Abstract
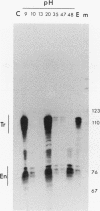
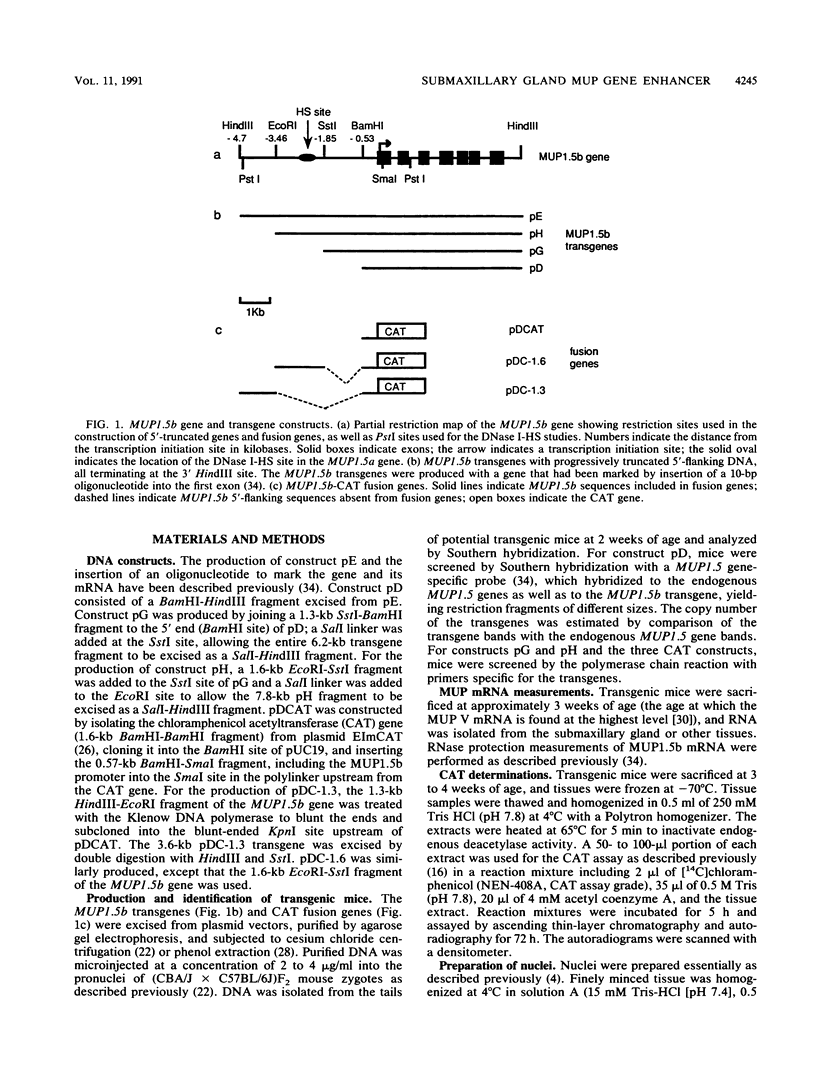
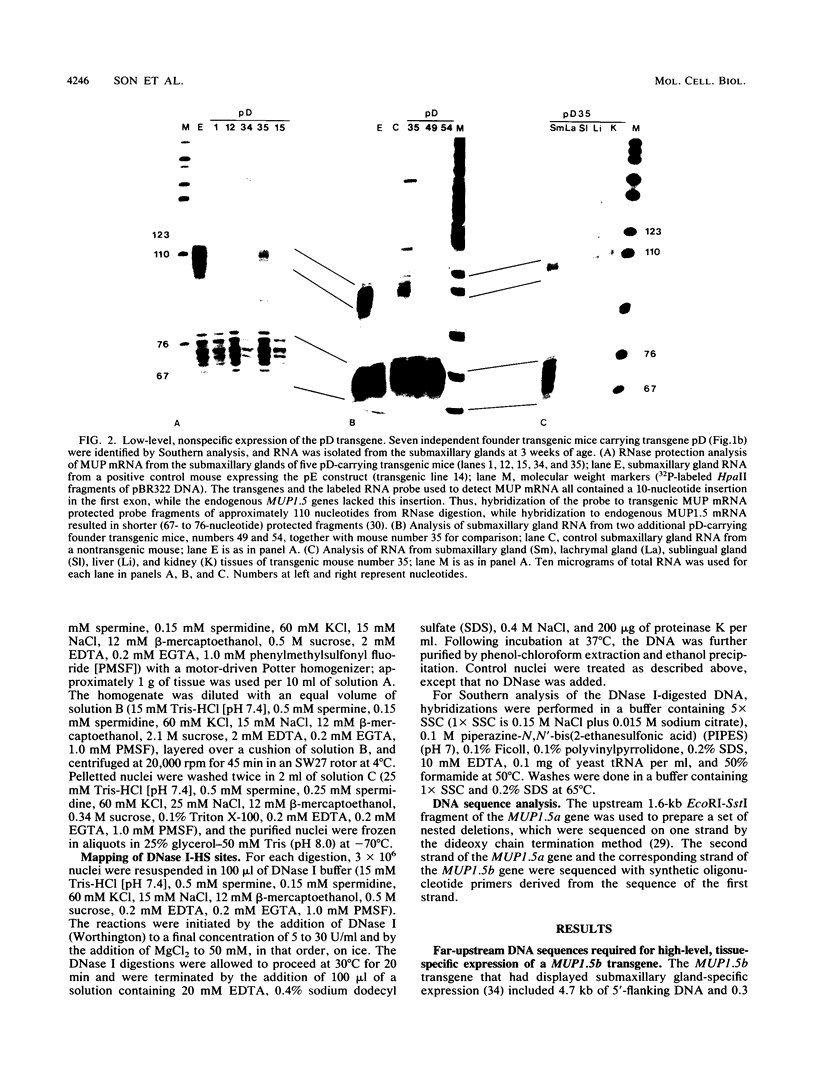
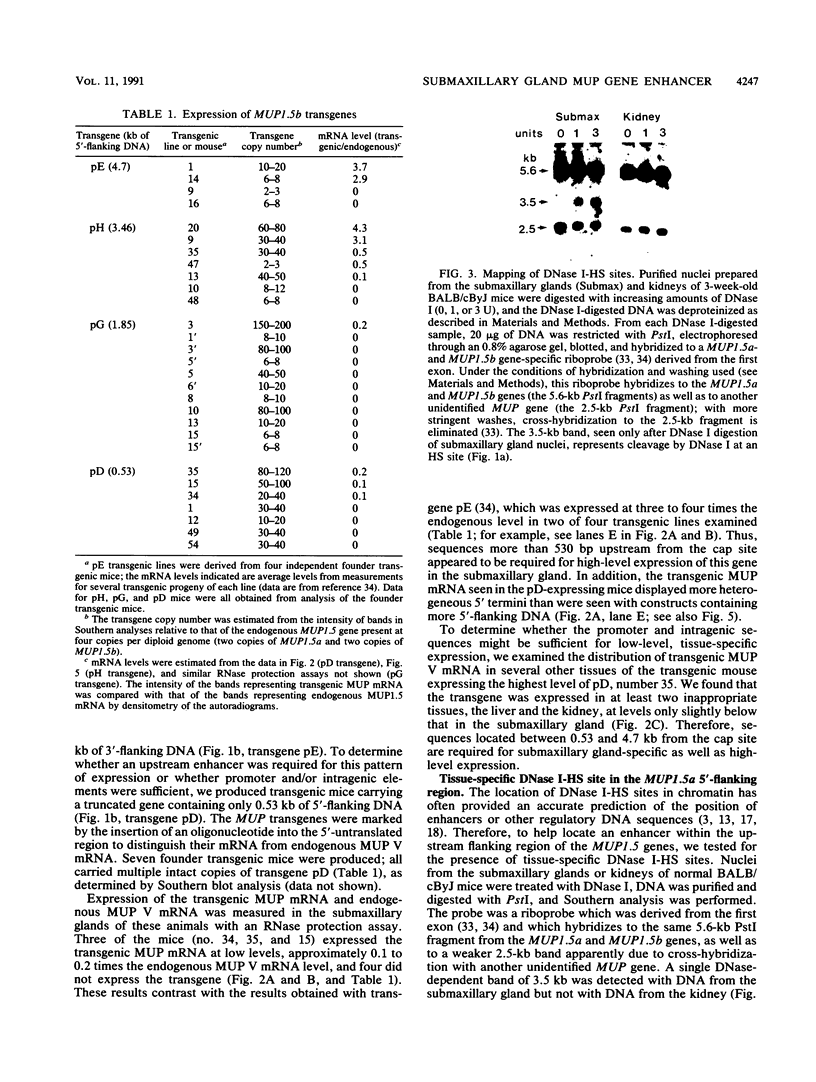
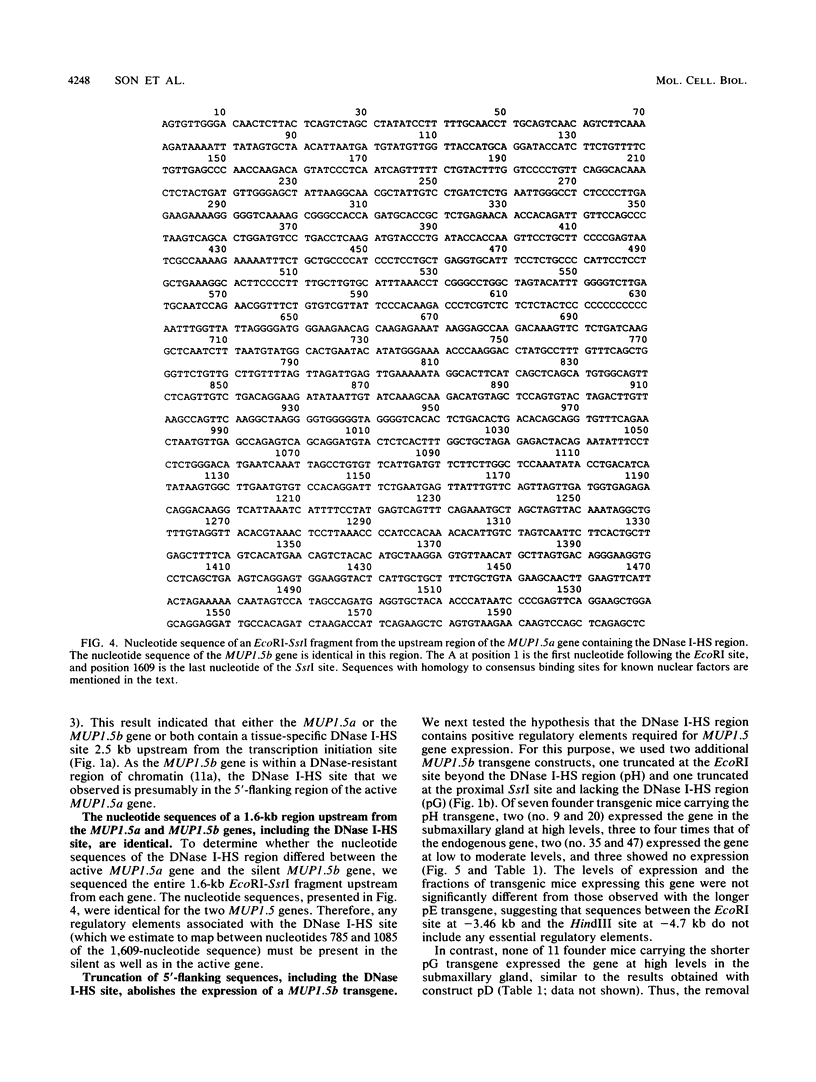
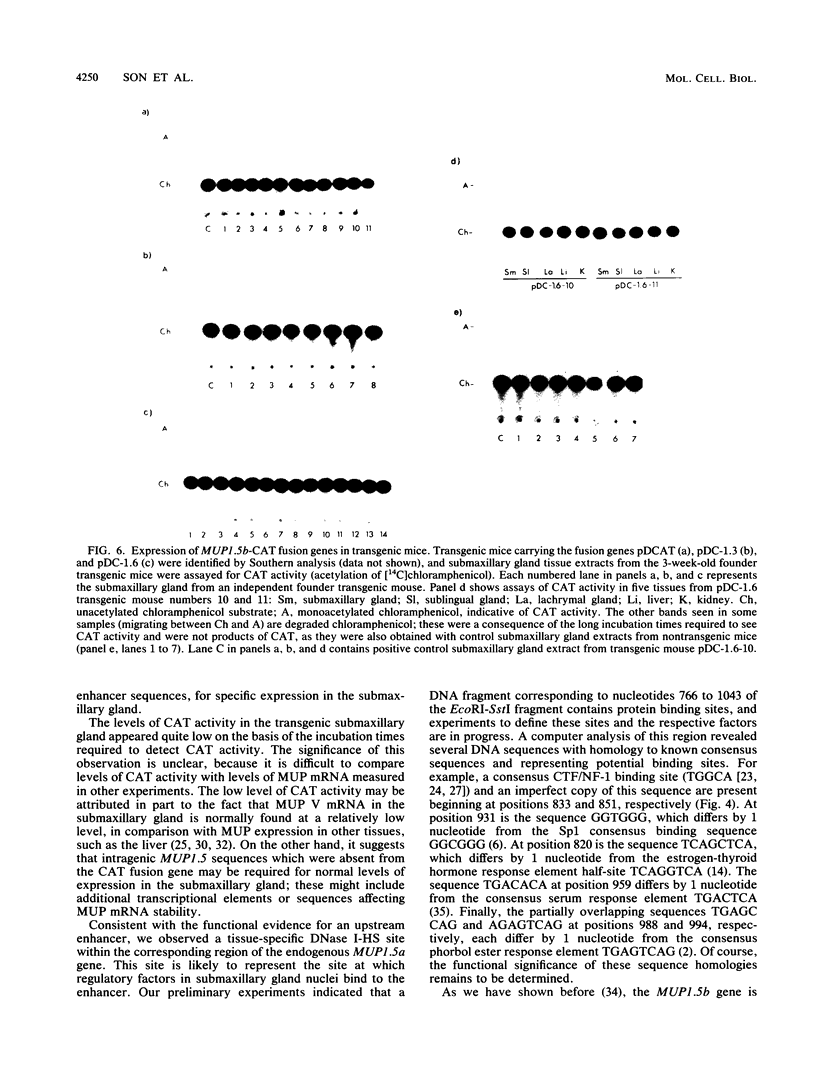
The MUP1.5b gene was previously found to be expressed specifically in the submaxillary gland and at high levels when introduced into mice as a transgene including 4.7 kb of 5'-flanking DNA and 0.3 kb of 3'-flanking DNA. To localize regulatory elements responsible for this tissue-specific pattern of expression, we tested the expression of three additional MUP1.5b transgenes including various amounts of 5'-flanking DNA. These experiments indicated that sequences between -1.85 and -3.46 kb from the transcription initiation site were required for high-level expression in the submaxillary gland. The presence of regulatory elements in this region was also suggested by the detection of a DNase I-hypersensitive site, seen only in submaxillary gland nuclei, at position -2.5 kb upstream from the MUP1.5a gene, a member of the same MUP gene subfamily and virtually identical to the MUP1.5b gene. Further evidence for enhancer activity was provided by the ability of the 1.6-kb DNA fragment including sequences between -1.85 and -3.46 kb to stimulate the expression of an otherwise inactive MUP1.5b-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion gene specifically in the submaxillary gland. The nucleotide sequence of this 1.6-kb DNA fragment was found to be identical for the MUP1.5a and MUP1.5b genes. Together, these results provide the first localization of a cis-acting regulatory sequence involved in the differential tissue-specific expression of the MUP gene family.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Shawi R., Burke J., Jones C. T., Simons J. P., Bishop J. O. A Mup promoter-thymidine kinase reporter gene shows relaxed tissue-specific expression and confers male sterility upon transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4821–4828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Oudet P., Chambon P. Disruption of the typical chromatin structure in a 2500 base-pair region at the 5' end of the actively transcribed ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Selman G. G., Hickman J., Black L., Saunders R. D., Clark A. J. The 45-kb unit of major urinary protein gene organization is a gigantic imperfect palindrome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1591–1600. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Chave-Cox A., Ma X., Bishop J. O. Analysis of mouse major urinary protein genes: variation between the exonic sequences of group 1 genes and a comparison with an active gene out with group 1 both suggest that gene conversion has occurred between MUP genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3167–3171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ghazal P., Bingham R. W., Barrett D., Bishop J. O. Sequence structures of a mouse major urinary protein gene and pseudogene compared. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3159–3165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Hickman J., Bishop J. A 45-kb DNA domain with two divergently orientated genes is the unit of organisation of the murine major urinary protein genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2055–2064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E. Isolation of a cDNA clone for mouse urinary proteins: age- and sex-related expression of mouse urinary protein genes is transcriptionally controlled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5425–5429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson J. S., Asofsky R., Potter M., Runner C. C. Major urinary protein complex of normal mice: origin. Science. 1965 Aug 27;149(3687):981–982. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3687.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A., Toole J. J. Multiple genes coding for the androgen-regulated major urinary proteins of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Gallagher J. F., Hohman C. M., Kuhn N. J., Sampsell B. M., Hughes R. G., Jr Identification and characterization of functional genes encoding the mouse major urinary proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Mullins J. J., Kuhn N. J., Gallagher J. F., Gu G. D., Gross K. W. T antigen expression and tumorigenesis in transgenic mice containing a mouse major urinary protein/SV40 T antigen hybrid gene. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):183–191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Gallagher J. F., Held W. A. Differential, multihormonal regulation of the mouse major urinary protein gene family in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2232–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Komro C. T., Michnoff C. H., MacDonald R. J. The cell-specific elastase I enhancer comprises two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):893–902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Stable C., Costantini F. Roles of fetal G gamma-globin promoter elements and the adult beta-globin 3' enhancer in the stage-specific expression of globin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1116–1125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
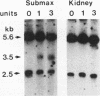
- Shahan K., Denaro M., Gilmartin M., Shi Y., Derman E. Expression of six mouse major urinary protein genes in the mammary, parotid, sublingual, submaxillary, and lachrymal glands and in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1947–1954. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahan K., Gilmartin M., Derman E. Nucleotide sequences of liver, lachrymal, and submaxillary gland mouse major urinary protein mRNAs: mosaic structure and construction of panels of gene-specific synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1938–1946. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. H., Held W. A., Hastie N. D. The gene family for major urinary proteins: expression in several secretory tissues of the mouse. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Rodriguez M., Shahan K., Derman E. Subfamily of submaxillary gland-specific Mup genes: chromosomal linkage and sequence comparison with liver-specific Mup genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6191–6203. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Son H. J., Shahan K., Rodriguez M., Costantini F., Derman E. Silent genes in the mouse major urinary protein gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4584–4588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares V. da C., Gubits R. M., Feigelson P., Costantini F. Tissue-specific and hormonally regulated expression of a rat alpha 2u globulin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3749–3758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]