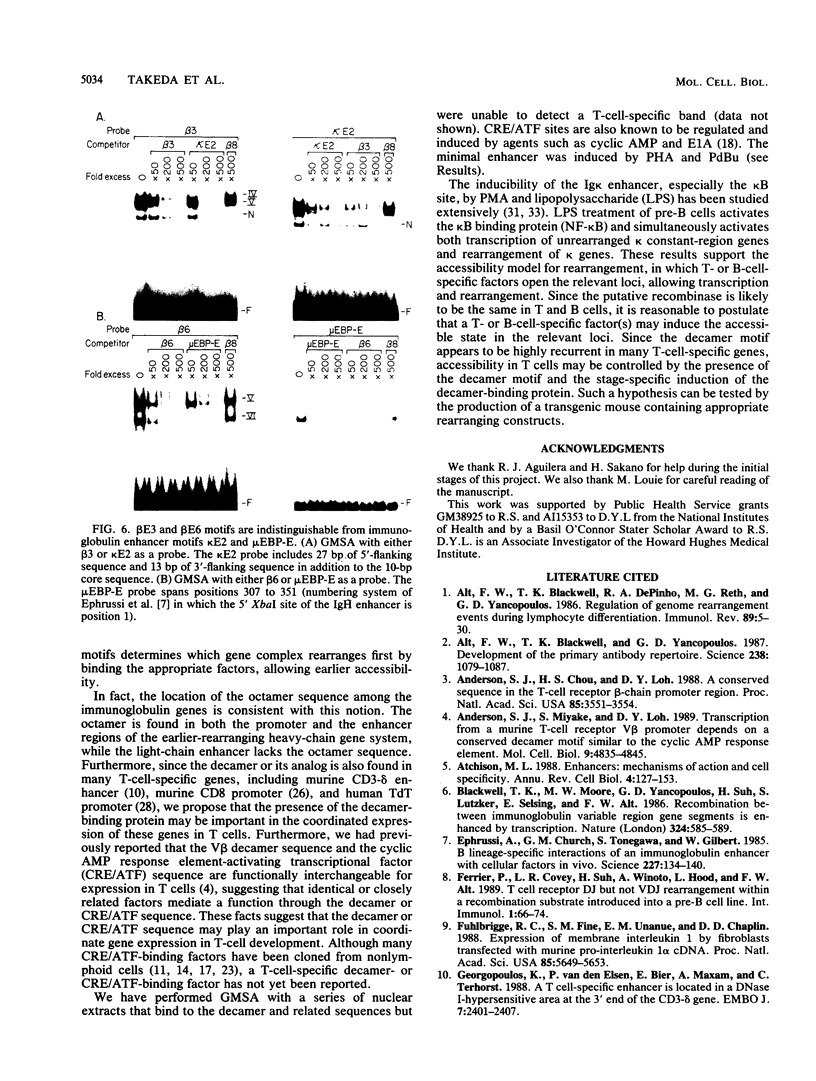
The minimal T-cell receptor (TCR) beta-chain (TCR beta) enhancer has been identified by transfection into lymphoid cells. The minimal enhancer was active in T cells and in some B-lineage cells. When a larger fragment containing the minimal enhancer was used, its activity was apparent only in T cells. Studies with phytohemagglutinin and 4 beta-phorbol-12,13-dibutyrate revealed that the enhancer activity was increased by these agents. By a combination of DNase I footprinting, gel mobility shift assay, and methylation interference analysis, seven different motifs were identified within the minimal enhancer. Furthermore, competition experiments showed that some of these elements bound identical or similar factors that are known to bind to the TCR V beta promoter decamer or to the immunoglobulin enhancer kappa E2 or muEBP-E motif. These shared motifs may be important in the differential gene activity among the different lymphoid subsets.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. J., Chou H. S., Loh D. Y. A conserved sequence in the T-cell receptor beta-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. J., Miyake S., Loh D. Y. Transcription from a murine T-cell receptor V beta promoter depends on a conserved decamer motif similar to the cyclic AMP response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4835–4845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Moore M. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Suh H., Lutzker S., Selsing E., Alt F. W. Recombination between immunoglobulin variable region gene segments is enhanced by transcription. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):585–589. doi: 10.1038/324585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Covey L. R., Suh H., Winoto A., Hood L., Alt F. W. T cell receptor DJ but not VDJ rearrangement within a recombination substrate introduced into a pre-B cell line. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):66–74. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlbrigge R. C., Fine S. M., Unanue E. R., Chaplin D. D. Expression of membrane interleukin 1 by fibroblasts transfected with murine pro-interleukin 1 alpha cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5649–5653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., van den Elsen P., Bier E., Maxam A., Terhorst C. A T cell-specific enhancer is located in a DNase I-hypersensitive area at the 3' end of the CD3-delta gene. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2401–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y. T cell receptor beta gene has two downstream DNase I hypersensitive regions. Possible mechanisms of tissue- and stage-specific gene regulation. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2097–2107. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Yang L. H., Morle G., Leiden J. M. A T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer element 3' of C alpha in the human T-cell receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6714–6718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Complexities of gene regulation by cAMP. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., de Jong R., Uematsu Y., Dembic Z., Ryser S., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M., Berns A. Transcription of T cell receptor beta-chain genes is controlled by a downstream regulatory element. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B. Transcription of T cell antigen receptor genes is induced by protein kinase C activation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1769–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall S., Peterson C. L., Calame K. A transcriptional enhancer 3' of C beta 2 in the T cell receptor beta locus. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):205–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2968651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakauchi H., Tagawa M., Nolan G. P., Herzenberg L. A. Isolation and characterization of the gene for the murine T cell differentiation antigen and immunoglobulin-related molecule, Lyt-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4337–4347. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. L. Complex protein binding within the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4194–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Morrow J. K., Danton M. J., Coleman M. S. Human terminal deoxyribonucleotidyltransferase: molecular cloning and structural analysis of the gene and 5' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2489–2493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Baltimore D. Activation of immunoglobulin kappa gene rearrangement correlates with induction of germline kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Jensen J. P., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and expression in diffuse histiocytic lymphomas reveal cellular lineage, molecular defects, and sites of chromosomal translocation. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):391–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U. Transgenic mice with immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:151–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. E., Peterlin B. M. Transcriptional enhancers in the HLA-DQ subregion. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3315–3319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. Alpha beta lineage-specific expression of the alpha T cell receptor gene by nearby silencers. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]