Abstract
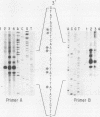
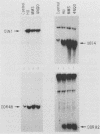
The sequence of the DIN1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is identical to RNR3, a gene encoding a DNA damage-inducible regulatory subunit of ribonucleotide reductase. Two sequence elements located upstream of DIN1 (RNR3) are homologous to putative DNA damage regulatory elements in the promoter of the reductase catalytic subunit gene, RNR2. The transcript start sites for DIN1(RNR3) have been localized, and induction by different agents has been compared with other DNA damage-regulated genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caras I. W., Levinson B. B., Fabry M., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloned mouse ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 cDNA reveals amino acid sequence homology with Escherichia coli and herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7015–7022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory J. G., Rey D. A., Carter G. L., Bacon P. E. Nucleoside 5'-diphosphates as effectors of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12001–12007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. DNA damage induction of ribonucleotide reductase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4932–4940. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Identification and isolation of the gene encoding the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DNA damage-inducible gene required for mitotic viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2783–2793. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Identification of the DNA damage-responsive element of RNR2 and evidence that four distinct cellular factors bind it. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5373–5386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Two genes differentially regulated in the cell cycle and by DNA-damaging agents encode alternative regulatory subunits of ribonucleotide reductase. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):740–751. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd H. K., Roberts C. W., Roberts J. W. Identification of the gene for the yeast ribonucleotide reductase small subunit and its inducibility by methyl methanesulfonate. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3673–3677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd H. K., Roberts J. W. Upstream regulatory sequences of the yeast RNR2 gene include a repression sequence and an activation site that binds the RAP1 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5359–5372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan T., McEntee K. DNA damage and heat shock dually regulate genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W., Murray A. W. Cloning regulated yeast genes from a pool of lacZ fusions. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:253–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W. Specific Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes are expressed in response to DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander M., Gräslund A., Thelander L. Subunit M2 of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Characterization of a homogeneous protein isolated from M2-overproducing mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2737–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treger J. M., Heichman K. A., McEntee K. Expression of the yeast UB14 gene increases in response to DNA-damaging agents and in meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treger J. M., McEntee K. Structure of the DNA damage-inducible gene DDR48 and evidence for its role in mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3174–3184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]