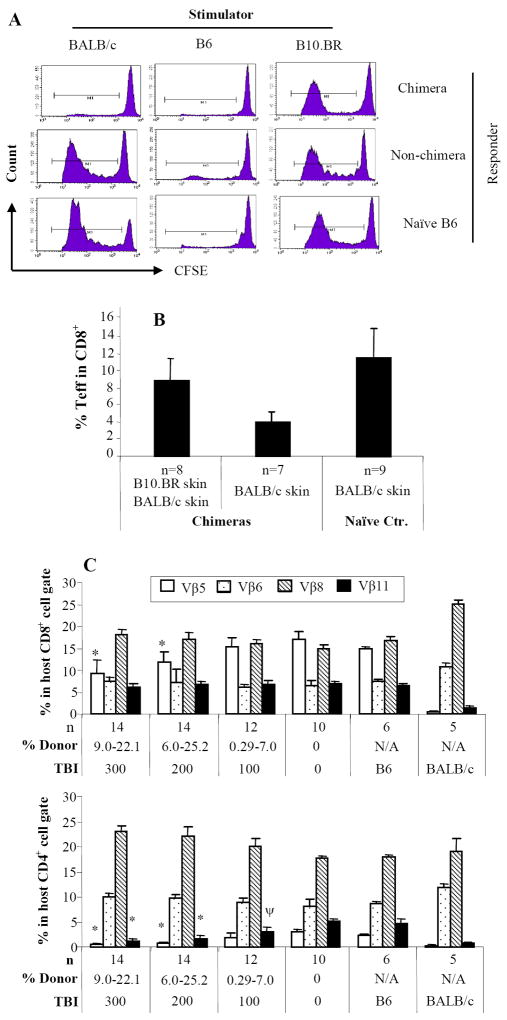
Figure 2. Donor-specific T-cell, humoral, and innate immune tolerance in mixed chimeras.
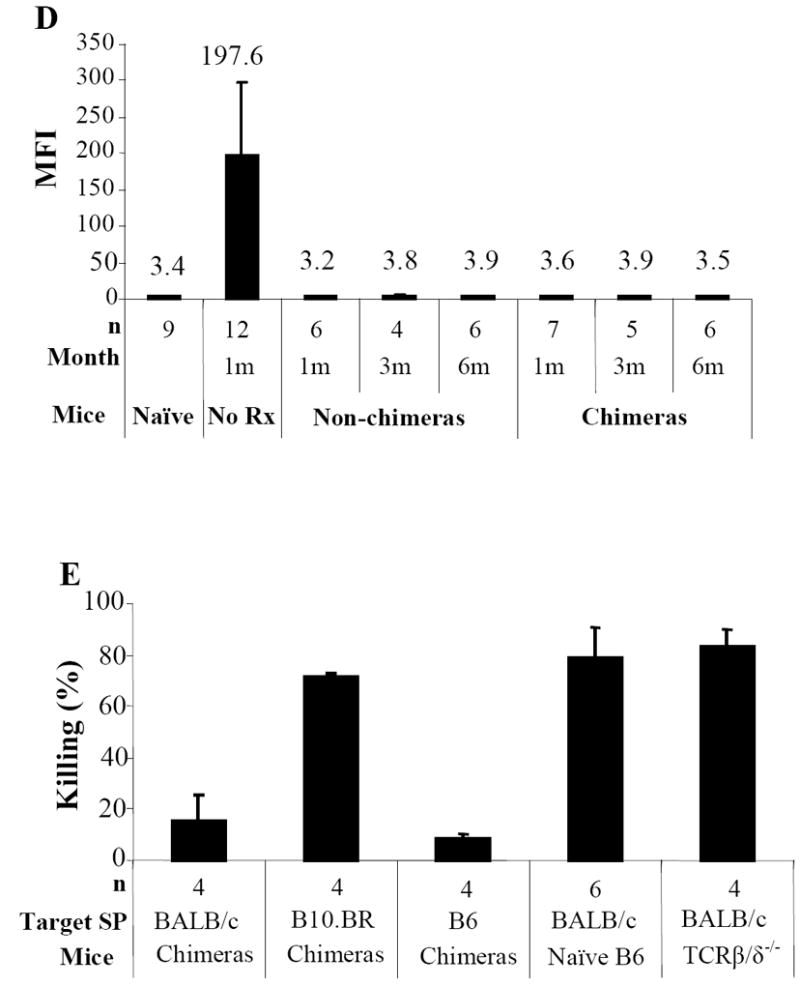
Chimeras (BALB/c → B6) were evaluated for donor-specific T-cell tolerance with in vivo MLR (A). Twenty million carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-labeled splenocytes from chimeras, non-chimeras or naïve B6 were injected i.v. into irradiated (1000cGy) stimulators of donor BALB/c, recipient B6, or third-party B10.BR mice. At day 3, the spleens were harvested and stained with anti-mouse CD8 PerCP and anti-CD4-APC. CFSE intensities were analyzed in CD4+ or CD8+ cells. The proliferating T-cells lost half CFSE fluorescence intensity sequentially with each division. The proliferation resulted in cell events towards downstream divisions. Data from one representative experiment of 3 are shown. Each chimeric animal received skin grafts from donor-specific (BALB/c) and third-party (B10.BR, H-2k) Donor-specific tolerance was further evaluated with effector/memory T-cell expression in chimeras received donor or donor/third-party skin grafts (B). Mixed chimeras received either donor BALB/c or both BALB/c and third-party skin grafts. Recipient PB was collected at day 14 after skin transplantation and cells were stained with anti-CD44-FITC, anti-CD62L-PE, anti-CD4-PerCP, and anti-CD8-APC. Percentages of CD8+/CD44high/CD62Llow/-effector/memory T-cells were measured in CD8+ T-cell gate. For clonal deletion of activated T-cells, expression of Vβ5.1/2, Vβ6, Vβ8.1/2, and Vβ11 in unmanipulated hosts (B6), unmanipulated donors (BALB/c), experimental animals with different levels of donor chimerism from groups of 0 to 300cGy TBI were measured by FACS analysis (C). Relative expression represents the percentage of Vβ-positive cells within the CD8+ or CD4+ T-cell subsets of the host (H2Kb) lymphogate in peripheral blood. Data from 3 experiments are depicted as mean ± SD. Vβ-TCR expression in either experimental group was compared with that in B6 mice using two tailed t-test. Significant P values are indicated above the respective data bars (* P ≤ 0.0005 and ψ P ≤ 0.05). Humoral tolerance in mixed chimeras was studied with FCXM assay (D). Sera were collected from chimeric or non-chimeric mice 1, 3 and 6 months after BMT. Sera from mice receive BMC infusion only and naïve served as controls. Anti-donor antibodies were detected by FCXM assay. One half-million splenocytes from naive BALB/c mice were incubated with 10 μl of sera for 30 minutes. Cells were washed and incubated with FITC-conjugated polyclonal goat anti-mouse Ig, followed by third incubation with PE-conjugated anti-mouse CD4 plus CD8. Gating was carried out on the CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell fraction, and reported as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Innate immune tolerance in mixed chimeras was analyzed using in vivo cytotoxicity assays (E). Single splenocyte suspensions were prepared. Target (BALB/c) and internal control (B6) splenocytes (100 × 106/mL in PBS) were incubated with 4.0 μM or 0.2 μM CFSE, respectively, at room temperature for 10 minutes. Fetal bovine serum was added to quench the reaction. Cells were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and resuspended in PBS, and 20 × 106 cells from each were injected intravenously to chimeras, non-chimeras, T-cell deficient mice (TCRβ/δ-/-), and naïve B6 mice. Chimeras received target and internal control cells both from B6 was served as one of controls. Peripheral blood was collected 18 hours after cell infusion. Peripheral-blood lymphocytes were analyzed for CFSE expression. The percentage of killing was determined by calculating the ratio of target to internal control cells.