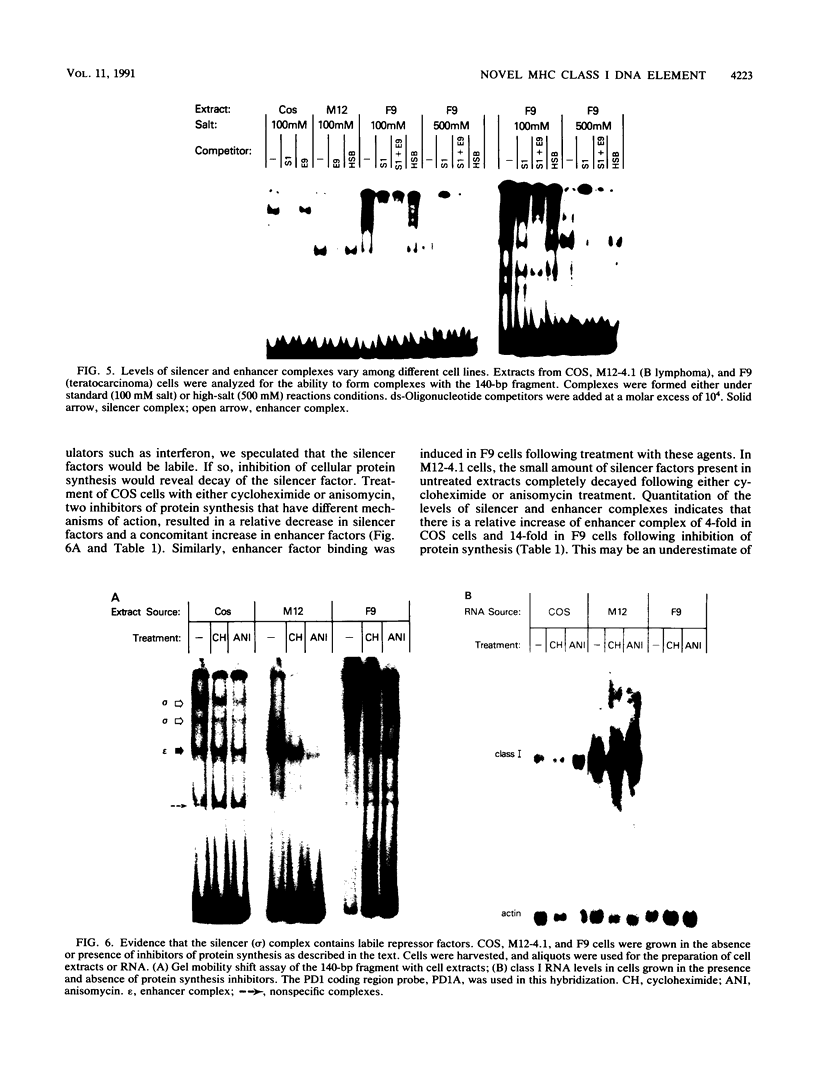
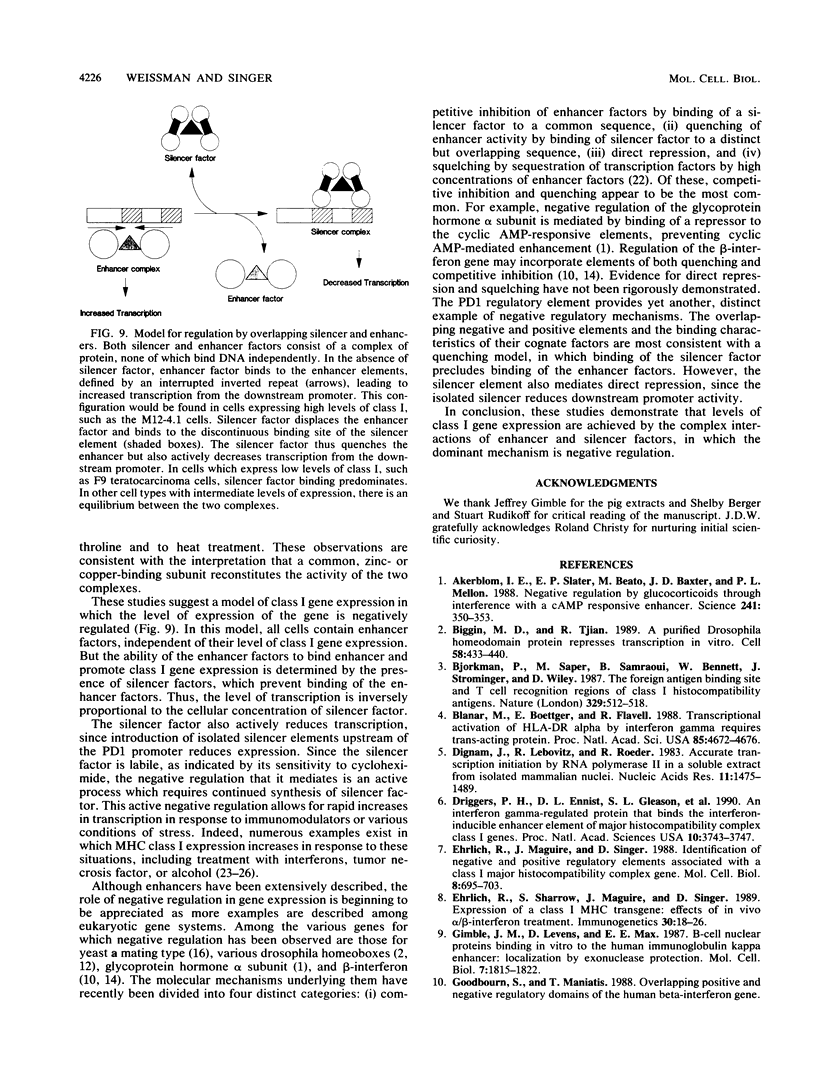
Abstract
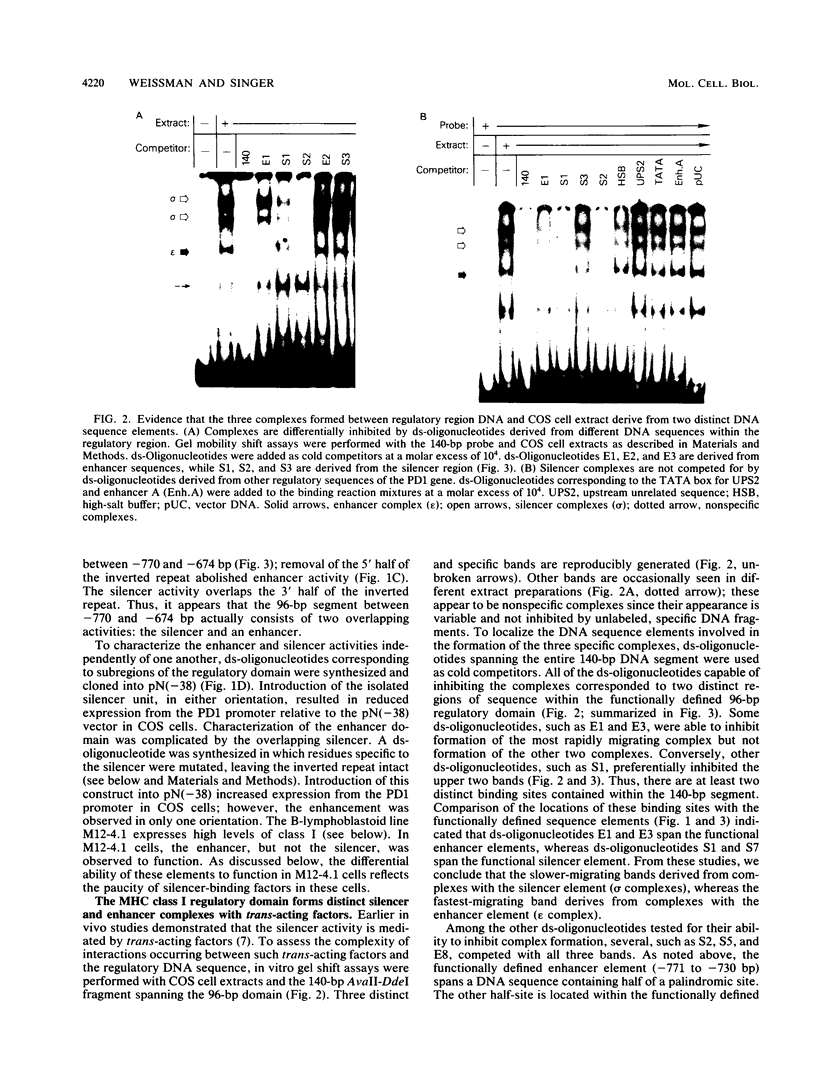
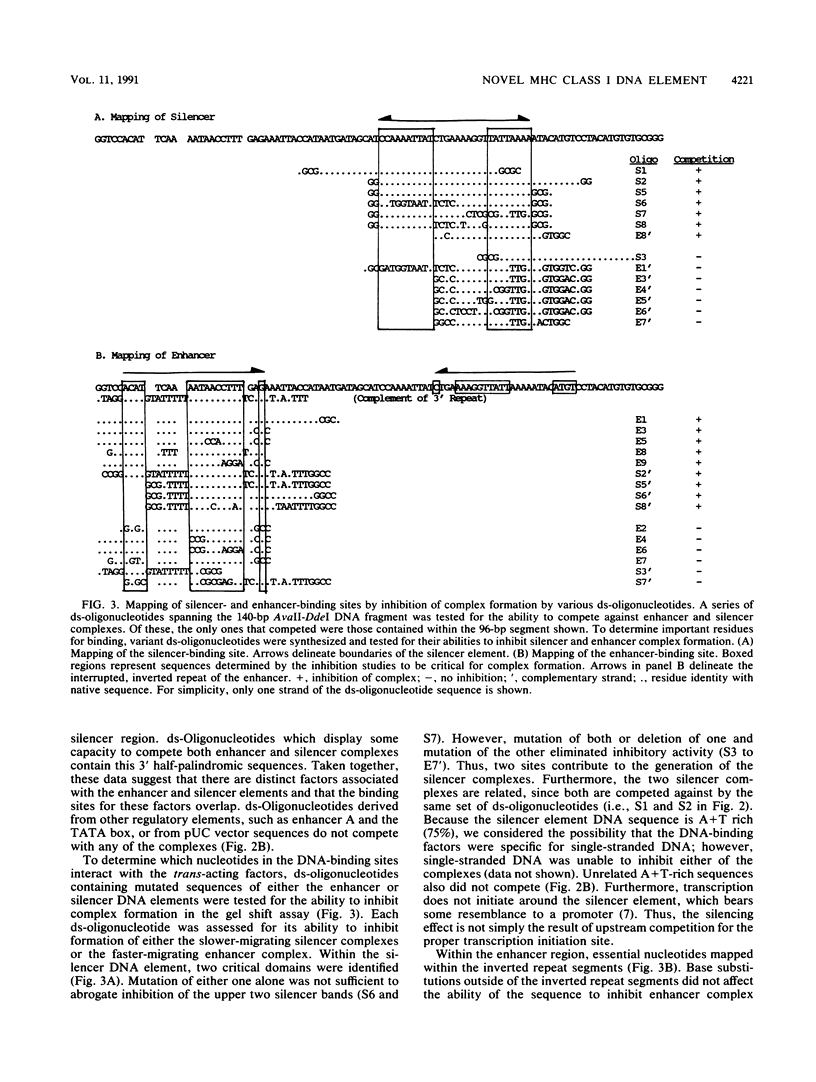
A novel regulatory element which contributes to the regulation of quantitative, tissue-specific differences in gene expression has been found between -771 and -676 bp upstream of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene, PD1. Molecular dissection of this element reveals the presence of two overlapping functional activities: an enhancer and a silencer. Distinct nuclear factors bind to the overlapping enhancer and silencer DNA sequence elements within the regulatory domain. The levels of factors binding the silencer DNA sequence in different cell types are inversely related to levels of class I expression; in contrast, factors binding the enhancer DNA sequence can be detected in all cells. In cultured cell lines, inhibition of protein synthesis leads to the rapid loss of silencer complexes, with a concomitant increase in both enhancer complexes and MHC class I RNA. From these data, we conclude that a labile silencer factor competes with a constitutively expressed, stable enhancer factor for overlapping DNA-binding sites; the relative abundance of the silencer factor contributes to establishing steady-state levels of MHC class I gene expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. A purified Drosophila homeodomain protein represses transcription in vitro. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Maguire J. E., Singer D. S. Identification of negative and positive regulatory elements associated with a class I major histocompatibility complex gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):695–703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Sharrow S. O., Maguire J. E., Singer D. S. Expression of a class I MHC transgene: effects of in vivo alpha/beta-interferon treatment. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(1):18–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02421465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble J. M., Levens D., Max E. E. B-cell nuclear proteins binding in vitro to the human immunoglobulin kappa enhancer: localization by exonuclease protection. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1815–1822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handy D. E., Burke P. A., Ozato K., Coligan J. E. Site-specific mutagenesis of the class I regulatory element the Q10 gene allows expression in non-liver tissues. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):1015–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Gresser I., Leary P., Tovey M. Interferon treatment of mice: enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent L. J., Ehrlich R., Matis L., Singer D. S. Ethanol: an enhancer of major histocompatibility complex antigen expression. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):469–473. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3678702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances HLA-A,B,C and HLA-DR gene expression in human tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):975–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satz M. L., Singer D. S. Effect of mouse interferon on the expression of a porcine major histocompatibility gene introduced into mouse L cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Maguire J. E. Regulation of the expression of class I MHC genes. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(3):235–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. D., Singer D. S. Striking similarities between the regulatory mechanisms governing yeast mating-type genes and mammalian major histocompatibility complex genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4228–4234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]