Abstract
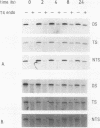
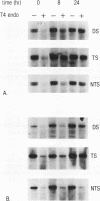
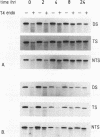
We have measured the removal of UV-induced pyrimidine dimers from DNA fragments of the adenosine deaminase (ADA) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) genes in primary normal human and xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C (XP-C) cells. Using strand-specific probes, we show that in normal cells, preferential repair of the 5' part of the ADA gene is due to the rapid and efficient repair of the transcribed strand. Within 8 h after irradiation with UV at 10 J m-2, 70% of the pyrimidine dimers in this strand are removed. The nontranscribed strand is repaired at a much slower rate, with 30% dimers removed after 8 h. Repair of the transcribed strand in XP-C cells occurs at a rate indistinguishable from that in normal cells, but the nontranscribed strand is not repaired significantly in these cells. Similar results were obtained for the DHFR gene. In the 3' part of the ADA gene, however, both normal and XP-C cells perform fast and efficient repair of either strand, which is likely to be caused by the presence of transcription units on both strands. The factor defective in XP-C cells is apparently involved in the processing of DNA damage in inactive parts of the genome, including nontranscribed strands of active genes. These findings have important implications for the understanding of the mechanism of UV-induced excision repair and mutagenesis in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkvens T. M., Gerritsen E. J., Oldenburg M., Breukel C., Wijnen J. T., van Ormondt H., Vossen J. M., van der Eb A. J., Meera Khan P. Severe combined immune deficiency due to a homozygous 3.2-kb deletion spanning the promoter and first exon of the adenosine deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9365–9378. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Göbel U. B., Köster H. New bacteriophage vectors for the large scale production of single stranded insert DNA. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1989 Aug-Sep;19(2-3):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(89)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Göbel U. B., Köster H. Preparation of single stranded insert DNA free of vector sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):810–810. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Okumoto D. S., Ho L., Hanawalt P. C. Characterization of a DNA repair domain containing the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16666–16672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in an active gene: removal of pyrimidine dimers from the DHFR gene of CHO cells is much more efficient than in the genome overall. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan G. L., Little J. B. Resistance of plateau-phase human normal and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts to the cytotoxic effect of ultraviolet light. Mutat Res. 1979 Dec;63(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Beratis N. G., Martiniuk F. Adenosine deaminase. Alterations in activity and isozymes during growth of normal and genetically deficient fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Nov;117(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho L., Bohr V. A., Hanawalt P. C. Demethylation enhances removal of pyrimidine dimers from the overall genome and from specific DNA sequences in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1594–1603. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. J., Barsalou L. S., Hanawalt P. C. Selective repair of specific chromatin domains in UV-irradiated cells from xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C. Mutat Res. 1990 May;235(3):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90071-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. J., Elking C. F. Biological significance of domain-oriented DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):844–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. J., Hull D. R. The rate of removal of pyrimidine dimers in quiescent cultures of normal human and xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Mutat Res. 1984 Jul-Aug;132(1-2):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Lee M. M., Scotto J. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Cutaneous, ocular, and neurologic abnormalities in 830 published cases. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Feb;123(2):241–250. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattier D. L., States J. C., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Cell type-specific transcriptional regulation of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1061–1076. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leadon S. A., Snowden M. M. Differential repair of DNA damage in the human metallothionein gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5331–5338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Wilson B., Fortier C. The limits of the DNase I-sensitive domain of the human apolipoprotein B gene coincide with the locations of chromosomal anchorage loops and define the 5' and 3' boundaries of the gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21196–21204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loc P. V., Strätling W. H. The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme gene co-map with the boundaries of the chromatin domain. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne L. V., Lehmann A. R. Failure of RNA synthesis to recover after UV irradiation: an early defect in cells from individuals with Cockayne's syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum. Cancer Res. 1982 Apr;42(4):1473–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Hanawalt P. C. Induction of the Escherichia coli lactose operon selectively increases repair of its transcribed DNA strand. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):95–98. doi: 10.1038/342095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Spivak G., Hanawalt P. C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Haipek C. A., Clarkson J. M. (6-4)Photoproducts are removed from the DNA of UV-irradiated mammalian cells more efficiently than cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. Mutat Res. 1985 Jul;143(3):109–112. doi: 10.1016/s0165-7992(85)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullenders L. H., van Kesteren A. C., Bussmann C. J., van Zeeland A. A., Natarajan A. T. Preferential repair of nuclear matrix associated DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C. Mutat Res. 1984 Oct;141(2):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(84)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Yamashita K., Sekiguchi M. Purification and characterization of normal and mutant forms of T4 endonuclease V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2556–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumoto D. S., Bohr V. A. DNA repair in the metallothionein gene increases with transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10021–10030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Kraemer K. H., Lutzner M. A., Festoff B. W., Coon H. G. Xeroderma pigmentosum. An inherited diseases with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):221–248. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief A., Winter D. M., Strätling W. H., Sippel A. E. A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):343–345. doi: 10.1038/341343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi K., Toyoda M., Hashimoto T., Furuyama J., Kurihara T., Inoue M., Takebe H. Differential hypersensitivity of xeroderma pigmentosum lymphoblastoid cell lines to ultraviolet light mutagenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Jan;8(1):53–57. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
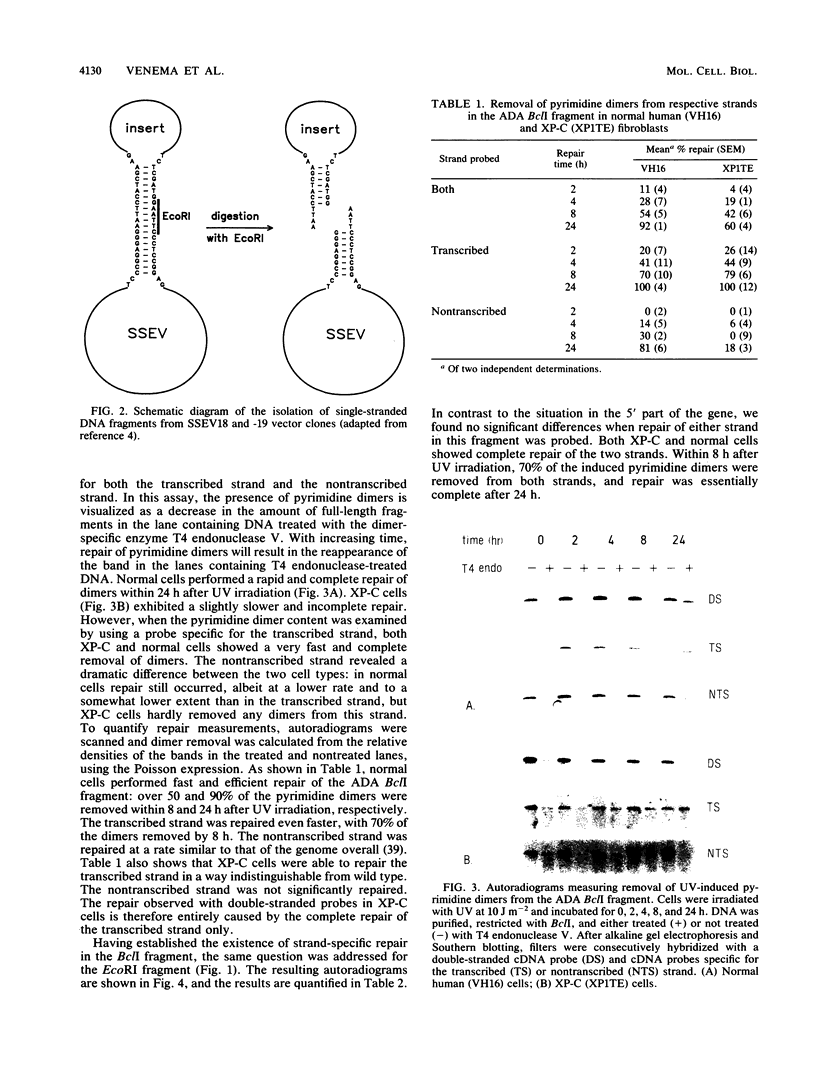
- Terleth C., Schenk P., Poot R., Brouwer J., van de Putte P. Differential repair of UV damage in rad mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a possible function of G2 arrest upon UV irradiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4678–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., van Hoffen A., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mullenders L. H. The residual repair capacity of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C fibroblasts is highly specific for transcriptionally active DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):443–448. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling H., Van Rooijen M. L., Groen N. A., Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W., Lohman P. H., van Zeeland A. A. DNA strand specificity for UV-induced mutations in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling H., Venema J., van Rooyen M. L., van Hoffen A., Menichini P., Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W., Mullenders L. H., van Zeeland A. A. Strand specificity for UV-induced DNA repair and mutations in the Chinese hamster HPRT gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2411–2415. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Kaplan D. J., States J. C., Akeson A. L., Perme C. M., Bilyk I. J., Vaughn A. J., Lattier D. L., Hutton J. J. Complete sequence and structure of the gene for human adenosine deaminase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8234–8244. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will C. L., Dolnick B. J. 5-Fluorouracil augmentation of dihydrofolate reductase gene transcripts containing intervening sequences in methotrexate-resistant KB cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;29(6):643–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. K., Masters J. N., Attardi G. Human dihydrofolate reductase gene organization. Extensive conservation of the G + C-rich 5' non-coding sequence and strong intron size divergence from homologous mammalian genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):169–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Ubaidi M. R., Ramamurthy V., Maa M. C., Ingolia D. E., Chinsky J. M., Martin B. D., Kellems R. E. Structural and functional analysis of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):476–485. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeeland A. A., Vrieling H., van Rooijen M. L., Venema J., Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W., Mullenders L. H., Lohman P. H. Influence of DNA excision repair on UV-induced mutation spectra in Chinese hamster cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;340A:249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]