Abstract
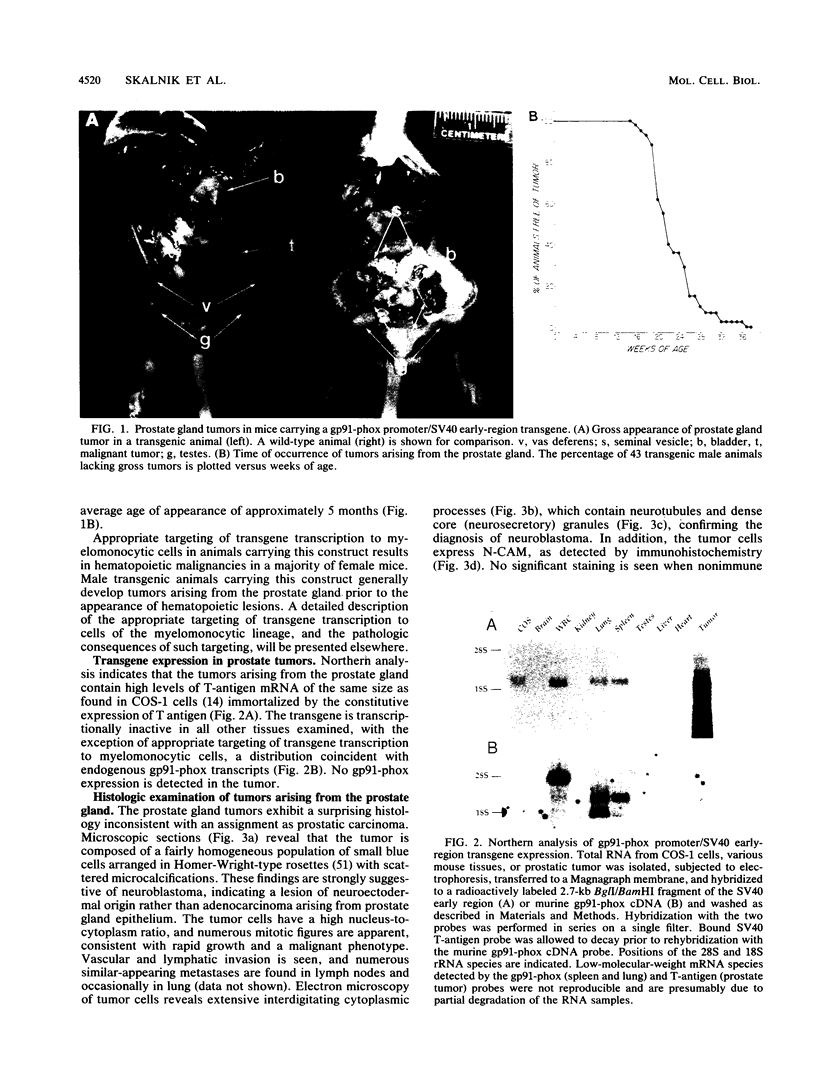
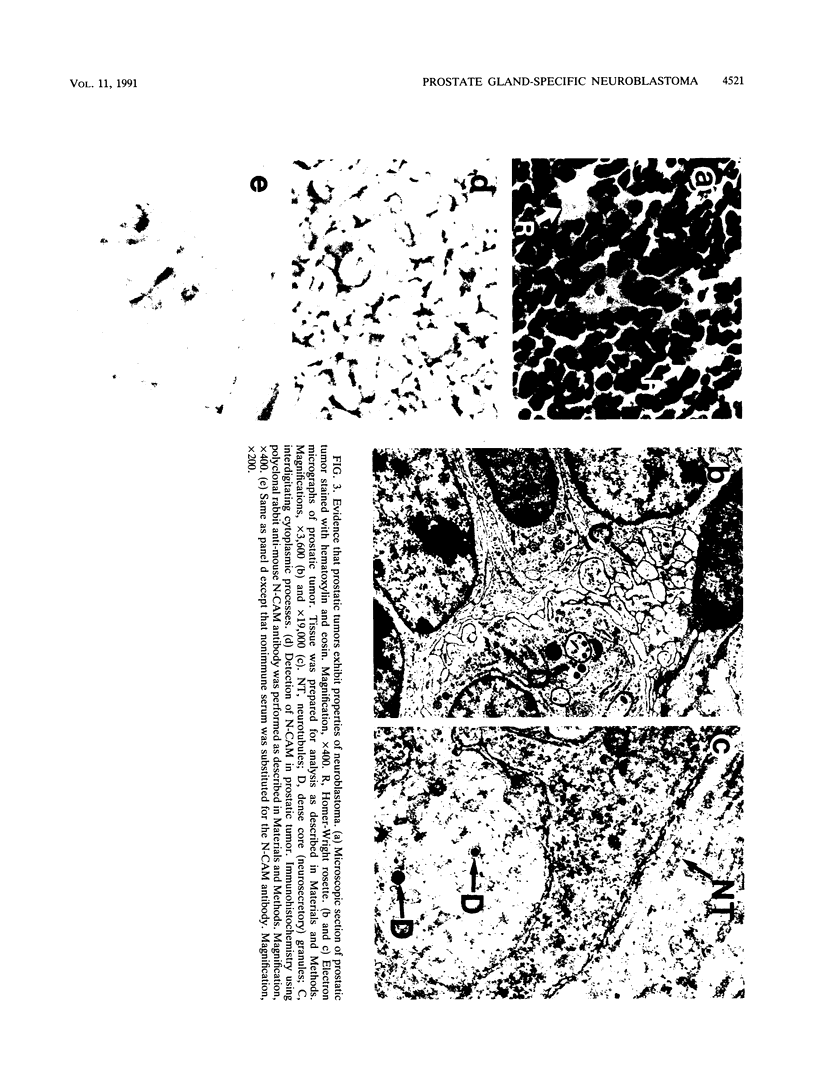
Male transgenic mice that carry a construct containing 5'-flanking sequences of the gp91-phox gene linked to the early region of the simian virus 40 (SV40) genome reproducibly develop tumors arising from the prostate gland. As gp91-phox is expressed exclusively in terminally differentiating hematopoietic cells of the myelomonocytic lineage, the induction of tumors arising from the prostate gland was unexpected. These lesions appear to be due to a novel transcription signal that was generated during the construction of the transgene. Surprisingly, the histopathological and biochemical properties of the tumor are diagnostic of neuroblastoma rather than of adenocarcinoma of the prostate gland. Tumors produce SV40 T antigen and isoforms of neural cell adhesion molecule characteristic of neuronal cells, and they occur in a testosterone-independent manner. Microscopic examination of prostate glands from young transgenic mice reveals the presence of small lesions arising outside of the prostate gland epithelium, which is consistent with the diagnosis of neuroblastoma and further distinguishes this tumor from prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate gland tumors occur in all male animals of susceptible lines carrying the gp91-phox promoter/SV40 early-region transgene. However, variability in the time at which gross tumors appear and the presence of cells expressing T antigen prior to tumorigenesis suggest that somatic events in addition to T-antigen production are required for the development of a malignancy. The extraordinary restriction of the site of tumorigenesis in these animals indicates the presence in the prostate gland of a novel, tissue-specific neuroectodermal cell of origin. These transgenic animals provide a model system for the study of neuroectodermal malignancies.
Full text
PDF

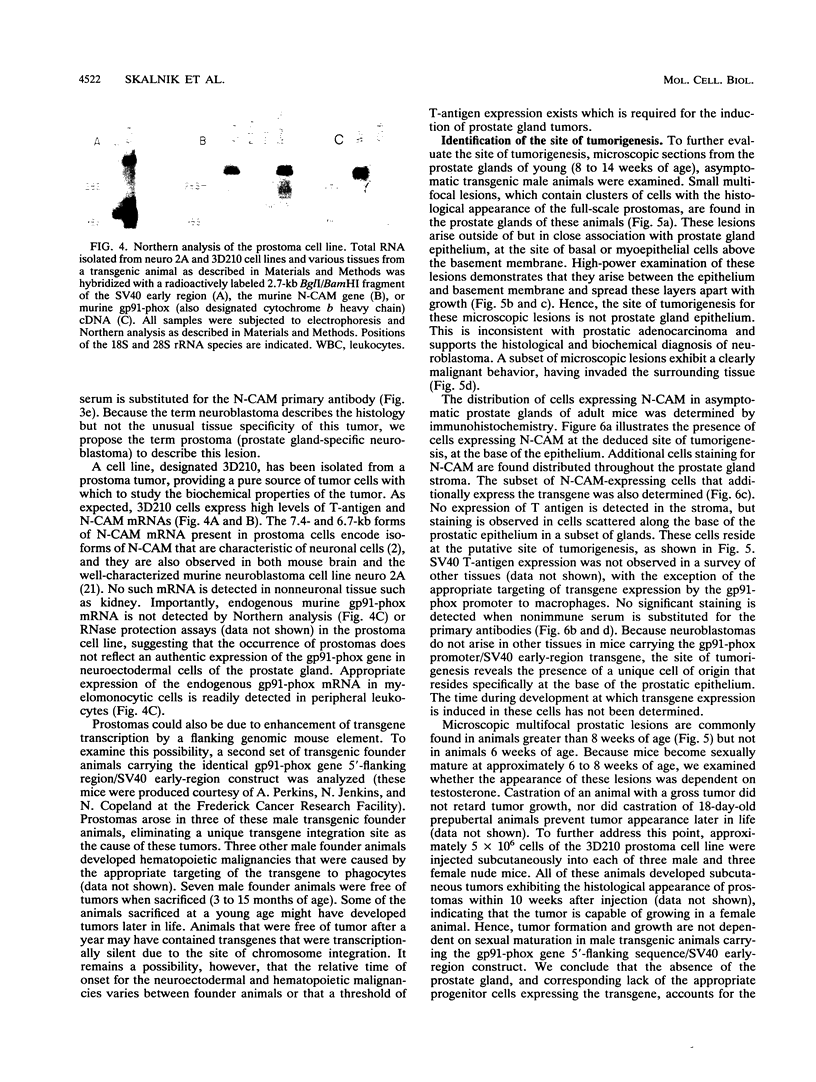
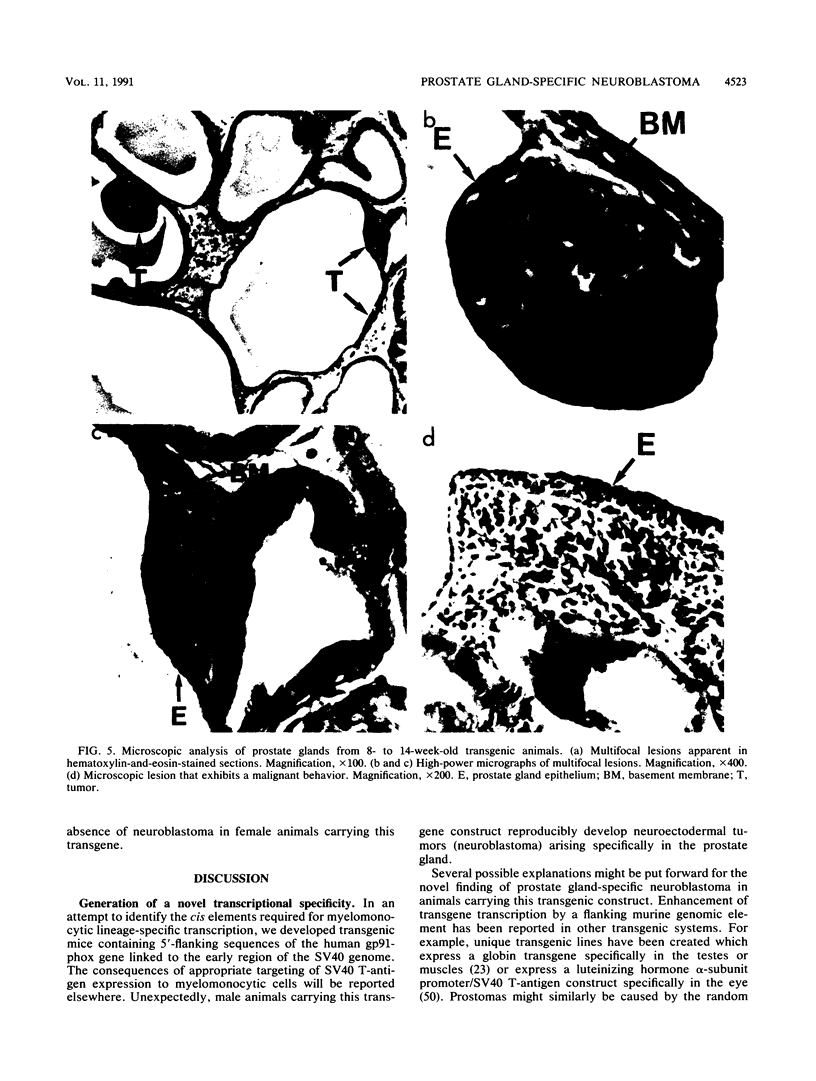




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguzzi A., Wagner E. F., Williams R. L., Courtneidge S. A. Sympathetic hyperplasia and neuroblastomas in transgenic mice expressing polyoma middle T antigen. New Biol. 1990 Jun;2(6):533–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas J. A., Chaix J. C., Steinmetz M., Goridis C. Differential splicing and alternative polyadenylation generates distinct NCAM transcripts and proteins in the mouse. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):625–632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Peschon J. J., Messing A., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Heart and bone tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2648–2652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botteri F. M., van der Putten H., Wong D. F., Sauvage C. A., Evans R. M. Unexpected thymic hyperplasia in transgenic mice harboring a neuronal promoter fused with simian virus 40 large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3178–3184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehling H. J., Viville S., van Ewijk W., Benoist C., Mathis D. Fine-tuning of MHC class II gene expression in defined microenvironments. Trends Genet. 1989 Oct;5(10):342–347. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J. Atrial natriuretic factor-SV40 T antigen transgenes produce tumors and cardiac arrhythmias in mice. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.2964082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Watson K., Ingber D., Hanahan D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):58–61. doi: 10.1038/339058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N., Crooke R., Hwang L. H., Schibler U., Knowles B. B., Solter D. Metastatic hibernomas in transgenic mice expressing an alpha-amylase-SV40 T antigen hybrid gene. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):460–463. doi: 10.1126/science.2785714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Clerc R. G., Sharp P. A. The DNA-binding homeo domain of the Oct-2 protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):739–745. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Dissecting multistep tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:479–519. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Transgenic mice as probes into complex systems. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1265–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.2686032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Mullins J. J., Kuhn N. J., Gallagher J. F., Gu G. D., Gross K. W. T antigen expression and tumorigenesis in transgenic mice containing a mouse major urinary protein/SV40 T antigen hybrid gene. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):183–191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Roberts S., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Costantini F. D. A foreign beta-globin gene in transgenic mice: integration at abnormal chromosomal positions and expression in inappropriate tissues. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon K. A., Chepelinsky A. B., Khillan J. S., Overbeek P. A., Piatigorsky J., Westphal H. Oncogenesis of the lens in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1622–1628. doi: 10.1126/science.3029873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold R. F., Overell R. W. Fibroblast immortality is a prerequisite for transformation by EJ c-Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):648–651. doi: 10.1038/304648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Molecular genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Hammer R. E., Messing A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic neoplasia induced by SV40 T-antigen expression in acinar cells of transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):188–193. doi: 10.1126/science.2821617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittius C. W., Hennighausen L., Lee E., Westphal H., Nicols E., Vitale J., Gordon K. A milk protein gene promoter directs the expression of human tissue plasminogen activator cDNA to the mammary gland in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5874–5878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. K., Hoekzema G. S., Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Jay G. Multiple endocrine neoplasia induced by the promiscuous expression of a viral oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3135–3139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. High-level erythroid expression of human alpha-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):37–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Stanton L. W., Riley S. C., Marcu K. B., Witte O. N. Synergism of v-myc and v-Ha-ras in the in vitro neoplastic progression of murine lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3221–3231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinn E., Muller W., Pattengale P., Tepler I., Wallace R., Leder P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Orkin S. A rapid method for characterizing transgenic mice. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):34–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Khoury G., Jay G., Howley P. M., Scangos G. A. Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda Y., Aizawa S., Hirai S., Inoue T., Furuta Y., Suzuki M., Hirohashi S., Ikawa Y. Driven by the same Ig enhancer and SV40 T promoter ras induced lung adenomatous tumors, myc induced pre-B cell lymphomas and SV40 large T gene a variety of tumors in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4055–4065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Simmons D. M., Arriza J., Hammer R., Brinster R., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Novel developmental specificity in the nervous system of transgenic animals expressing growth hormone fusion genes. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):363–366. doi: 10.1038/317363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Hauft S. M., Hoppe P. C., Birkenmeier E. H., Gordon J. I. Transgenic mice containing intestinal fatty acid-binding protein-human growth hormone fusion genes exhibit correct regional and cell-specific expression of the reporter gene in their small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9611–9615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Kruse F., MacDonald R. J., Hammer R. E. Differential requirements for cell-specific elastase I enhancer domains in transfected cells and transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):687–696. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Borregaard N., Simons E., Wright J. Chronic granulomatous disease: a syndrome of phagocyte oxidase deficiencies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. C., Southgate J., Kitchener G., Land H. Multistage carcinogenesis induced by ras and myc oncogenes in a reconstituted organ. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):917–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Albert D. M., O'Brien J. M., Marcus D. M., Disteche C. M., Bernards R., Mellon P. L. Retinoblastoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):665–669. doi: 10.1038/343665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nisen P. D., Tesfaye A., Kohl N. E., Goldfarb M. P., Alt F. W. N-myc can cooperate with ras to transform normal cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]