Abstract
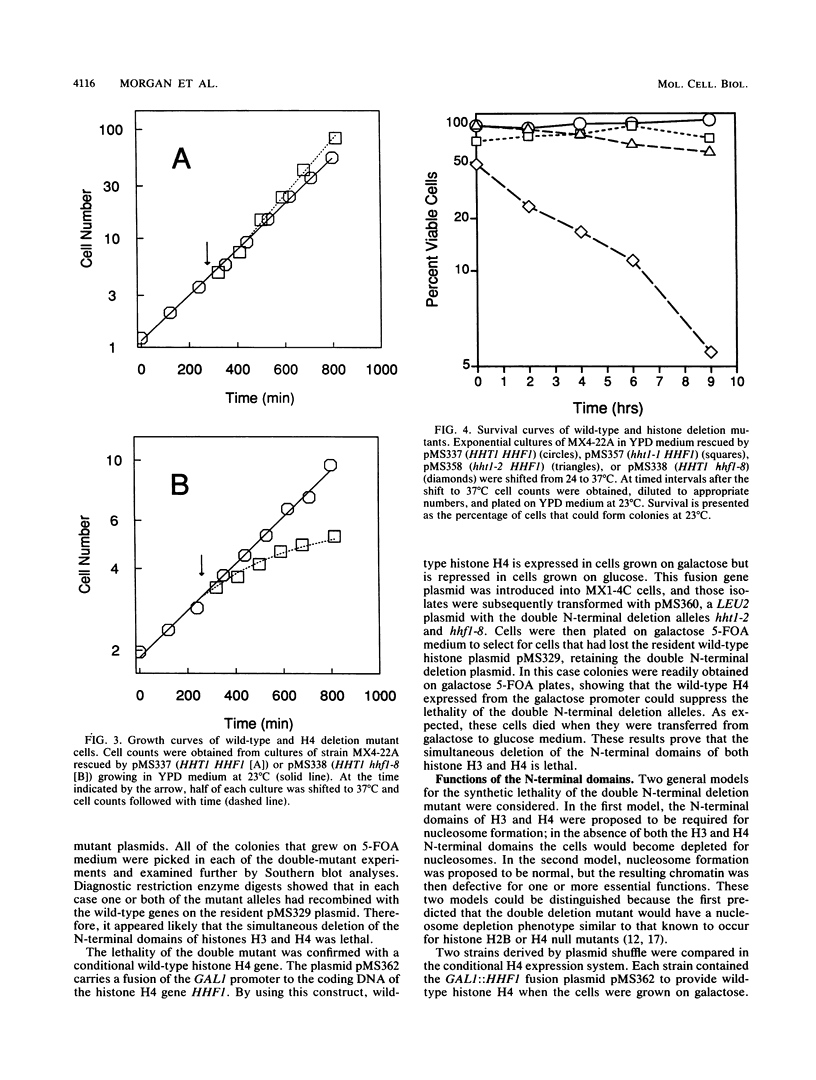
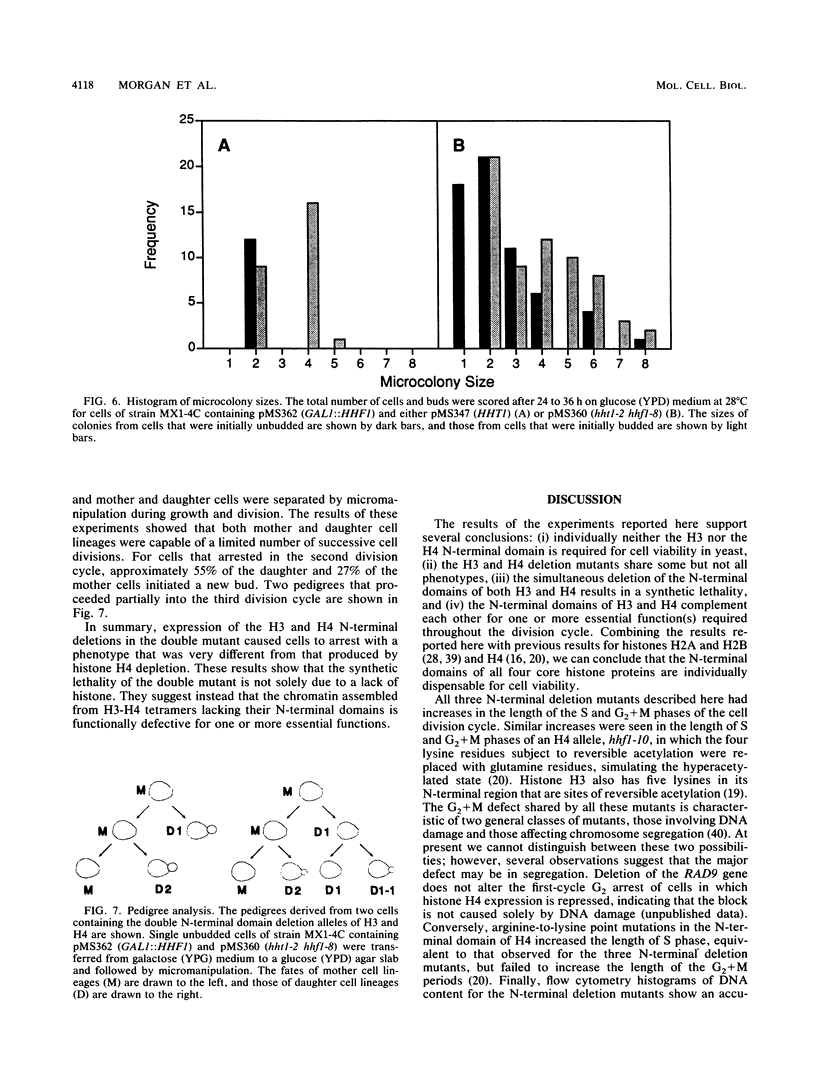
The N-terminal domains of the histones H3 and H4 are highly conserved throughout evolution. Mutant alleles deleted for these N-terminal domains were constructed in vitro and examined for function in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cells containing a single deletion allele of either histone H3 or histone H4 were viable. Deletion of the N-terminal domain of histone H4 caused cells to become sterile and temperature sensitive for growth. The normal cell cycle progression of these cells was also altered, as revealed by a major delay in progression through the G2 + M periods. Deletion of the N-terminal domain of histone H3 had only minor effects on mating and the temperature-sensitive growth of mutant cells. However, like the H4 mutant, the H3 mutants had a significant delay in completing the G2 + M periods of the division cycle. Double mutants containing N-terminal domain deletions of both histone H3 and histone H4 were inviable. The phenotypes of cells subject to this synthetic lethality suggest that the N-terminal domains are required for functions essential throughout the cell division cycle and provide genetic evidence that histones are randomly distributed during chromosome replication.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Harborne N., Rau D. C., Gould H. Participation of core histone "tails" in the stabilization of the chromatin solenoid. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):285–297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Dong F., van Holde K. E. Use of selectively trypsinized nucleosome core particles to analyze the role of the histone "tails" in the stabilization of the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton A. H., Stirling V. B., Smith M. M. Analysis of DNA sequences homologous with the ARS core consensus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1987 Jun;3(2):107–115. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm L., Briand G., Sautière P., Crane-Robinson C. Proteolytic digestion studies of chromatin core-histone structure. Identification of the limit peptides of histones H3 and H4. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahal S. S., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Acetylation of histone H4 and its role in chromatin structure and function. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):76–79. doi: 10.1038/287076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinault A. C., Carbon J. Overlap hybridization screening: isolation and characterization of overlapping DNA fragments surrounding the leu2 gene on yeast chromosome III. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corliss D. A., White W. E., Jr Fluorescence of yeast vitally stained with ethidium bromide and propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Jan;29(1):45–48. doi: 10.1177/29.1.6162881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebralidse K. K., Grachev S. A., Mirzabekov A. D. A highly basic histone H4 domain bound to the sharply bent region of nucleosomal DNA. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):365–367. doi: 10.1038/331365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. M., Grigera P. R., Bergmann I. E., Zibert A., Multhaup G., Beck E. Foot-and-mouth disease virus protease 3C induces specific proteolytic cleavage of host cell histone H3. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):748–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.748-756.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Chang M., Kim U. J., Grunstein M. Histone H2B repression causes cell-cycle-specific arrest in yeast: effects on chromosomal segregation, replication, and transcription. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Kayne P. S., Kahn E. S., Grunstein M. Genetic evidence for an interaction between SIR3 and histone H4 in the repression of the silent mating loci in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6286–6290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. J., Han M., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Effects of histone H4 depletion on the cell cycle and transcription of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2211–2219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Tatchell K. Chromatin core particle unfolding induced by tryptic cleavage of histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):2039–2055. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin K. W., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Isolation and characterization of acetylated histones H3 and H4 and their assembly into nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19839–19847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Marvin K. W., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Nucleosome linking number change controlled by acetylation of histones H3 and H4. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19848–19852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva R., Bazett-Jones D. P., Locklear L., Dixon G. H. Histone hyperacetylation can induce unfolding of the nucleosome core particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2739–2747. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. C., Szostak J. W. Point mutations in the yeast histone H4 gene prevent silencing of the silent mating type locus HML. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4932–4934. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N. L., Smith R. M., Rill R. L. The action of chymotrypsin on nucleosome cores. Histone products and conformational effects of limited digestion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12375–12383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster T., Han M., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H2A and H2B amino termini have interchangeable functions. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Andrésson O. S. DNA sequences of yeast H3 and H4 histone genes from two non-allelic gene sets encode identical H3 and H4 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):663–690. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Murray K. Yeast H3 and H4 histone messenger RNAs are transcribed from two non-allelic gene sets. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):641–661. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Stirling V. B. Histone H3 and H4 gene deletions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):557–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Chalkley R. The structure and assembly of active chromatin. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90074-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar M., Marquardt O. Foot-and-mouth disease virus protease 3C inhibits cellular transcription and mediates cleavage of histone H3. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):364–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90090-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J. W., Rykowski M., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H2B containing large amino terminus deletions can function in vivo. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Stein A. Folding of DNA by histones which lack their NH2-terminal regions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3857–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Panusz H. T., Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M. Histones and their modifications. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(2):201–263. doi: 10.3109/10409238609083735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]