Abstract
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephelopathy is an autosomal dominant disease affecting small vessels and often resulting in subcortical infarcts. A skin biopsy may facilitate its diagnosis as the cutaneous surface is much easier to sample than the central nervous system’s tissue. Unfortunately, there is no effective treatment available today.
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is an autosomal dominant, small-vessel disease characterized by multiple subcortical ischemic infarcts. These infarcts mainly involve the central nervous system and can lead to disability and dementia.1,2 Linkage studies identified a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene on chromosome 19 as the genetic defect in CADASIL.3 The prevalence of the NOTCH3 gene mutation is 4.14 per 100,000 adults as estimated in a registry for CADASIL in Scotland.4 CADASIL is caused by mutations in one of the exons (from 2 to 24 out of the 33 exons) of the NOTCH3 gene within the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-like repeats in the extracellular domain of the NOTCH3 protein.5–7 More than 150 mutations have been identified so far and clustering of mutations on exons 3,4,5,8, and 11 has been reported.8,9 The missense mutations lead to a cysteine substitution in the EGFR on the extracellular N-terminal domain.8 This is thought to cause a defect in transendothelial exchange. Besides familial occurrence, sporadic cases are known to occur, which are more likely to go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed.10 In 70 percent of families, the mutations are located on exons 3 and 4 that encode the first 5 EGF domains.8
A skin biopsy from a normal appearing cutaneous area can be very helpful in diagnosing CADASIL as the vascular changes can be observed using electron microscopy.11,12 The knowledge of CADASIL among dermatopathologists is important as patients with CADASIL may be referred by neurologists to carry out and interpret skin biopsies, ultimately providing a key diagnostic input. Additionally, a skin biopsy also helps to detect a carrier status.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS
The clinical presentation of CADASIL mainly consists of a migraine with an aura, subcortical ischemic events, mood disturbances, motor disability, cognitive impairment, and apathy (Table 1).13–16
TABLE 1.
Neurological symptoms in CADASIL syndrome
| SYMPTOMS | FREQUENCY IN CADASIL PATIENTS | APPROXIMATE AGE OF ONSET (RANGE) | POSSIBLE PRESENTATIONS | OTHER COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine with aura (M/A) | 20-40%18,35,36 | 30 years (6-18 years)15,37 |
|
|
| Subcortical ischemic events (stroke/transient ischemic attacks [TIA]) | 60-80%2,14,38,39 | 45-50 years (20-70 years) in case of absence of conventional vascular risk factors14,35,36,40 |
|
|
| Mood disturbance | 20% mainly severe depressive episodes13,41 | Not described |
|
|
| Cognitive impairment, dementia, apathy | Dementia: 60% of patients >60 years of age42-44 Apathy: 40%16 | Not described |
|
|
| Motor disability | Median age for inability to walk without assistance: 59 years in males and 62 years in females51 |
|
Age at death has been noted to be significantly lower in men (median age—64.6 years) than in women (median age—70.7 years)51 | |
| Other neurological manifestations | Seizures (focal/generalize): 5-10% of the patients14,52 |
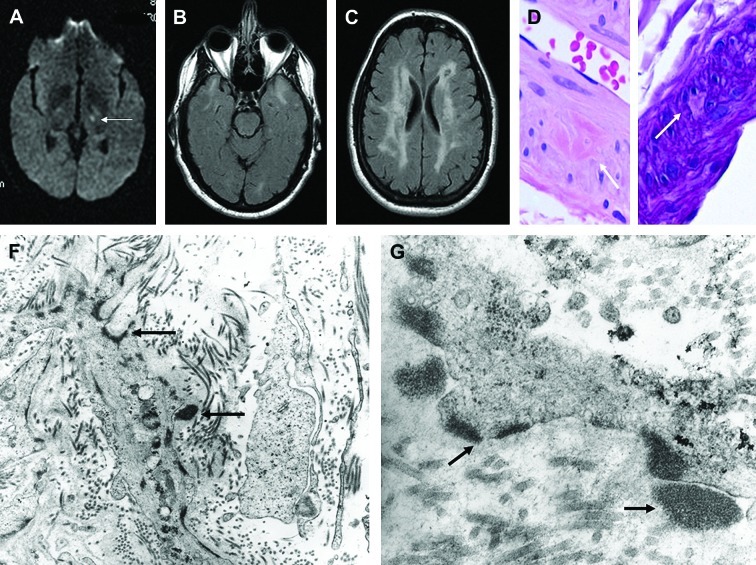
For the purpose of diagnosis, the history of multiple early-onset ischemic events is generally an important clue. These can be detected upon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cerebral angiography and seen as lacunar infarcts in the basal ganglia and brainstem. MRI on T2-weighted images or fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences may demonstrate hyperintensity in the white matter associated with areas of focal hyperintensity in the basal ganglia, thalamus, and brainstem (Figure 1).17,18 The extent varies greatly and generally worsens rapidly with age. Cerebral angiography can reveal intracranial stenosis, but it is not recommended due to a high rate of complications.19,20 CADASIL should be suspected with a high level of suspicion in the presence of a suspicious family history. Genetic testing is the gold standard for the diagnosis of CADASIL. A screening of the 23 exons that encode for the 34EGFR was shown to possess 100-percent specificity and almost 100-percent sensitivity,7,8,21 but 90 percent of mutations occur in exons 2 and 6.7
Figure 1.
Radiologic findings in patient with CADASIL disease. (A) Magnetic resonance imaging (at age 43 years, when patient developed acute-onset right hemiparesis and dysarthria), revealed left internal capsule lacunar infarct (arrow). On T2-weighted images, there were symmetric hyperintense signals in white matter of both temporal lobes (B), and diffuse hyperintense signals in subcortical and deep white matter (C). Light microscopic examination of skin biopsy specimen fixed in formalin revealed rare dermal arteriole exhibiting focal aggregates of eosinophilic material (D), which was PAS positive diastase resistant, and focally replaced smooth muscle cells of media (E). (F) and (G) On transmission electron microscopic examination of tissue fixed in glutaraldehyde, GOM deposits (black deposits marked by arrows) were identified in extracellular matrix, adjacent to and within smooth muscle cells of dermal arterioles. Some of the extracellular deposits appeared to indent cell membranes of atrophic/degenerated smooth muscle cells of media. (F and G, Original magnifications: F, x 23,000; G, x 73,000.) Reproduced with permission from Elsevier.
PATHOLOGY
The pathognomonic features of CADASIL observed on histology consist of an arteriopathy, mainly affecting small penetrating cerebral and lepto-meningeal arteries, which show wall thickening with subsequent stenosis of the lumen and ultimately ischemia. The ultrastructural features exhibit a typical granular osmiophilic material (GOM) deposited around the smooth muscle cells and pericytes of small- and medium-sized arterioles of mainly the brain, but could also involve skeletal muscles, myocardium, peripheral nerves, liver, kidney, intestines, and the skin (Figure 1).22–24 The chemical nature of GOM is unknown. The GOM in CADASIL stains with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) suggesting that it has acid polysaccharide, while it was demonstrated that the GOM does not contain amyloid, elastin, chromatin, calcium, or iron.22 The GOM has not been found to be consistent with metal, mineral, immunoglobulins, complement proteins, heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), cystatin C, transthyretin, gelsolin, fibrinogen, ubiquitin, cathepsin D, or a1-antichymotrypsin.22,25 Positive staining has been observed with aB crystallin, which is found within myocytes suggesting depositions from degenerating myocytes.26 The nonpathognomonic ultrastructural findings reported in CADASIL include reduplication of the basal lamina of the dermal capillaries, attenuation of endothelial cells, and abnormal elastic fibers.27,28
CADASIL AND THE SKIN
Walsh et al28 reported a case involving a 47-year-old woman who presented with a history of several early-onset ischemic strokes and a similar family history. Besides MRI and cerebral angiography that suggested CNS vasculitis, brain and skin biopsies were obtained. The specimen for skin biopsy was obtained from an area of normal-appearing abdominal skin. The electron microscopy of this biopsy showed scattered granular, electron dense material abutting the vascular smooth muscle cells in cutaneous arterioles.
Clinically evident skin lesions in CADASIL are almost never observed. However, Ratzinger et al29 reported a case of a 47-year-old man who presented with generalized, asymptomatic, reddish-brown, round-to-oval, well-defined, focally hemorrhagic macules and patches.29 The patient had continuously developed more skin lesions from the age of 25 years and had suffered from recurring transient ischemic attacks, multiple ischemic strokes, and cerebral bleeding as well as grand mal epilepsy with one episode of status epilepticus. Biopsies of lesional and nonlesional skin from the patient’s trunk revealed prominent superficial vascular plexus with an increased number of elongated and dilated vessels and a mild perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes. The walls of capillaries, postcapillary venules and small arteries were thickened and hyalinized by a homogeneous, eosinophilic material that stained positive for PAS. GOM was observed on electron microscopy. Direct immunofluorescence showed an increased number of vessels with markedly thickened walls by deposits of fibrin, C3, immunoglobulin (Ig) M, and IgA. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of CADASIL with cutaneous involvement, reported for the first time.
MANAGEMENT
The management of CADASIL is multidisciplinary with involvement of neurologists, neurosurgeons, dermatologists, dermatopathologists, family practitioners and internists. Awareness of this condition can lead to its early recognition and hence prevent complications mainly related to ischemic events. Genetic testing in asymptomatic patients is a topic of debate due to associated ethical and psychological impacts, as seen with other familial neurological diseases.30
Currently, there is no effective treatment of CADASIL. The use of aspirin is common as a secondary prevention to reduce the risk of cerebral ischemic phenomena. However, it can cause hemorrhagic events and should be used with caution.31–33 Migraine with an aura should be managed with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) and analgesics. Vasoconstrictors (such as triptans) are not recommended due to the possibility of inducing an ischemic event. For prophylaxis, the usual antiepileptic drugs and beta blockers can be used. Caution should be used to avoid hypoperfusion in ischemic locations. Statins can be used in patients with hypercholesterolemia and may also be helpful in preventing/delaying arterial disease. Donepezil showed no effect on cognitive scales, but demonstrated improvement of executive functions.34 Rehabilitation, physiotherapy, and support from family and relatives is an important component.
Footnotes
DISCLOSURE:The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Tournier-Lasserve E, Joutel A, Melki J, et al. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy maps to chromosome 19q12. Nat Genet. 1993;3:256–259. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E. Summary of the proceedings of the First International Workshop on CADASIL Paris, May 19-21, 1993. Stroke. 1994;25:704–707. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.3.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, et al. Notch3 mutations in CADASIL a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature. 1996;383:707–710. doi: 10.1038/383707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Razvi SS, Davidson R, Bone I, Muir KW. The prevalence of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL) in the west of Scotland. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:739–741. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.051847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, et al. Notch3 mutations in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), a mendelian condition causing stroke and vascular dementia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;826:213–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dotti MT, Federico A, Mazzei R, et al. The spectrum of Notch3 mutations in 28 Italian CADASIL families. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:736–738. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.048207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Peters N, Opherk C, Bergmann T, et al. Spectrum of mutations in biopsy-proven CADASIL: implications for diagnostic strategies. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1091–1094. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.7.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Joutel A, Vahedi K, Corpechot C, et al. Strong clustering and stereotyped nature of Notch3 muations in CADASIL patients. Lancet. 1997;350:1511–1515. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)08083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Federico A, Bianchi S, Dotti MT. The spectrum of mutations for CADASIL diagnosis. Neurol Sci. 2005;26:117–124. doi: 10.1007/s10072-005-0444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Joutel A, Dodick DD, Parisi JE, et al. De novo mutation in the Notch3 gene causing CADASIL. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ebke M, Dichgans M, Bergmann M, et al. CADASIL: skin biopsy allows diagnosis in early stages. Acta Neurol Scand. 1997;95:351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1997.tb00224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goebel HH, Meyermann R, Rosin R, Schlote W. Characteristic morphologic manifestation of CADASIL cerebral autosomal-dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, in skeletal muscle and skin. Muscle Nerve. 1997;20:625–627. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199705)20:5<625::aid-mus17>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chabriat H, Vahedi K, Iba-Zizen MT, et al. Clinical spectrum of CADASIL: a study of 7 families. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1995;346:934–939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91557-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dichgans M, Mayer M, Uttner I, et al. The phenotypic spectrum of CADASIL: clinical findings in 102 cases. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:731–739. doi: 10.1002/ana.410440506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Desmond DW, Moroney JT, Lynch T, et al. The natural history of CADASIL: a pooled analysis of previously published cases. Stroke. 1999;30:1230–1233. doi: 10.1161/01.str.30.6.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Reyes S, Viswanathan A, Godin O, et al. Apathy: a major symptom in CADASIL. Neurology. 2009;72:905–910. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000344166.03470.f8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chabriat H, Levy C, Taillia H, et al. Patterns of MRI lesions in CADASIL. Neurology. 1998;51:452–457. doi: 10.1212/wnl.51.2.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dichgans M, Filippi M, Bruning R, et al. Quantitative MRI in CADASIL: correlation with disability and cognitive performance. Neurology. 1999;52:1361–1367. doi: 10.1212/wnl.52.7.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Choi EJ, Choi CG, Kim JS. Large cerebral artery involvement in CADASIL. Neurology. 2005;65:1322–1324. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000180965.79209.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dichgans M, Petersen D. Angiographic complications in CADASIL. Lancet. 1997;349:776–777. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)60202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Monet M, Domenga V, Lemaire B, et al. The archetypal R90CCADASIL-NOTCH3 mutation retains NOTCH3 function in vivo. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:982–992. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.LaPoint SF, Patel U, Rubio A. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) Adv Anat Pathol. 2000;7:307–321. doi: 10.1097/00125480-200007050-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ruchoux MM, Guerouaou D, Vandenhaute B, et al. Systemic vascular smooth muscle cell impairment in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1995;89:500–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00571504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ruchoux MM, Chabriat H, Bousser MG, Baudrimont M, Tournier-Lasserve E. Presence of ultrastructural arterial lesions in muscle and skin vessels of patients with CADASIL. Stroke. 1994;25:2291–2292. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.11.2291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schroder J, Sebold V, Isenberg C, et al. Eels-analysis revealed negative metal and mineral evidence in GOM-deposits in a CADASIL patient (Abstract) J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:929. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rubio A, Rifkin D, Powers JM, et al. Phenotypic variability of CADASIL and novel morphologic findings. Acta Neuropathol. 1997;94:247–254. doi: 10.1007/s004010050700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ruchoux MM, Maurage CA. Endothelial changes in muscle and skin biopsies in patients with CADASIL. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1998;24:60–65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.1998.00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Walsh JS, Perniciaro C, Meschia JF. CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy): diagnostic skin biopsy changes determined by electron microscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:1125–1127. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2000.110895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ratzinger G, Ransmayr G, Romani N, Zelger B. CADASIL—an unusual manifestation with prominent cutaneous involvement. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152:346–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chabriat H, Joutel A, Dichgans M, Tournier-Lasserve E, Bousser MG. CADASIL. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:643–653. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Baudrimont M, Dubas F, Joutel A, Tournier-Lasserve E, Bousser MG. Autosomal dominant leukoencephalopathy and subcortical ischemic stroke. A clinicopathological study. Stroke. 1993;24:122–125. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Maclean AV, Woods R, Alderson LM, et al. Spontaneous lobar haemorrhage in CADASIL. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:456–457. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.042564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ragoschke-Schumm A, Axer H, Fitzek C, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage in CADASIL. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:1606–1607. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.059212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dichgans M, Markus HS, Salloway S, et al. Donepezil in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment: a randomised double-blind trial in CADASIL. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:310–318. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chabriat H, Joutel A, Vahedi K, et al. [CADASIS. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalophathy] Rev Neurol (Paris). 1997;153:376–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Desmond DW, Moroney JT, Lynch T, et al. CADASIL in a North American family: clinical, pathologic, and radiologic findings. Neurology. 1998;51:844–849. doi: 10.1212/wnl.51.3.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vahedi K, Chabriat H, Levy C, et al. Migraine with aura and brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in patients with CADASIL. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:1237–1240. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.8.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Peters N, Herzog J, Opherk C, Dichgans M. A two-year clinical follow-up study in 80 CADASIL subjects: progression patterns and implications for clinical trials. Stroke. 2004;35:1603–1608. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000131546.71733.f1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Singhal S, Bevan S, Barrick T, Rich P, Markus HS. The influence of genetic and cardiovascular risk factors on the CADASIL phenotype. Brain. 2004;127:2031–2038. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chabriat H, Tournier-Lasserve E, Vahedi K, et al. Autosomal dominant migraine with MRI white-matter abnormalities mapping to the CADASIL locus. Neurology. 1995;45:1086–1091. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chabriat H, Joutel A, Vahedi K, et al. [CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy): clinical features and neuroimaging] Bull Acad Natl Med. 2000;184:1523–1531. discussion 31-33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Buffon F, Porcher R, Hernandez K, et al. Cognitive profile in CADASIL. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77:175–180. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2005.068726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Taillia H, Chabriat H, Kurtz A, Verin M, Levy C, Vahedi K, et al. Cognitive alterations in non-demented CADASIL patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1998;8:97–101. doi: 10.1159/000015825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Peters N, Opherk C, Danek A, et al. The pattern of cognitive performance in CADASIL: a monogenic condition leading to subcortical ischemic vascular dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162:2078–2085. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.11.2078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hedera P, Friedland RP. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy: study of two American families with predominant dementia. J Neurol Sci. 1997;146:27–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(96)00272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Blanco Menendez R, Aguado Balsas AM, Blanco E, Lobo Rodriguez B, Vera De La Puente E. [The CADASIL syndrome: a model of subcortical-cortical disconnection] Rev Neurol. 2001;32:750–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tatsch K, Koch W, Linke R, et al. Cortical hypometabolism and crossed cerebellar diaschisis suggest subcortically induced disconnection in CADASIL: an 18F-FDG PET study. JNucl Med. 2003;44:862–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.O’Sullivan M, Barrick TR, Morris RG, Clark CA, Markus HS. Damage within a network of white matter regions underlies executive dysfunction in CADASIL. Neurology. 2005;65:1584–1590. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000184480.07394.fb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Felician O, Barbeau E, Gavaret M, et al. A case of late-onset CADASIL with interhemispheric disconnection features. J Neurol. 2003;250:1242–1244. doi: 10.1007/s00415-003-0162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Herve D, Chabriat H. Cadasil. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2010;23:269–276. doi: 10.1177/0891988710383570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Opherk C, Peters N, Herzog J, Luedtke R, Dichgans M. Long-term prognosis and causes of death in CADASIL: a retrospective study in 411 patients. Brain. 2004;127:2533–2539. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Malandrini A, Carrera P, Ciacci G, et al. Unusual clinical features and early brain MRI lesions in a family with cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy. Neurology. 1997;48:1200–1203. doi: 10.1212/wnl.48.5.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]