Abstract
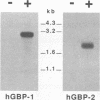
The primary structures of interferon (IFN)-induced guanylate-binding proteins (GBPs) were deduced from cloned human and murine cDNAs. These proteins contained only two of the three sequence motifs typically found in GTP/GDP-binding proteins. The N(T)KXD motif, which is believed to confer guanine specificity in other nucleotide-binding proteins, was absent. Nevertheless, the IFN-induced GBPs exhibited a high degree of selectivity for binding to agarose-immobilized guanine nucleotides. An interesting feature of IFN-induced GBPs is that they strongly bound to GMP agarose in addition to GDP and GTP agaroses but failed to bind to ATP agarose and all other nucleotide agaroses tested. Both GTP and GMP, but not ATP, competed for binding of murine GBP-1 to agarose-immobilized GMP. The IFN-induced GBPs thus define a distinct novel family of proteins with GTP-binding activity. We further demonstrate that human and murine cells contain at least two genes encoding IFN-induced GBPs. The cloned murine cDNA codes for GBP-1, an IFN-induced protein previously shown to be absent from mice of Gbp-1b genotype.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Becker-Manley M. F., Chow T. P., Horan D. C. Affinity purification of an interferon-induced human guanylate-binding protein and its characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15834–15839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Becker-Manley M. F., Nguyen T. D., DeGrado W. F., Jonak G. J. Nonidentical induction of the guanylate binding protein and the 56K protein by type I and type II interferons. J Interferon Res. 1986 Aug;6(4):417–427. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Colonno R. J., Yin F. H. Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7746–7750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Vogel J. P., Deschenes R. J., Stock J. Posttranslational modification of the Ha-ras oncogene protein: evidence for a third class of protein carboxyl methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn S. A., Ingold A. L., Scholey J. M. Quantitative analysis of sea urchin egg kinesin-driven microtubule motility. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4290–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., McMaster G. K., Zeller H., Wathelet M. G., Dellis J., Content J. Cloning and sequence analyses of cDNAs for interferon- and virus-induced human Mx proteins reveal that they contain putative guanine nucleotide-binding sites: functional study of the corresponding gene promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1171–1181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1171-1181.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Gelfand V. I. Bovine brain kinesin is a microtubule-activated ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8530–8534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Alpha interferon and gamma interferon stimulate transcription of a single gene through different signal transduction pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5404–5411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Collins C. A., Hammarback J. A., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):256–261. doi: 10.1038/347256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic J., Zürcher T., Haller O., Staeheli P. Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3370–3375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3370-3375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Staeheli P., Holmes R. S., Haller O. Interferon-induced guanylate-binding proteins: mapping of the murine Gbp-1 locus to chromosome 3. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjo K., Koland J. G., Hart M. J., Narasimhan V., Johnson D. I., Evans T., Cerione R. A. Molecular cloning of the gene for the human placental GTP-binding protein Gp (G25K): identification of this GTP-binding protein as the human homolog of the yeast cell-division-cycle protein CDC42. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9853–9857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Grob R., Meier E., Sutcliffe J. G., Haller O. Influenza virus-susceptible mice carry Mx genes with a large deletion or a nonsense mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4518–4523. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P. Interferon-induced proteins and the antiviral state. Adv Virus Res. 1990;38:147–200. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60862-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Prochazka M., Steigmeier P. A., Haller O. Genetic control of interferon action: mouse strain distribution and inheritance of an induced protein with guanylate-binding property. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorburger K., Kitten G. T., Nigg E. A. Modification of nuclear lamin proteins by a mevalonic acid derivative occurs in reticulocyte lysates and requires the cysteine residue of the C-terminal CXXM motif. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4007–4013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]