Abstract
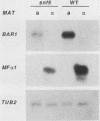
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF5 gene affects expression of both glucose- and phosphate-regulated genes and appears to function in transcription. We report the nucleotide sequence, which predicts that SNF5 encodes a 102,536-dalton protein. The N-terminal third of the protein is extremely rich in glutamine and proline. Mutants carrying a deletion of the coding sequence were viable but grew slowly, indicating that the SNF5 gene is important but not essential. Evidence that SNF5 affects expression of the cell type-specific genes MF alpha 1 and BAR1 at the RNA level extends the known range of SNF5 function. SNF5 is apparently required for expression of a wide variety of differently regulated genes. A bifunctional SNF5-beta-galactosidase fusion protein was localized in the nucleus by immunofluorescence. No DNA-binding activity was detected for SNF5. A LexA-SNF5 fusion protein, when bound to a lexA operator, functioned as a transcriptional activator.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Karlin S. Association of charge clusters with functional domains of cellular transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The yeast SNF3 gene encodes a glucose transporter homologous to the mammalian protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M., Williamson V. M. Analysis of mutations affecting Ty-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):159–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00422784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Adams C. D., Winston F. The SPT6 gene is essential for growth and is required for delta-mediated transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):679–686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Malvar T. The CCR4 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for both nonfermentative and spt-mediated gene expression. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):283–291. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Takahara Y., Kishi F., Nakazawa A., Brent R. LexA protein is a repressor of the colicin E1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13258–13261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estruch F., Carlson M. SNF6 encodes a nuclear protein that is required for expression of many genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2544–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Guarente L. Identification and characterization of HAP4: a third component of the CCAAT-bound HAP2/HAP3 heteromer. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1166–1178. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V. L., Welch S. K., Insley M. Y., Manney T. R., Holly J., Saari G. C., Parker M. L. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae BAR1 gene encodes an exported protein with homology to pepsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):55–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle C. M., Jones E. W. Consequences of growth media, gene copy number, and regulatory mutations on the expression of the PRB1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Jan;124(1):39–55. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Genes affecting the regulation of SUC2 gene expression by glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):845–858. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Celenza J. L., Carlson M. SSN20 is an essential gene with mutant alleles that suppress defects in SUC2 transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):672–678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Rubin K., Carlson M. Suppressors of SNF2 mutations restore invertase derepression and cause temperature-sensitive lethality in yeast. Genetics. 1986 Apr;112(4):741–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarokin L., Carlson M. Comparison of two yeast invertase genes: conservation of the upstream regulatory region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6089–6103. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarokin L., Carlson M. Upstream region required for regulated expression of the glucose-repressible SUC2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2750–2757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Control of yeast cell type by the mating type locus. I. Identification and control of expression of the a-specific gene BAR1. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):305–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Molecular mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:1051–1077. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Carlson M., Winston F. SPT6, an essential gene that affects transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, encodes a nuclear protein with an extremely acidic amino terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4935–4941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., LaMarco K. L., McKnight S. L. Evidence of DNA: protein interactions that mediate HSV-1 immediate early gene activation by VP16. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):730–742. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chaleff D. T., Valent B., Fink G. R. Mutations affecting Ty-mediated expression of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):179–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]