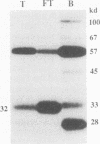
Abstract
A detailed analysis of RNA-protein complex formation in the 3' untranslated region of spinach chloroplast petD mRNA has been carried out. Five chloroplast proteins that interact with petD RNA in this region, which contains an inverted repeat sequence capable of forming a hairpin structure, have been identified. A 33-kDa protein recognizes specifically the double-stranded stem of the hairpin structure; mutations that disrupt base pairing at the base of the stem reduce or eliminate protein binding. A 57-kDa protein recognizes specifically an AU-rich sequence motif that is highly conserved in petD genes of different higher plant species. The 57-kDa protein and possibly the 33-kDa protein form stable complexes with petD RNA in vitro and may interact with each other. In addition, their interaction with petD RNA is highly sensitive to heparin. The three other proteins, of 100, 32, and 28 kDa, display little sequence or structural binding specificity apart from their preference for uridine-rich sequences. They also interact with the 3' untranslated regions of other chloroplast RNAs such as those of psbA and rbcL. The functions of these proteins in the regulation of petD gene expression, including possible roles in transcription termination and RNA stability, are discussed.
Full text
PDF

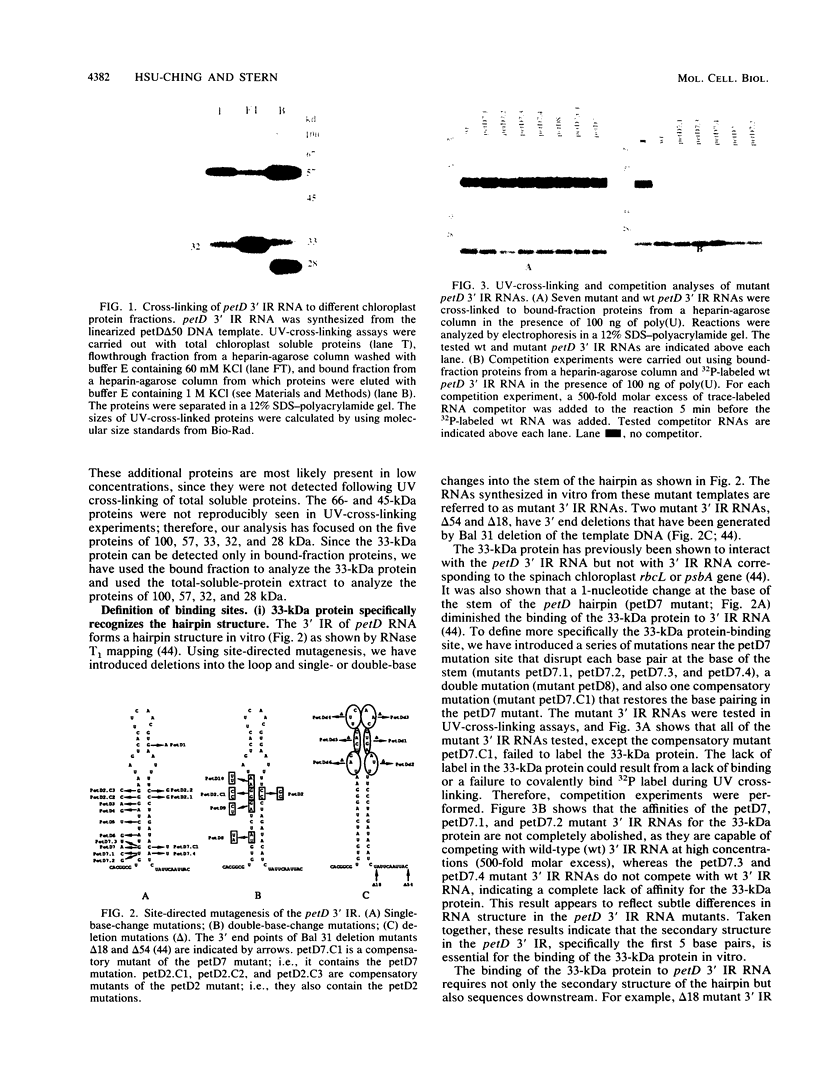






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel K., Bogorad L. Light-induced increase in the activity of maize plastid DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):615–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Proteins encoded by a complex chloroplast transcription unit are each translated from both monocistronic and polycistronic mRNAs. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2637–2644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Beatty J. T., Cohen S. N., Belasco J. G. An intercistronic stem-loop structure functions as an mRNA decay terminator necessary but insufficient for puf mRNA stability. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90473-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Orozco E. M., Jr Recognition of prokaryotic transcription terminators by spinach chloroplast RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8411–8431. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Constitutive transcription and regulation of gene expression in non-photosynthetic plastids of higher plants. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3301–3308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Tonkyn J. C., Peter G. F., Thornber J. P., Gruissem W. Post-transcriptional control of plastid mRNA accumulation during adaptation of chloroplasts to different light quality environments. Plant Cell. 1989 Jun;1(6):645–654. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.6.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Barkan A., Deng X. W., Stern D. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of plastid mRNA levels in higher plants. Trends Genet. 1988 Sep;4(9):258–263. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W. Chloroplast gene expression: how plants turn their plastids on. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90889-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast gene expression and promoter identification in chloroplast extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:253–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Laudano A., Yu Y. Structural requirements of iron-responsive elements for binding of the protein involved in both transferrin receptor and ferritin mRNA post-transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1819–1824. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3059–3066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Galloway J. L., Platt T. Maturation of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon mRNA: evidence for 3' exonucleolytic processing after rho-dependent termination. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1571–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbury S. F., Smith N. H., Higgins C. F. Differential mRNA stability controls relative gene expression within a polycistronic operon. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1131–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. Interaction of a 3' RNA region of the mustard trnK gene with chloroplast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9637–9648. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. D., Barkan A., Taylor W. C. The maize plastid psbB-psbF-petB-petD gene cluster: spliced and unspliced petB and petD RNAs encode alternative products. Curr Genet. 1987;12(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00420729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Maize plastid photogenes: mapping and photoregulation of transcript levels during light-induced development. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):463–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf M., Kössel H. Structure and expression of the gene coding for the alpha-subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from the chloroplast genome of Zea mays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5741–5754. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Dathan N. A., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. The U2B'' RNP motif as a site of protein-protein interaction. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3675–3681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijben-Müller G., Hallick R. B., Alt J., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Spinach plastid genes coding for initiation factor IF-1, ribosomal protein S11 and RNA polymerase alpha-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1029–1044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end maturation is biochemically distinct from prokaryotic mRNA processing. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):615–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00016017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Jones H., Gruissem W. Function of plastid mRNA 3' inverted repeats. RNA stabilization and gene-specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18742–18750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Radwanski E. R., Kindle K. L. A 3' stem/loop structure of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast atpB gene regulates mRNA accumulation in vivo. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):285–297. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M, Obokata J, Chunwongse J, Shinozaki K, Sugiura M. Rapid splicing and stepwise processing of a transcript from the psbB operon in tobacco chloroplasts: determination of the intron sites in petB and petD. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):427–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00331145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Farchaus J. W., Herrmann R. G. The gene for the Mr 10,000 phosphoprotein associated with photosystem II is part of the psbB operon of the spinach plastid chromosome. Curr Genet. 1986;11(3):165–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00420602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Complex RNA maturation in chloroplasts. The psbB operon from spinach. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):551–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. S., Kung S. D., Bogorad L. Phytochrome control of levels of mRNA complementary to plastid and nuclear genes of maize. Plant Physiol. 1985 Oct;79(2):371–376. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]