Abstract
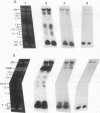
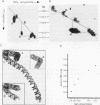
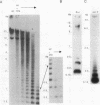
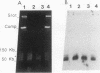
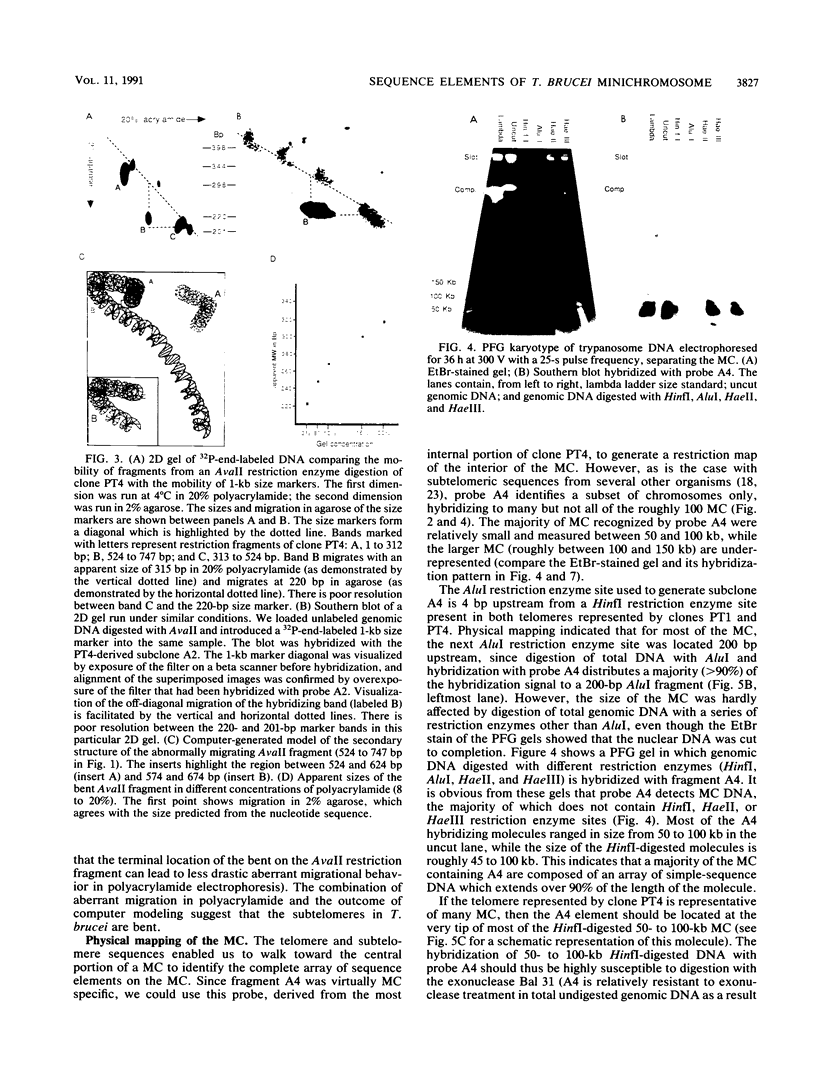
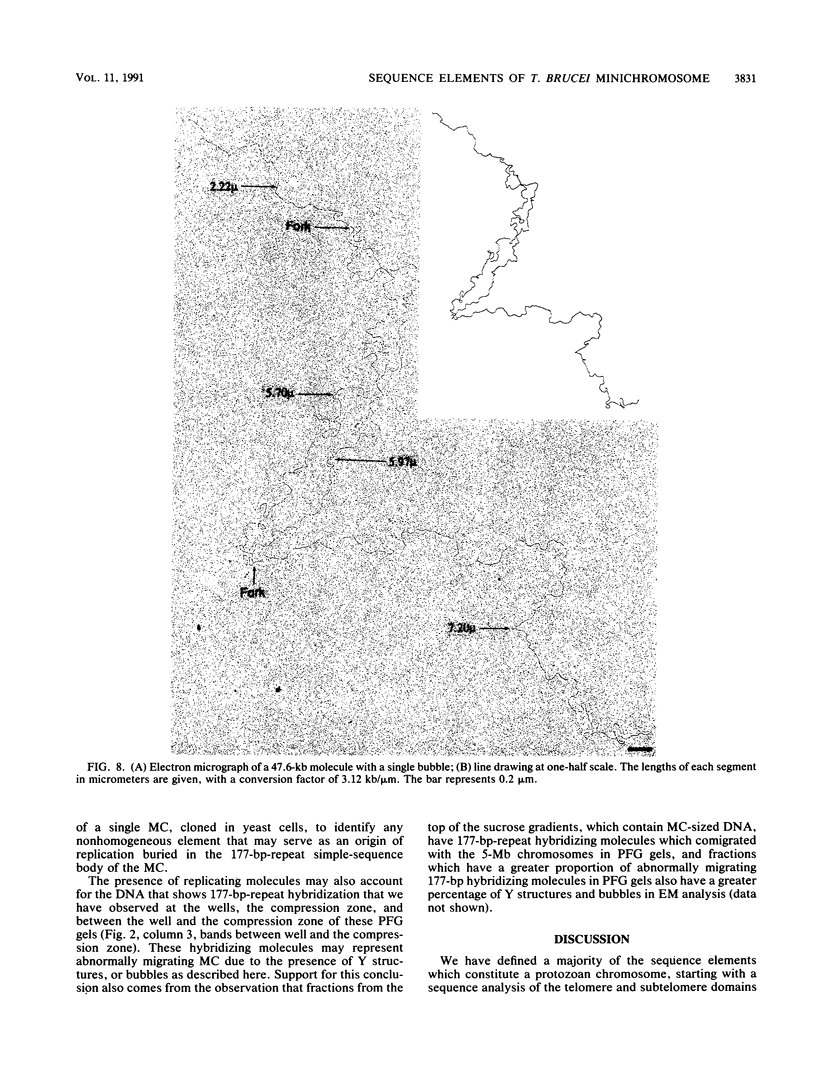
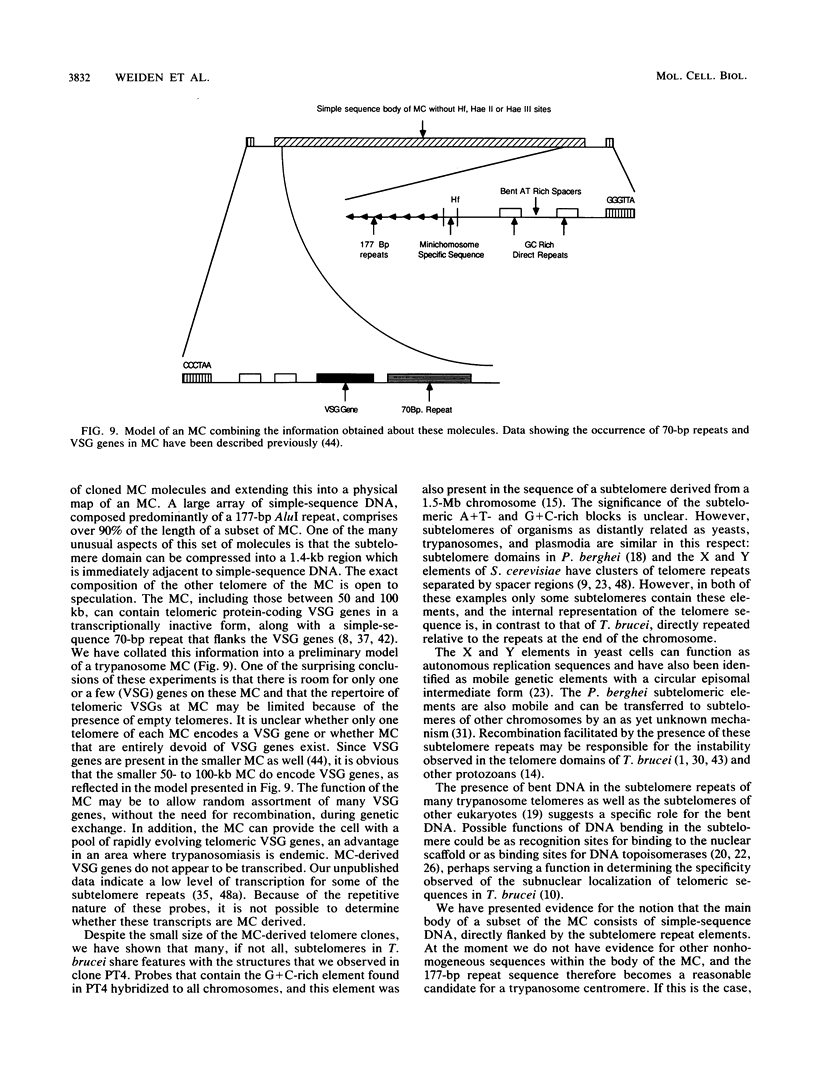
The genome of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei contains a set of about 100 minichromosomes of about 50 to 150 kb in size. The small size of these chromosomes, their involvement in antigenic variation, and their mitotic stability make them ideal candidates for a structural analysis of protozoan chromosomes and their telomeres. We show that a subset of the minichromosomes is composed predominantly of simple-sequence DNA, with over 90% of the length of the minichromosome consisting of a tandem array of 177-bp repeats, indicating that these molecules have limited protein-coding capacity. Proceeding from the tip of the telomere to a chromosome internal position, a subset of the minichromosomes contained the GGGTTA telomere repeat, a 29-bp telomere-derived repeat, a region containing 74-bp G + C-rich direct repeats separated by approximately 155 bp of A + T-rich DNA that has a bent character, and 50 to 150 kb of the 177-bp repeat. Several of the minichromosome-derived telomeres did not encode protein-coding genes, indicating that the repertoire of telomeric variant cell surface glycoprotein genes is restricted to some telomeres only. The telomere organization in trypanosomes shares striking similarities to the organization of telomeres and subtelomeres in humans, yeasts, and plasmodia. An electron microscopic analysis of the minichromosomes showed that they are linear molecules without abnormal structures in the main body of the chromosome. The structure of replicating molecules indicated that minichromosomes probably have a single bidirectional origin of replication located in the body of the chromosome. We propose a model for the structure of the trypanosome minichromosomes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernards A., Michels P. A., Lincke C. R., Borst P. Growth of chromosome ends in multiplying trypanosomes. Nature. 1983 Jun 16;303(5918):592–597. doi: 10.1038/303592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Challoner P. B. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres and their synthesis. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):489–490. doi: 10.1126/science.2200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Discontinuous transcription and antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:701–732. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., van Bree M. P., Boothroyd J. C. The 5'-limit of transposition and upstream barren region of a trypanosome VSG gene: tandem 76 base-pair repeats flanking (TAA)90. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2759–2774. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. F., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Isolation and characterization of a human telomere. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6109–6127. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. M., Shea C., Fields S., Taub R. N., Van der Ploeg L. H., Tse D. B. Architectural organization in the interphase nucleus of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei: location of telomeres and mini-chromosomes. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2611–2619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Baum M. P. Functional analysis of a centromere from fission yeast: a role for centromere-specific repeated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1863–1872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of a yeast centromere and construction of functional small circular chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):504–509. doi: 10.1038/287504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. The molecular biology of the Kinetoplastidae. Genet Eng. 1988;(7):1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Kemp D. J. Homologous recombination within subtelomeric repeat sequences generates chromosome size polymorphisms in P. falciparum. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Kooter J. M., Michels P. A., Borst P. Telomere conversion in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8149–8165. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Zarling D. A. Unique poly(dA).poly(dT) B'-conformation in cellular and synthetic DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6063–6074. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore E., Pace T., Ponzi M., Picci L., Frontali C. Organization of subtelomeric repeats in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2423–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore E., Pace T., Ponzi M., Scotti R., Frontali C. A site of intrinsic bending in a highly repeated element of Plasmodium berghei genome. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairlamb A. H., Weislogel P. O., Hoeijmakers J. H., Borst P. Isolation and characterization of kinetoplast DNA from bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):293–309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesdiener K., Garciá-Anoveros J., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Chromosome organization of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6079–6083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homberger H. P. Bent DNA is a structural feature of scaffold-attached regions in Drosophila melanogaster interphase nuclei. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00291044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Haber J. E. Identification of autonomously replicating circular subtelomeric Y' elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2369–2380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Mitani M. Simplified quantitative electron microscopy of biopolymers. Biopolymers. 1970;9(3):373–379. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Shlomai J. A unique endonuclease from Crithidia fasciculata which recognizes a bend in the DNA helix. Specificity of the cleavage reaction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Janse C., Mons B., Frontali C. Long insertions within telomeres contribute to chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6759–6764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E. Pseudogenes, chimaeric genes and the timing of antigen variation in African trypanosomes. Trends Genet. 1989 Dec;5(12):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Zakian V. A. Recombination occurs during telomere formation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):429–433. doi: 10.1038/337429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Transcription of telomere repeats in protozoa. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2633–2638. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah J. S., Young J. R., Kimmel B. E., Iams K. P., Williams R. O. The 5' flanking sequence of a Trypanosoma brucei variable surface glycoprotein gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Bos J. L., Konings A. F., Menke H. H., Borst P., Gutteridge W. E., Leon W. Characterization of satellite DNA in Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Menke H. H., Caspers M. P., Borst P. Size fractionation of Trypanosoma brucei DNA: localization of the 177-bp repeat satellite DNA and a variant surface glycoprotein gene in a mini-chromosomal DNA fraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3889–3901. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Cornelissen A. W., Barry J. D., Borst P. Chromosomes of kinetoplastida. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3109–3115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Borst P. Structure of the growing telomeres of Trypanosomes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R., Borst P. Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei analyzed by electrophoretic separation of chromosome-sized DNA molecules. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smith C. L., Polvere R. I., Gottesdiener K. M. Improved separation of chromosome-sized DNA from Trypanosoma brucei, stock 427-60. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3217–3227. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Valerio D., De Lange T., Bernards A., Borst P., Grosveld F. G. An analysis of cosmid clones of nuclear DNA from Trypanosoma brucei shows that the genes for variant surface glycoproteins are clustered in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5905–5923. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. M., Prospero T. D., Jenni L., Le Page R. W. DNA contents and molecular karyotypes of hybrid Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]