Abstract
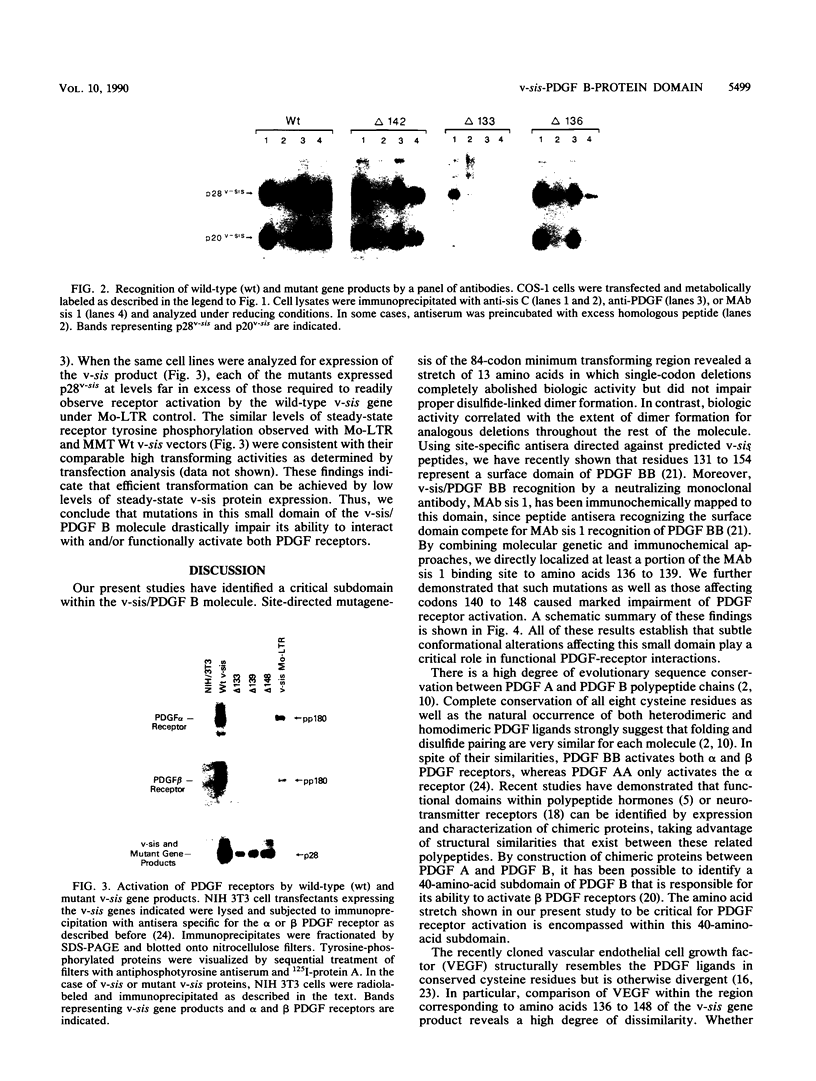
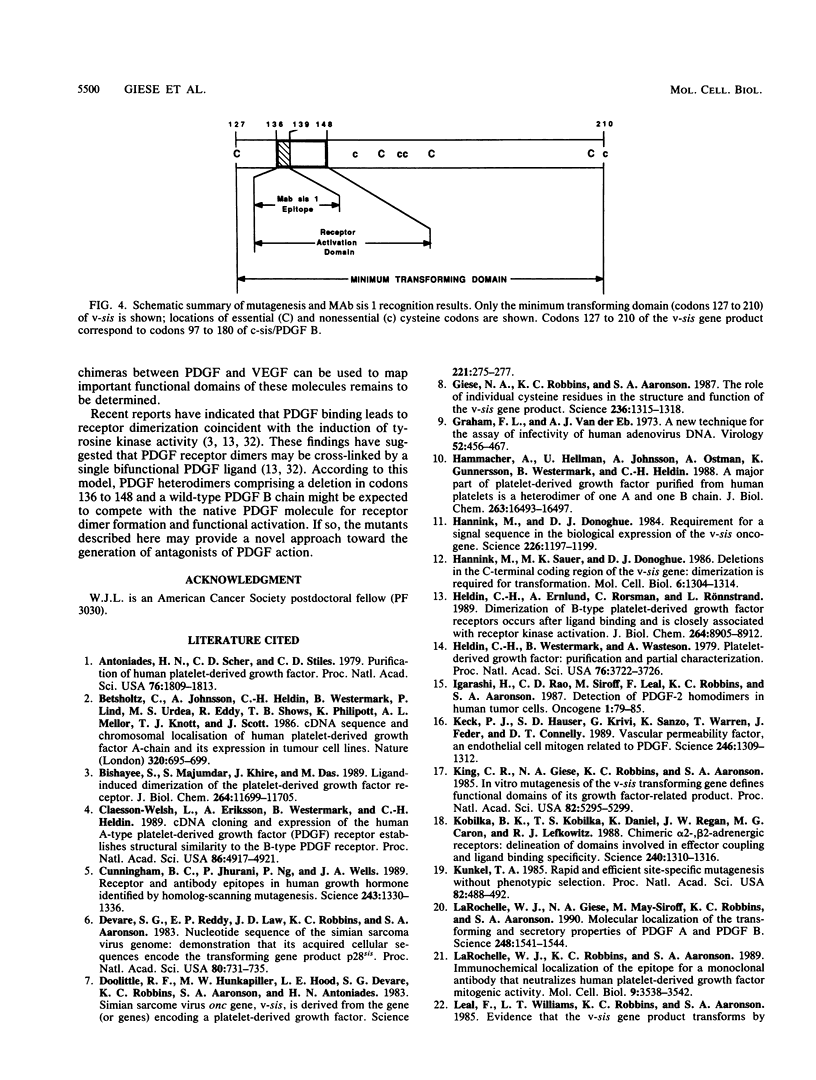
Deletion scanning mutagenesis within the transforming region of the v-sis oncogene was used to dissect structure-function relationships. Mutations affecting codons within a domain encoding amino acids 136 through 148 had no effect upon homodimer formation or recognition by antisera which detect determinants dependent upon native intrachain disulfide linkages, yet the same mutations completely abolished transforming activity. A platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGF B) monoclonal antibody that prevents its interaction with PDGF receptors recognized v-sis, delta 142 (deletion of codon 142), and delta 148 but not delta 136, delta 137, or delta 139 mutants. These findings mapped the epitope recognized by this monoclonal antibody to include amino acid residues 136 to 139. Furthermore, mutations in the codon 136 to 148 domain caused markedly impaired ability to induce PDGF receptor tyrosine phosphorylation. Thus, subtle conformational alterations in this small domain critically affect PDGF receptor recognition and/or functional activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D., Stiles C. D. Purification of human platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Lind P., Urdea M. S., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Philpott K., Mellor A. L. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):695–699. doi: 10.1038/320695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishayee S., Majumdar S., Khire J., Das M. Ligand-induced dimerization of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Monomer-dimer interconversion occurs independent of receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11699–11705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Eriksson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H. cDNA cloning and expression of the human A-type platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor establishes structural similarity to the B-type PDGF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Jhurani P., Ng P., Wells J. A. Receptor and antibody epitopes in human growth hormone identified by homolog-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1330–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2466339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Law J. D., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the simian sarcoma virus genome: demonstration that its acquired cellular sequences encode the transforming gene product p28sis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese N. A., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. The role of individual cysteine residues in the structure and function of the v-sis gene product. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1315–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.3035718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammacher A., Hellman U., Johnsson A., Ostman A., Gunnarsson K., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. A major part of platelet-derived growth factor purified from human platelets is a heterodimer of one A and one B chain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16493–16498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Requirement for a signal sequence in biological expression of the v-sis oncogene. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.6095451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Sauer M. K., Donoghue D. J. Deletions in the C-terminal coding region of the v-sis gene: dimerization is required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1304–1314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: purification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3722–3726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi H., Rao C. D., Siroff M., Leal F., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Detection of PDGF-2 homodimers in human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck P. J., Hauser S. D., Krivi G., Sanzo K., Warren T., Feder J., Connolly D. T. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1309–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.2479987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Giese N. A., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. In vitro mutagenesis of the v-sis transforming gene defines functional domains of its growth factor-related product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5295–5299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRochelle W. J., Giese N., May-Siroff M., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Molecular localization of the transforming and secretory properties of PDGF A and PDGF B. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1541–1544. doi: 10.1126/science.2163109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRochelle W. J., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Immunochemical localization of the epitope for a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes human platelet-derived growth factor mitogenic activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3538–3542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal F., Williams L. T., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Evidence that the v-sis gene product transforms by interaction with the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.2996133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Heidaran M., Miki T., Popescu N., La Rochelle W., Kraus M., Pierce J., Aaronson S. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):800–804. doi: 10.1126/science.2536956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Antoniades H. N., Devare S. G., Hunkapiller M. W., Aaronson S. A. Structural and immunological similarities between simian sarcoma virus gene product(s) and human platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):605–608. doi: 10.1038/305605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. In vivo identification of the transforming gene product of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.6293053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Leal F., Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A. The v-sis/PDGF-2 transforming gene product localizes to cell membranes but is not a secretory protein. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1783–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer M. K., Donoghue D. J. Identification of nonessential disulfide bonds and altered conformations in the v-sis protein, a homolog of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1011–1018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Hart C. E., Phillips P. E., Forstrom J. W., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8771–8778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]