Abstract
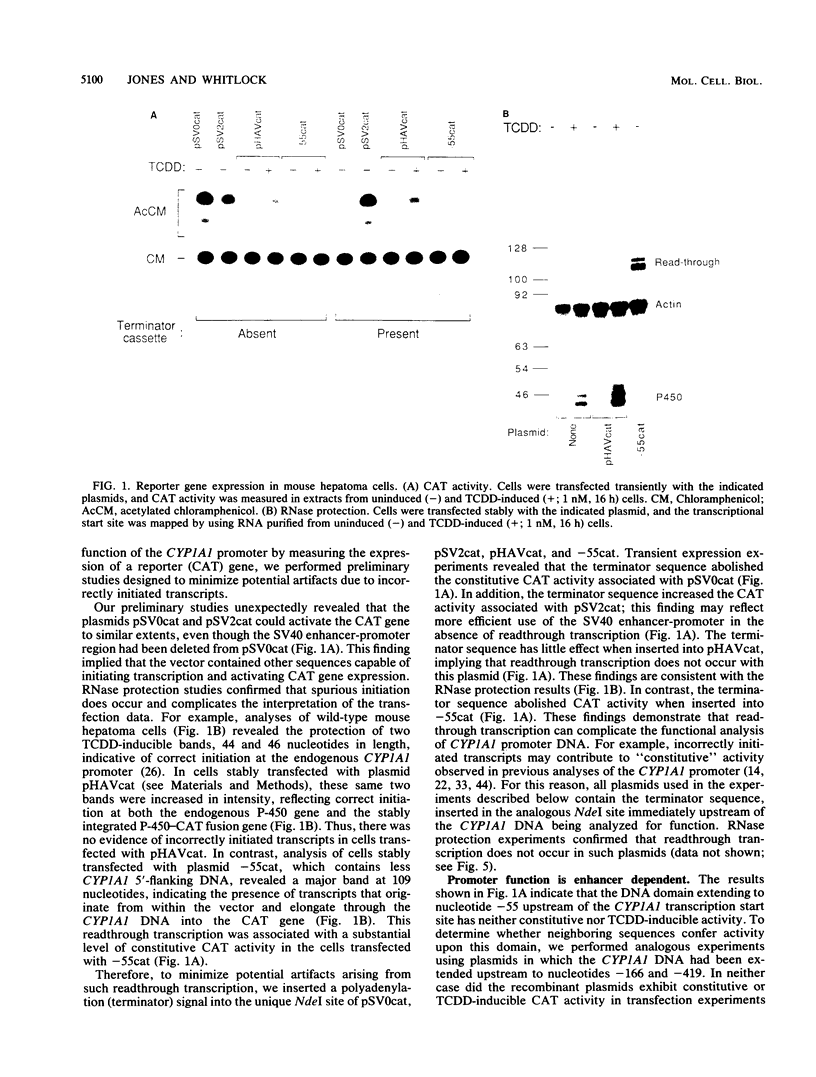
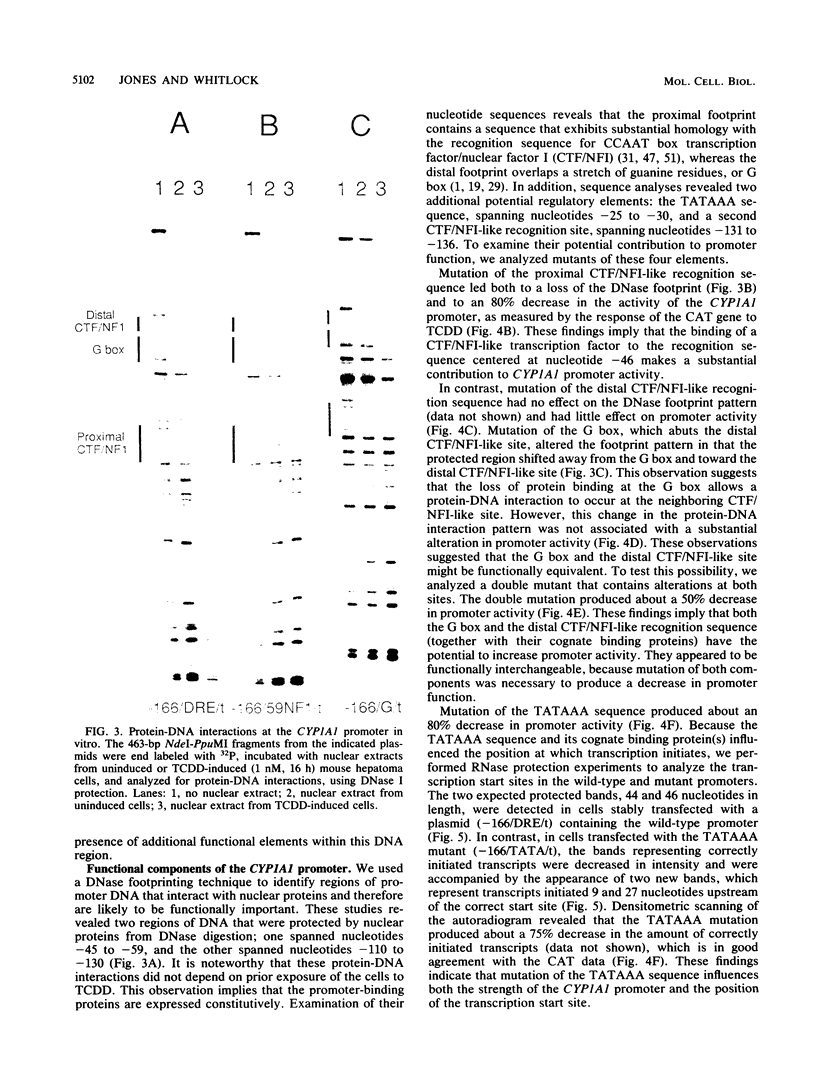
In mouse hepatoma cells, the environmental contaminant 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases the transcription rate of the CYP1A1 gene, which encodes a cytochrome P-450 enzyme. In this study, we analyzed the DNA region immediately upstream of the CYP1A1 gene. A domain that extends upstream to nucleotide--166 was found to function as a transcriptional promoter. The promoter was silent when uncoupled from the dioxin-responsive enhancer located farther upstream. DNase footprinting experiments indicated that nuclear proteins interact with distinct domains of the promoter in a TCDD-independent fashion. Mutational analyses indicated that the CYP1A1 promoter contains at least three functional domains, including a TATAAA sequence, a CCAAT box transcription factor/nuclear factor I-like recognition motif, and a guanine-rich G box.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. Improved oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:382–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Inducible, receptor-dependent protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at recognition sites for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16478–16482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr The DNA recognition site for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17221–17224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Whitlock J. P., Jr 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated change in CYP1A1 chromatin structure occurs independently of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5733–5737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Whitlock J. P., Jr 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible, Ah receptor-mediated bending of enhancer DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5718–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Jones K. W., Whitlock J. P., Jr Activation of transcription as a general mechanism of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin action. Mol Carcinog. 1989;1(4):216–221. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Wu L., Denison M. S., Whitlock J. P., Jr Organization and function of a dioxin-responsive enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9676–9681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Characterization of xenobiotic responsive elements upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene: a similarity to glucocorticoid regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4179–4191. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A DNA-binding factor specific for xenobiotic responsive elements of P-450c gene exists as a cryptic form in cytoplasm: its possible translocation to nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5859–5863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. Benzo[alpha]pyrene metabolism, activation and carcinogenesis: role and regulation of mixed-function oxidases and related enzymes. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1107–1166. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Frisque R. J., Gluzman Y. Identification of a promoter component involved in positioning the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding C. R., Temperley S. M., Fisher F. Multiple transcription factors interact with the adenovirus-2 EII-late promoter: evidence for a novel CCAAT recognition factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7761–7780. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S., Nebert D. W. Comparison of the flanking regions and introns of the mouse 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5040–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Autoregulation plus upstream positive and negative control regions associated with transcriptional activation of the mouse P1(450) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7269–7288. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O., Andersen R. D., Birren B. W., Sander F., Negishi M., Nebert D. W. Mutations affecting the regulation of transcription of the cytochrome P1-450 gene in the mouse Hepa-1 cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1790–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapgood J., Cuthill S., Denis M., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Specific protein-DNA interactions at a xenobiotic-responsive element: copurification of dioxin receptor and DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst M. A., Jones K. W., Whitlock J. P., Jr Activation of cytochrome P450IA1 gene expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild-type and high-activity variant mouse hepatoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(1):40–46. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Induction of mRNA specific for cytochrome P1-450 in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10390–10394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Regulation of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5400–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. A method for mapping intranuclear protein-DNA interactions and its application to a nuclease hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Durrin L. K., Galeazzi D. R., Whitlock J. P., Jr Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression: analysis of a dioxin-responsive enhancer system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2802–2806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Galeazzi D. R., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression by dioxin. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1499–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.3856321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D. Human health effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs). Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Israel D., Whitlock J. P., Jr Biochemical and genetic analysis of variant mouse hepatoma cells defective in the induction of benzo(a)pyrene-metabolizing enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3523–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhold L. A., Gonzalez F. J., Jaiswal A. K., Nebert D. W. Dioxin-inducible enhancer region upstream from the mouse P(1)450 gene and interaction with a heterologous SV40 promoter. DNA. 1986 Oct;5(5):403–411. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhold L. A., Shirayoshi Y., Ozato K., Jones J. E., Nebert D. W. Regulation of mouse CYP1A1 gene expression by dioxin: requirement of two cis-acting elements during induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2378–2386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S. H. Comparative toxicology and mechanism of action of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:371–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen E. S., Whitlock J. P., Jr The potential role of DNA methylation in the response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17754–17758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr Genetic and molecular aspects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:251–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida A., Sogawa K., Yasumoto K. I., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A novel cis-acting DNA element required for a high level of inducible expression of the rat P-450c gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1470–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:329–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]