Abstract
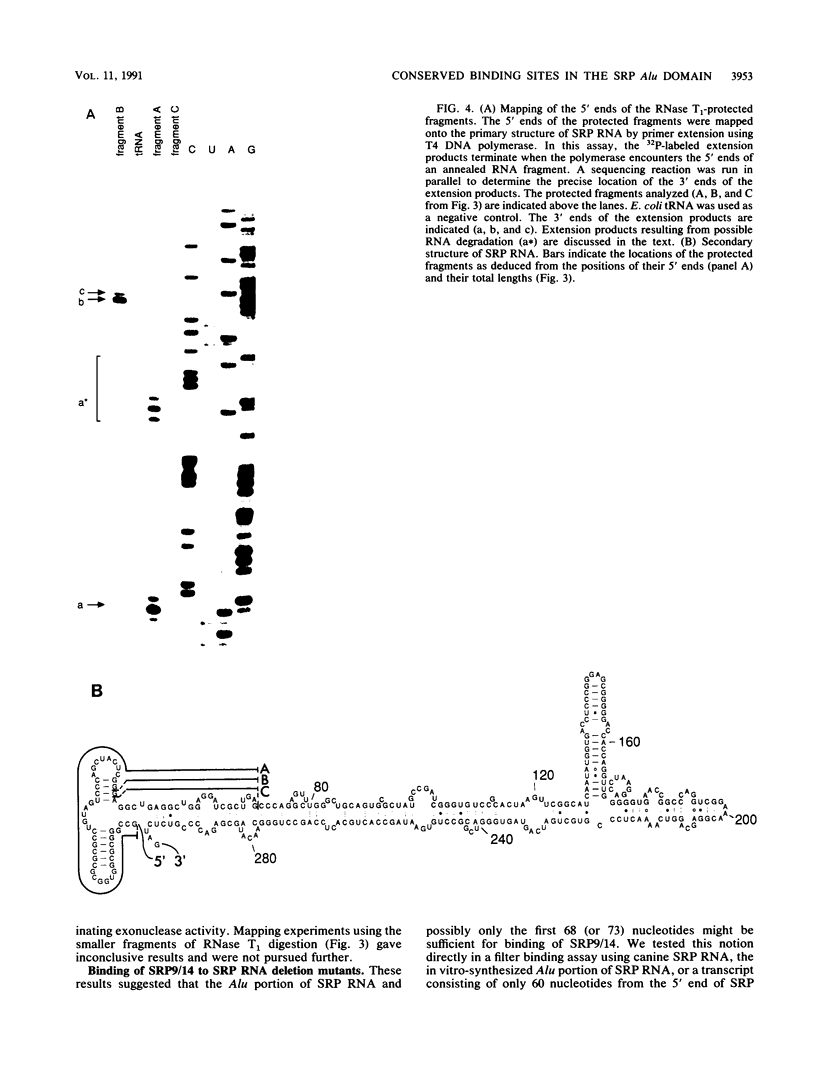
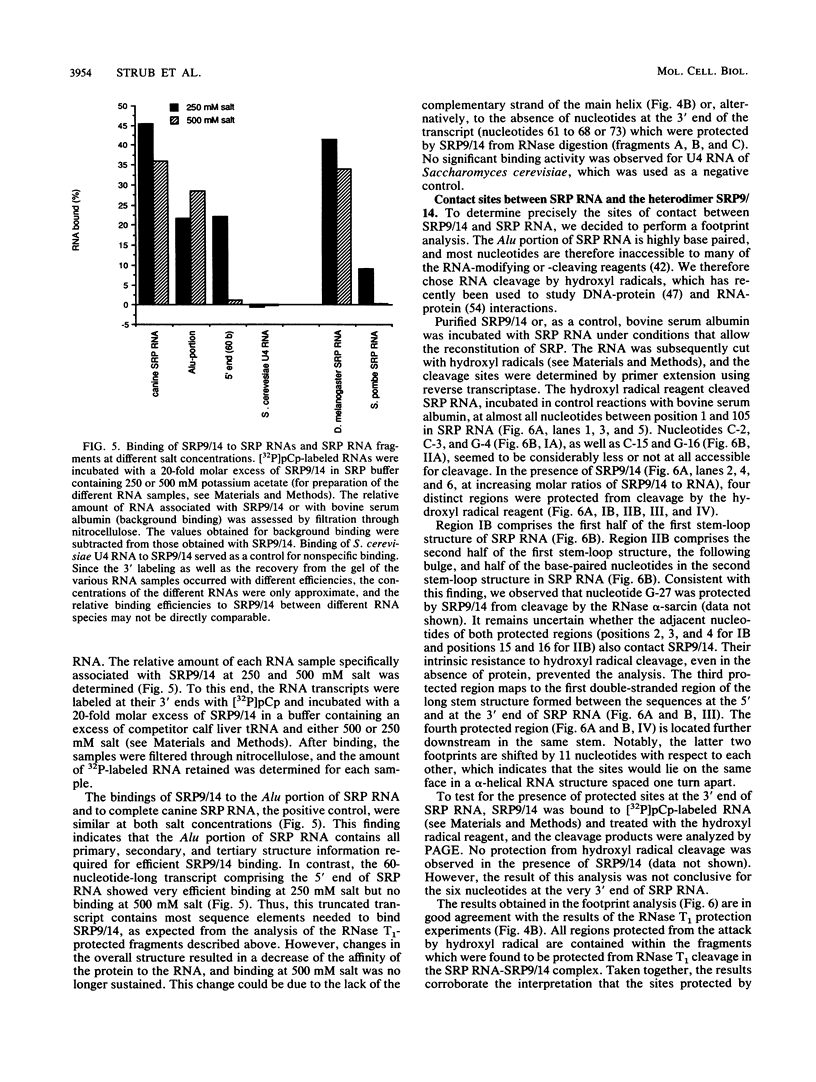
The mammalian signal recognition particle (SRP) is a small cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein required for the cotranslational targeting of secretory proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The heterodimeric protein subunit SRP9/14 was previously shown to be essential for SRP to cause pausing in the elongation of secretory protein translation. RNase protection and filter binding experiments have shown that binding of SRP9/14 to SRP RNA depends solely on sequences located in a domain of SRP RNA that is strongly homologous to the Alu family of repetitive DNA sequences. In addition, the use of hydroxyl radicals, as RNA-cleaving reagents, has revealed four distinct regions in this domain that are in close contact with SRP9/14. Surprisingly, the nucleotide sequence in one of these contact sites, predicted to be mostly single stranded, was found to be extremely conserved in SRP RNAs of evolutionarily distant organisms ranging from eubacteria and archaebacteria to yeasts and higher eucaryotic cells. This finding suggests that SRP9/14 homologs may also exist in these organisms, where they possibly contribute to the regulation of protein synthesis similar to that observed for mammalian SRP in vitro.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya Y., Nakano A., Ito K., Mori M. Isolation of a yeast gene, SRH1, that encodes a homologue of the 54K subunit of mammalian signal recognition particle. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):457–463. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Sequence and factor requirements for faithful in vitro transcription of human 7SL DNA. Gene. 1990 Feb 14;86(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90282-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Liao X., Holm K., Porter G., Wise J. A. Identification of an essential Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA homologous to the 7SL component of signal recognition particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1580–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos N., Palau J., Zwieb C. Diversity of 7 SL RNA from the signal recognition particle of maize endosperm. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1573–1588. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felici F., Cesareni G., Hughes J. M. The most abundant small cytoplasmic RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has an important function required for normal cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3260–3268. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G., Walter P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Detection in the microsomal membrane of a receptor for the signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):463–469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundelfinger E. D., Di Carlo M., Zopf D., Melli M. Structure and evolution of the 7SL RNA component of the signal recognition particle. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2325–2332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas B., Klanner A., Ramm K., Sänger H. L. The 7S RNA from tomato leaf tissue resembles a signal recognition particle RNA and exhibits a remarkable sequence complementarity to viroids. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4063–4074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe contain a homologue to the 54-kD subunit of the signal recognition particle that in S. cerevisiae is essential for growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3223–3230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P., Merkel V. L. Isolation and characterization of the 7S RNA gene from Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4261–4266. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4261-4266.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P. Structure of the archaebacterial 7S RNA molecule. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 May;221(3):315–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00259394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya Y., Kato K., Hayashizaki Y., Himeno S., Tarui S., Matsubara K. Revision of consensus sequence of human Alu repeats--a review. Gene. 1987;53(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert H., Gladen A., Geisler M., Benecke B. J. Differential regulation of transcription of human 7 S K and 7 S L RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11511–11515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Walter P., Johnson A. E. Photocrosslinking of the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin to the 54-kilodalton polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8604–8608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Wiedmann M., Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):634–636. doi: 10.1038/320634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Zwieb C. SRP-RNA sequence alignment and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):209–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Cech T. R. Defining the inside and outside of a catalytic RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):276–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2501870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Y., Reddy R., Henning D., Epstein P., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of 7 S RNA. Homology to Alu DNA and La 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5136–5142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B., Haeuptle M. T. Signal recognition particle arrests elongation of nascent secretory and membrane proteins at multiple sites in a transient manner. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1680–1684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshallsay C., Prehn S., Zwieb C. cDNA cloning of the wheat germ SRP 7S RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1771–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A., Goebel W. Characterization of the 7S RNA and its gene from halobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6969–6979. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Siegel V., Hansen W., Walter P. Small ribonucleoproteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica homologous to signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Strub K., Walter P. Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Dehoux P., Tollervey D. 7SL RNA from Schizosaccharomyces pombe is encoded by a single copy essential gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):231–237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Lingelbach K., Gausepohl H., Dobberstein B. The 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle contains a methionine-rich RNA binding domain. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1793–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoulica E., Krause E., Meese K., Dobberstein B. Disassembly and domain structure of the proteins in the signal-recognition particle. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Mar 16;163(3):519–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Each of the activities of signal recognition particle (SRP) is contained within a distinct domain: analysis of biochemical mutants of SRP. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90529-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Elongation arrest is not a prerequisite for secretory protein translocation across the microsomal membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1913–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Moazed D., Noller H. F. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Isolation of a cDNA clone of the 14-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle by cross-hybridization of differently primed polymerase chain reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9747–9751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Toschka H. Y., Specht T., Erdmann V. A. Common structural features between eukaryotic 7SL RNAs, eubacterial 4.5S RNA and scRNA and archaebacterial 7S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7740–7740. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Vogel D. W., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. The Bacillus subtilis scRNA is related to the 4.5S RNA from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2719–2719. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Murphy S., Melli M. Human 7SL RNA consists of a 140 nucleotide middle-repetitive sequence inserted in an alu sequence. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Tschudi C. Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):171–172. doi: 10.1038/312171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Disassembly and reconstitution of signal recognition particle. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. D., Padgett R. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting" of RNA: application to pre-mRNA splicing complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7795–7799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2617–2622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Johnson A. E., Walter P. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an RNA binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]