Abstract
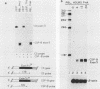
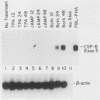
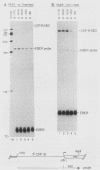
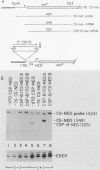
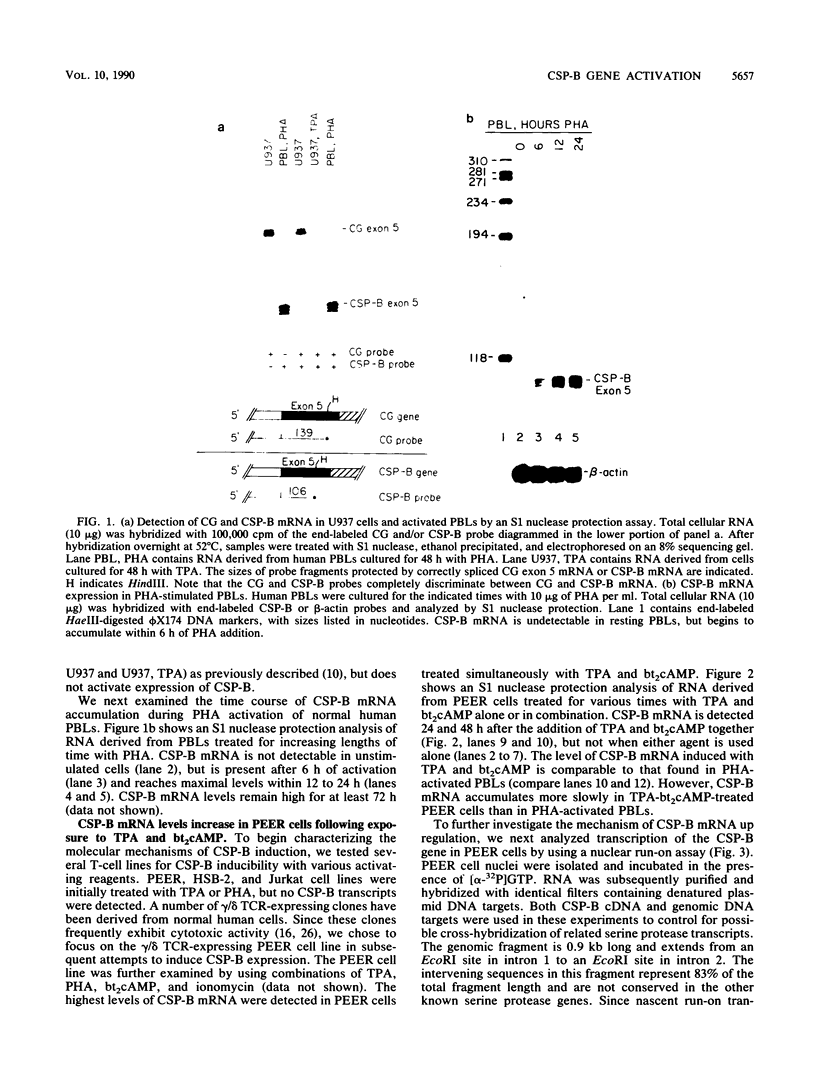
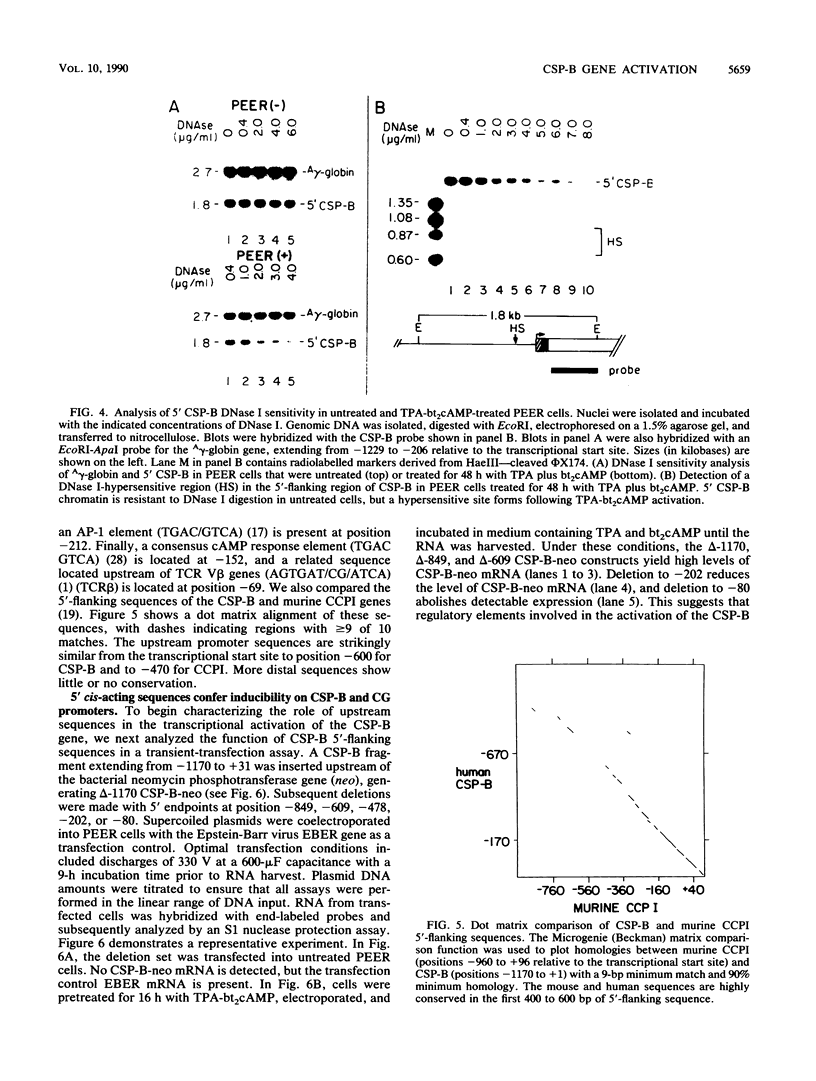
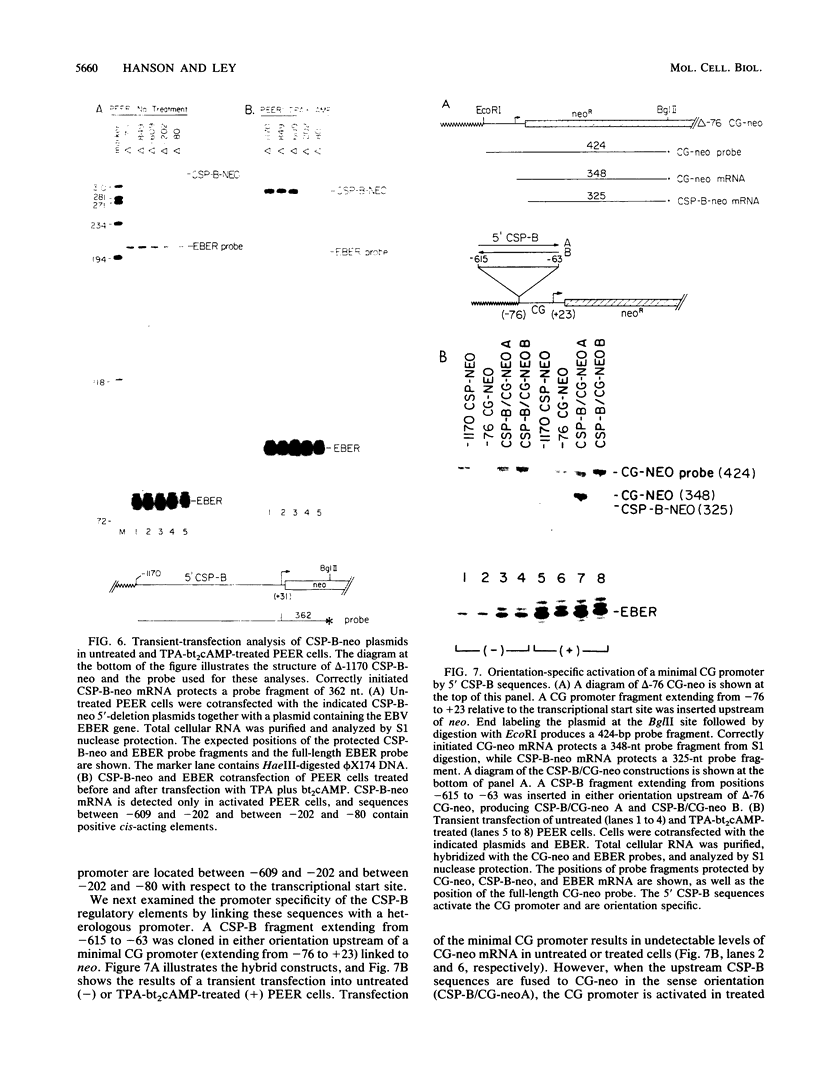
The cytotoxic serine protease B (CSP-B) gene is activated during cytotoxic T-lymphocyte maturation. In this report, we demonstrate that the PEER T-cell line (bearing gamma/delta T-cell receptors) accumulates CSP-B mRNA following exposure to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and N6-2'-O-dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (bt2cAMP) because of transcriptional activation of the CSP-B gene. TPA and bt2cAMP act synergistically to induce CSP-B expression, since neither agent alone causes activation of CSP-B transcription or mRNA accumulation. Chromatin upstream from the CSP-B gene is resistant to DNase I digestion in untreated PEER cells, but becomes sensitive following TPA-bt2cAMP treatment. Upon activation of PEER cells, a DNase I-hypersensitive site forms upstream from the CSP-B gene within a region that is highly conserved in the mouse. Transient transfection of CSP-B promoter constructs identified two regulatory regions in the CSP-B 5'-flanking sequence, located at positions -609 to -202 and positions -202 to -80. The region from -615 to -63 is sufficient to activate a heterologous promoter in activated PEER cells, but activation is orientation specific, suggesting that this region behaves as an upstream promoter element rather than a classical enhancer. Consensus AP-1, AP-2, and cAMP response elements are found upstream from the CSP-B gene (as are several T-cell-specific consensus elements), but the roles of these elements in CSP-B gene activation have yet to be determined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. J., Chou H. S., Loh D. Y. A conserved sequence in the T-cell receptor beta-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Dosseto M., Denizot F., Mattei M. G., Clark W. R., Haqqi T. M., Ferrier P., Nabholz M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Luciani M. F. The inducible cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated gene transcript CTLA-1 sequence and gene localization to mouse chromosome 14. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):268–271. doi: 10.1038/322268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Lonberg N., Dunlap S., Lacy E., Terhorst C. An enhancer located in a CpG-island 3' to the TCR/CD3-epsilon gene confers T lymphocyte-specificity to its promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Connolly N. L., Burnett D., Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., Ley T. J. Developmental regulation of the human cathepsin G gene in myelomonocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1524–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. D., Hohn P. A., Popescu N. C., Ley T. J. A cluster of hematopoietic serine protease genes is found on the same chromosomal band as the human alpha/delta T-cell receptor locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):960–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Berrebi G. A., Takayama H., Munger W. E., Sitkovsky M. V. Biochemical and functional properties of serine esterases in acidic cytoplasmic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2398–2405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Yang L. H., Morle G., Leiden J. M. A T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer element 3' of C alpha in the human T-cell receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6714–6718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn P. A., Popescu N. C., Hanson R. D., Salvesen G., Ley T. J. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the human cathepsin G gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13412–13419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide J., Rivas A., Engleman E. G. Natural killer (NK)-like cytotoxic activity of allospecific T cell receptor-gamma,delta+ T cell clones. Distinct receptor-ligand interactions mediate NK-like and allospecific cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4161–4168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Maloney K. A., Gordon J. I., Schwartz A. L. Globin gene expression in erythroid human fetal liver cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1032–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI113944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Shaw J., Fregeau C., Duggan B., Meier M., Brewer A., Upton C., McFadden G., Patient R. K., Paetkau V. Transcriptional regulation of two cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific serine protease genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5765–5779. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier M., Kwong P. C., Frégeau C. J., Atkinson E. A., Burrington M., Ehrman N., Sorensen O., Lin C. C., Wilkins J., Bleackley R. C. Cloning of a gene that encodes a new member of the human cytotoxic cell protease family. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4042–4049. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2379–2388. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Kane K. P., Mescher M. F., Clark W. R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated lysis without release of serine esterase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):71–72. doi: 10.1038/330071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Wacholtz M. C., Duby A. D., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Analysis of the functional capabilities of CD3+CD4-CD8- and CD3+CD4+CD8+ human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1108–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond M. J., Letellier M., Parker J. M., Lobe C., Havele C., Paetkau V., Bleackley R. C. A serine protease (CCP1) is sequestered in the cytoplasmic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3184–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Weissmann C. Induction of mRNA for a serine protease and a beta-thromboglobulin-like protein in mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. Evidence for the involvement of a T-cell-associated serine protease (TSP-1) in cell killing. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Mar-Apr;138(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Groudine M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D., Weintraub H. Hb switching in chickens. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapani J. A., Klein J. L., White P. C., Dupont B. Molecular cloning of an inducible serine esterase gene from human cytotoxic lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenn G., Takayama H., Sitkovsky M. V. Exocytosis of cytolytic granules may not be required for target cell lysis by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):72–74. doi: 10.1038/330072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Sheppard J. R., Foker J. E. Rise and fall of cyclic AMP required for onset of lymphocyte DNA synthesis. Science. 1978 Jul 14;201(4351):155–157. doi: 10.1126/science.208147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannelli J. R., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L., Engelhard V. H. Reorientation and fusion of cytotoxic T lymphocyte granules after interaction with target cells as determined by high resolution cinemicrography. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]