Abstract
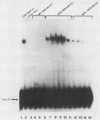
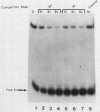
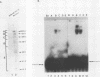
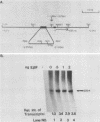
Previous studies in our laboratory have characterized a 174-base-pair (bp) enhancer sequence in the rat ribosomal DNA spacer region that exhibits all of the characteristics of a polymerase (Pol) II enhancer. Further studies showed that at least half of the enhancer activity resides in a 37-bp motif (E1) within the 174-bp spacer sequence that is located between positions -2.183 and -2.219 kilobase pairs upstream of the initiation site. To identify the factor(s) that binds specifically to the 37-bp enhancer domain, we fractionated whole-cell extract from rat adenocarcinoma ascites cells by chromatography on a series of columns, including an oligodeoxynucleotide affinity column. The final preparation contained two polypeptides of molecular weights 79,400 and 89,100 and was completely devoid of RNA Pol I activity. Electrophoretic mobility shift analysis showed that the polypeptides in the purified preparation (designated E1BF) interacted with both the enhancer element and the core promoter. To determine whether each polypeptide can separately bind to the core promoter and the enhancer, the individual components were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, renatured, and subjected to gel retardation analysis. This experiment demonstrated that both polypeptides interacted with the two cis-acting sequences. The specificity of the binding was demonstrated by competition with unlabeled 37-bp and core promoter fragments and lack of competition with nonspecific DNAs in the mobility shift assay. The 37-bp enhancer as well as the downstream sequence of the core promoter were protected by E1BF in the DNase I footprinting assay. Addition of E1BF to limiting amounts of fraction DE-B, which contains all factors essential for Pol I-directed transcription, resulted in three- to fourfold stimulation of ribosomal DNA transcription. Comparison of molecular weights and footprinting profiles did not reveal any relationship between E1BF and other Pol I trans-acting factors.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Transcriptional role for the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2766–2773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription in Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):813–827. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Chao W., Jacob S. T. An enhancer element in the far upstream spacer region of rat ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11616–11622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Jacob S. T. A cis-acting sequence within the rat ribosomal DNA enhancer region can modulate RNA polymerase II-directed transcription of the metallothionein I gene in vitro. DNA. 1989 Jun;8(5):311–320. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. Purification and characterization of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3496–3509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Jacob S. T. A 37-base pair element in the far upstream spacer region can enhance transcription of rat rDNA in vitro and can bind to the core promoter-binding factor(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Webb M. L., Jacob S. T. Interaction of a positive regulatory factor(s) with a 106-base pair upstream region controls transcription of metallothionein-I gene in the liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Steele W. J., Busch H. Turnover of 45 S RNA of regenerating liver and Walker tumor. Cancer Res. 1967 Jan;27(1):52–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T. Transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA gene. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Apr;70(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00233800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl R. N., Jacob S. T. Accurate initiation of rat ribosomal RNA gene transcription using a fractionated nuclear extract from normal liver and a hepatoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1059–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl R. N., Rothblum L. I., Jacob S. T. A purified fraction containing RNA polymerase I that can accurately transcribe rat ribosomal RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6672–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers function when inserted inside the gene they enhance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8999–9009. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Protein-nucleotide contacts in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchelson K., Moss T. The enhancement of ribosomal transcription by the recycling of RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9577–9596. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. L., Mealey-Cavender J. F., Jacob S. T. Glucocorticoid-induced stimulation of ribosomal gene transcription in rat hepatoma cells is mediated by modification of RNA polymerase I or an associated factor. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1861–1868. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Purification and characterization of a high-mobility-group-like DNA-binding protein that stimulates rRNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3406–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]