Abstract
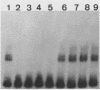
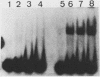
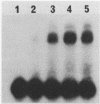
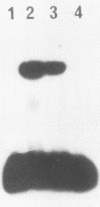
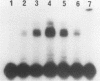
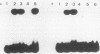
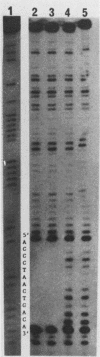
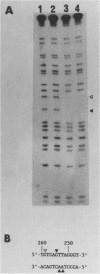
DNA damage-inducible responses in mammalian cells tend to lack specificity and can be activated by any one of a number of damaging agents. Although a number of different induced proteins have been described, their involvement in DNA processing and transcriptional control remains unresolved. We describe the appearance of a previously unreported, specific DNA-binding protein in nuclei from human cells exposed to ionizing radiation, which was not detected in nuclear extracts from unperturbed cells. The distal part of the simian virus 40 enhancer (without the AP-1 site) and oligonucleotide sequences derived from that sequence were used in binding studies. The appearance of this activity was dose dependent and transient, reaching a maximum at 1 h postirradiation and disappearing from nuclei by 9 h. This protein was induced in cells by a mechanism not requiring de novo protein synthesis, and the response was specific for ionizing radiation and radiomimetic agents; neither UV nor heat shock invoked a response. The DNA-binding protein was present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells, apparently being translocated to the nucleus only after radiation exposure. Southwestern (DNA-protein) analysis demonstrated that the nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins were approximately the same size, 43,000 daltons. The protected DNA-binding motif, using the distal fragment of the simian virus 40 enhancer as the substrate, was shown by DNase I footprint analysis to be pTGTCAGTTAGGGTACAGTCAATCCCAp. This was confirmed by dimethyl sulfate footprinting.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilera R. J., Akira S., Okazaki K., Sakano H. A pre-B cell nuclear protein that specifically interacts with the immunoglobulin V-J recombination sequences. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90578-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothman D. A., Bouvard I., Hughes E. N. Identification and characterization of X-ray-induced proteins in human cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2871–2878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1989 May;217(3):173–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer P. M., Greggio N. A., Metherall J. E., Summers W. C. UV-induced DNA-binding proteins in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1163–1167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Mallick U., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J. Genetic changes in mammalian cells reminiscent of an SOS response. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00291392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Cytoplasmic anchoring proteins and the control of nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):949–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90747-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Schuetz T. J., Larin Z. Heat-inducible human factor that binds to a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Petit-Frère C., Broughton B. C., Lehmann A. R., Green M. H. Inhibition of DNA replication by ionizing radiation is mediated by a trans-acting factor. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Aug;56(2):125–130. doi: 10.1080/09553008914551271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overberg R., Chandrasena G., Rupert C. S. Radiation-induced recovery processes in cultured marsupial cells. Mutat Res. 1988 Sep;194(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. B. Inhibition of mammalian cell DNA synthesis by ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1986 May;49(5):771–781. doi: 10.1080/09553008514552981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Thurston S. J. A negative regulatory element with properties similar to those of enhancers is contained within an Alu sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):355–364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Dasgupta U. B., Summers W. C. Error-prone mutagenesis detected in mammalian cells by a shuttle vector containing the supF gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2227–2230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbauch P., Sulica A., Givol D. General method for the detection of cells producing antibodies against haptens and proteins. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):68–69. doi: 10.1038/227068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez J. M., Lindquist S. hsp70: nuclear concentration during environmental stress and cytoplasmic storage during recovery. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendler I., Grossbach U. A blotting procedure which preserves specific protein-DNA interactions. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90407-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S., Afzal V., Wiencke J. K., Olivieri G., Michaeli A. Human lymphocytes exposed to low doses of ionizing radiations become refractory to high doses of radiation as well as to chemical mutagens that induce double-strand breaks in DNA. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Jan;53(1):39–47. doi: 10.1080/09553008814550401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]