Abstract
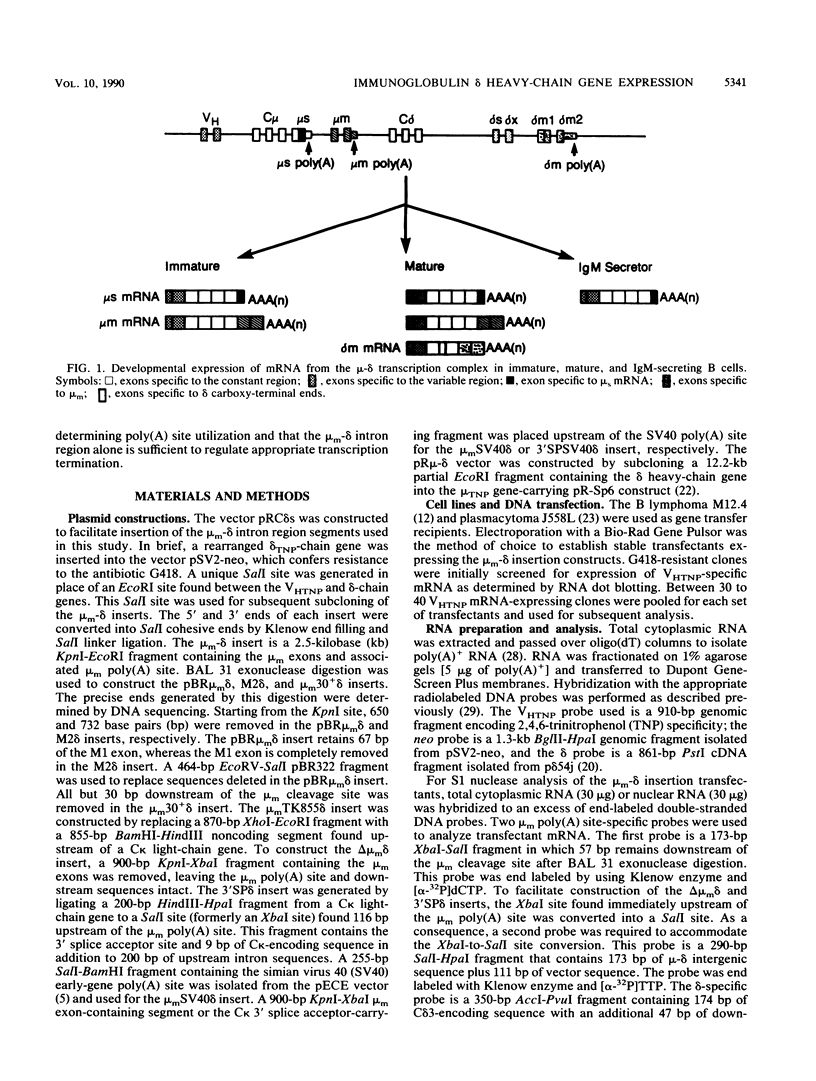
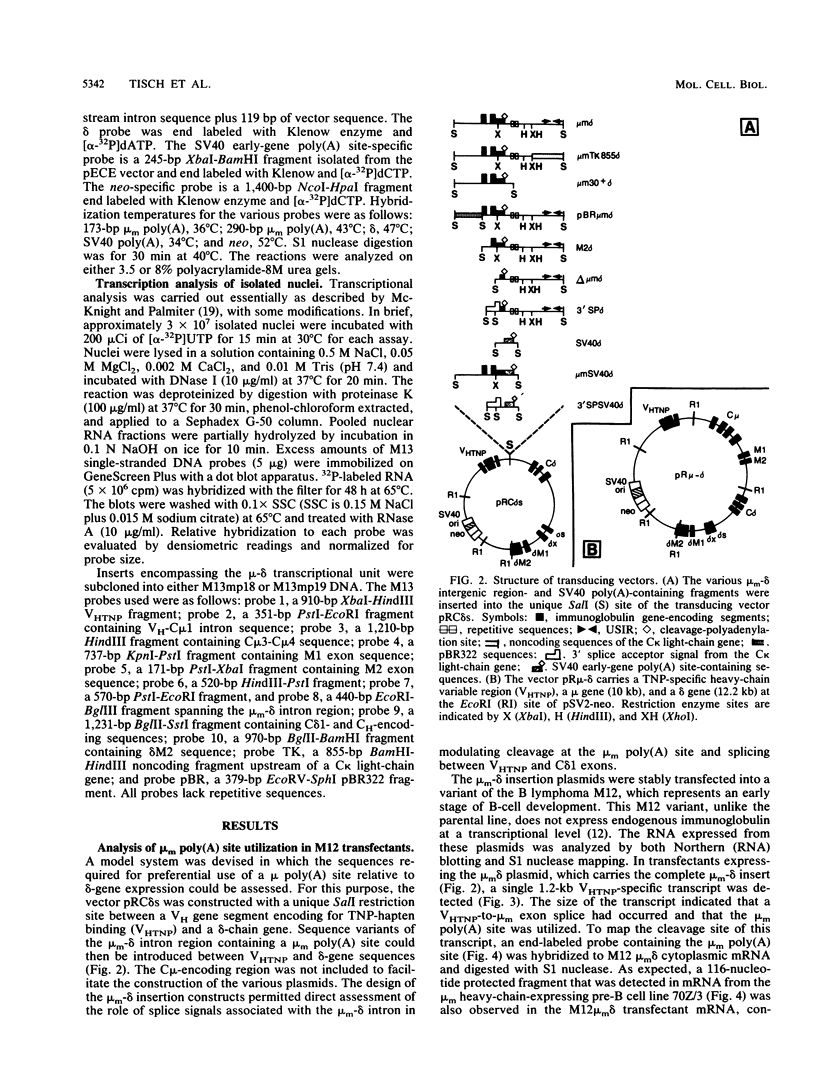
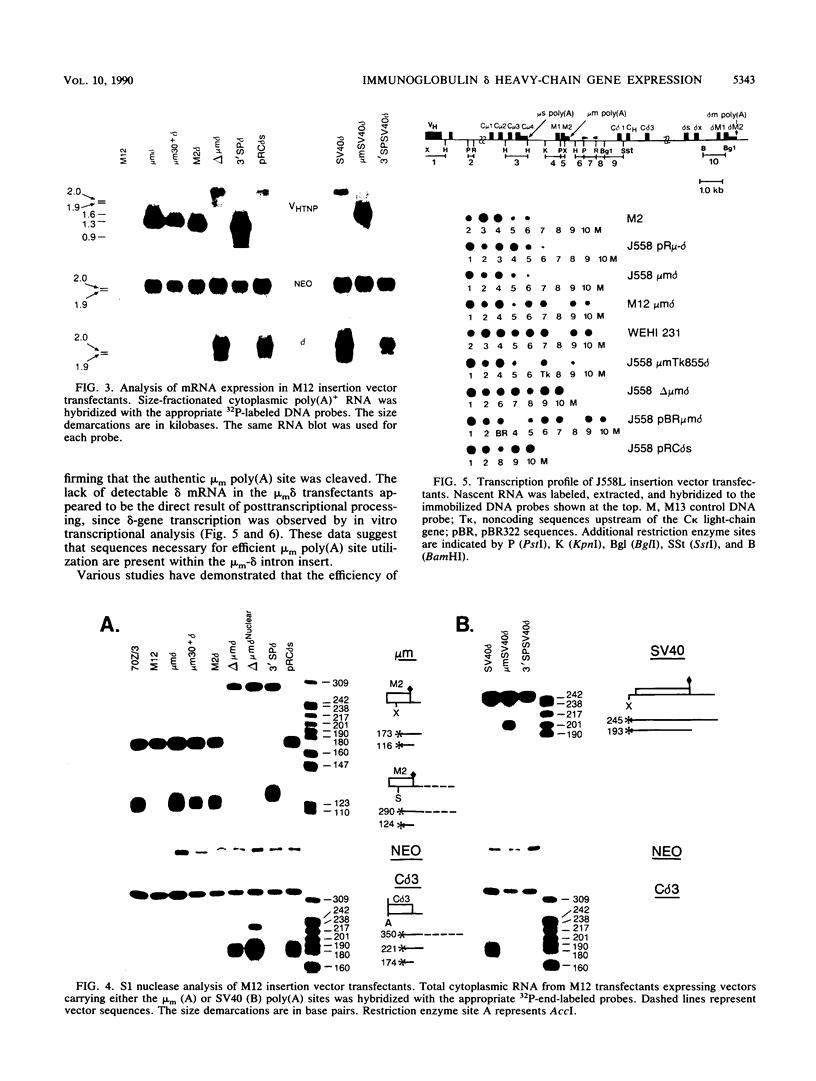
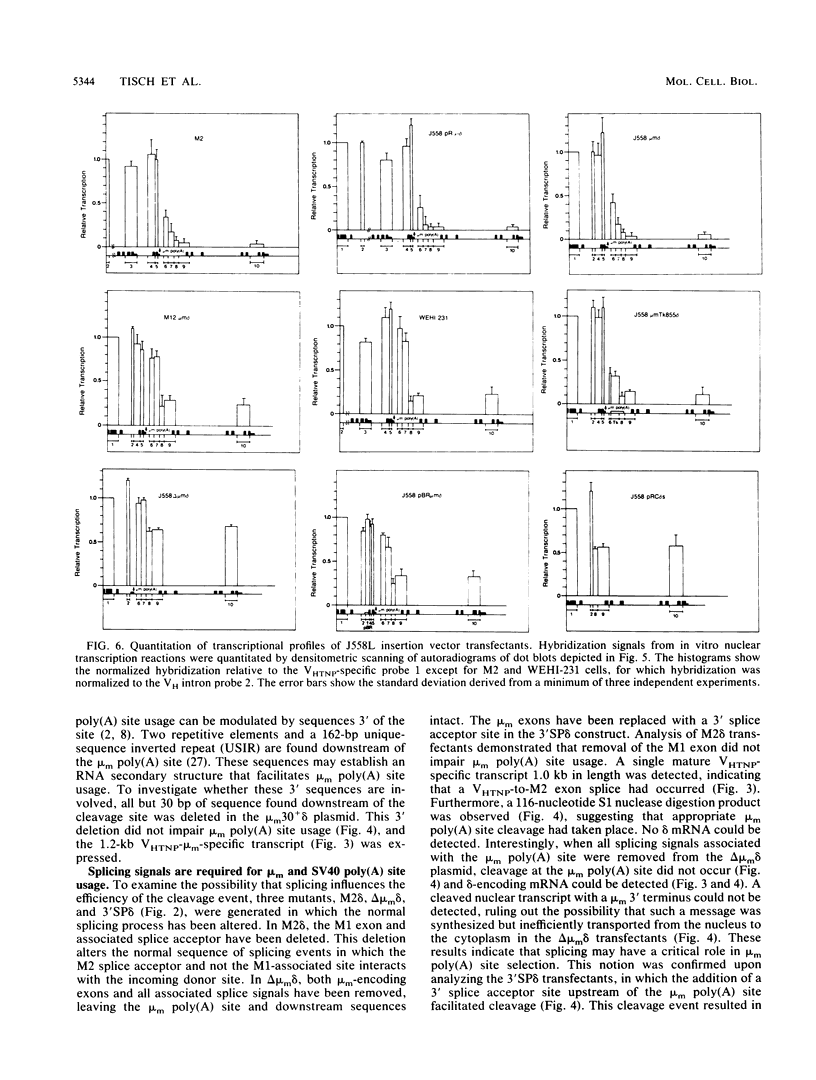
The mu and delta immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes comprise a complex transcriptional unit in which a single mRNA precursor gives rise to mu- and delta-specific transcripts. During the immature B-cell stage, posttranscriptional processing events involving alternate splicing and cleavage-polyadenylation site selection give rise to mu- but not delta-encoding transcripts. In terminally differentiated B cells, delta mRNA is not synthesized because of a transcription termination event occurring upstream of the delta-gene locus. In an attempt to gain insight into the respective contributions of alternate splicing and cleavage-polyadenylation in the control of delta mRNA synthesis, we have constructed a set of plasmids in which membrane mu (mu m)-delta intergenic sequences containing the mu m poly(A) site but differing in splicing capacity were inserted in between a VH and delta gene. The mu m-delta insertion vectors were transfected into a B lymphoma line representative of an immature stage, and proximal mu m poly(A) site usage and delta mRNA synthesis were assessed. To determine unequivocally whether the mu m-delta intergenic region can regulate termination, the insertion vectors were also transfected into a B myeloma line, and transcription through the region was measured. In immature B-cell transfectants, splicing site selection was found to have a key role in determining poly(A) site utilization and concomitant delta mRNA expression. Mature delta mRNA synthesis was blocked by an upstream cleavage-polyadenylation event only when the proximal poly(A) site was associated with appropriate splicing signals. Furthermore, in vitro transcription assays revealed that the mu m-delta intergenic region is sufficient to regulate transcription termination within a 1,2430-base-pair region containing the mu m poly(A) site in myeloma transfectants. The mu m-delta insertion vectors provide an excellent model system for studying the regulatory aspects of this transcription termination event.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G., Nevins J. R. Splice site selection dominates over poly(A) site choice in RNA production from complex adenovirus transcription units. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2107–2116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A CCAAT box sequence in the adenovirus major late promoter functions as part of an RNA polymerase II termination signal. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D., Leder P. Role of an RNA cleavage/poly(A) addition site in the production of membrane-bound and secreted IgM mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8658–8662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J., Shenk T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination within the E1A gene of adenovirus induced by insertion of the mouse beta-major globin terminator element. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Guise J. W., McDevitt M. A., Tucker P. W., Nevins J. R. Relative position and strengths of poly(A) sites as well as transcription termination are critical to membrane versus secreted mu-chain expression during B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):471–481. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guise J. W., Lim P. L., Yuan D., Tucker P. W. Alternative expression of secreted and membrane forms of immunoglobulin mu-chain is regulated by transcriptional termination in stable plasmacytoma transfectants. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3988–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of immunoglobulin mRNA production during B lymphocyte development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5431–5447. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. R., Liu C. P., Newell N., Ward R. B., Tucker P. W., Strober S., Blattner F. Simultaneous expression of immunoglobulin mu and delta heavy chains by a cloned B-cell lymphoma: a single copy of the VH gene is shared by two adjacent CH genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2996–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskov R., Kim J. K., Woods V. L., McKeever P. E., Asofsky R. Membrane immunoglobulins of spontaneous B lymphomas of aged BALB/c mice. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):462–468. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R., Kuwabara M. D., Briskin M., Fasel N., Hermanson G., Sigman D. S., Wall R. Protein-binding site at the immunoglobulin mu membrane polyadenylylation signal: possible role in transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9160–9164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. P., Tucker P. W., Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R. Mapping of heavy chain genes for mouse immunoglobulins M and D. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1348–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.6774414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Falck-Pedersen E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Shenk T. A poly(A) addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R., Owens J. D., Finkelman F. D., Kessler S. W., Fitzmaurice L., Potter M., Tucker P. W. Mouse immunoglobulin D: construction and characterization of a cloned delta chain cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Characterization of productive and sterile transcripts from the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: processing of micron and muS mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1317–1332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi A., Hawley R. G., Hawley T., Shulman M. J., Traunecker A., Köhler G., Hozumi N. Functional immunoglobulin M production after transfection of cloned immunoglobulin heavy and light chain genes into lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6351–6355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. Regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA requires linkage of the poly(A) addition sites and is dependent on the length of the mu s-mu m intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8883–8887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. The regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA is dependent on the relative efficiencies of mu s poly(A) site usage and the c mu 4-to-M1 splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):726–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam A. C., Shen A., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin mu-delta heavy-chain region. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):483–487. doi: 10.1038/306483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurushita N., Avdalovic N. M., Korn L. J. Regulation of differential processing of mouse immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4603–4615. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurushita N., Korn L. J. Effects of intron length on differential processing of mouse mu heavy-chain mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2602–2605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Tucker P. W. Transcriptional regulation of the mu-delta heavy chain locus in normal murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):564–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Witte P. L. Transcriptional regulation of mu and delta gene expression in bone marrow pre-B and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2808–2814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]