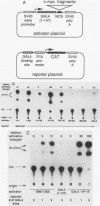
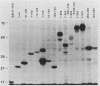
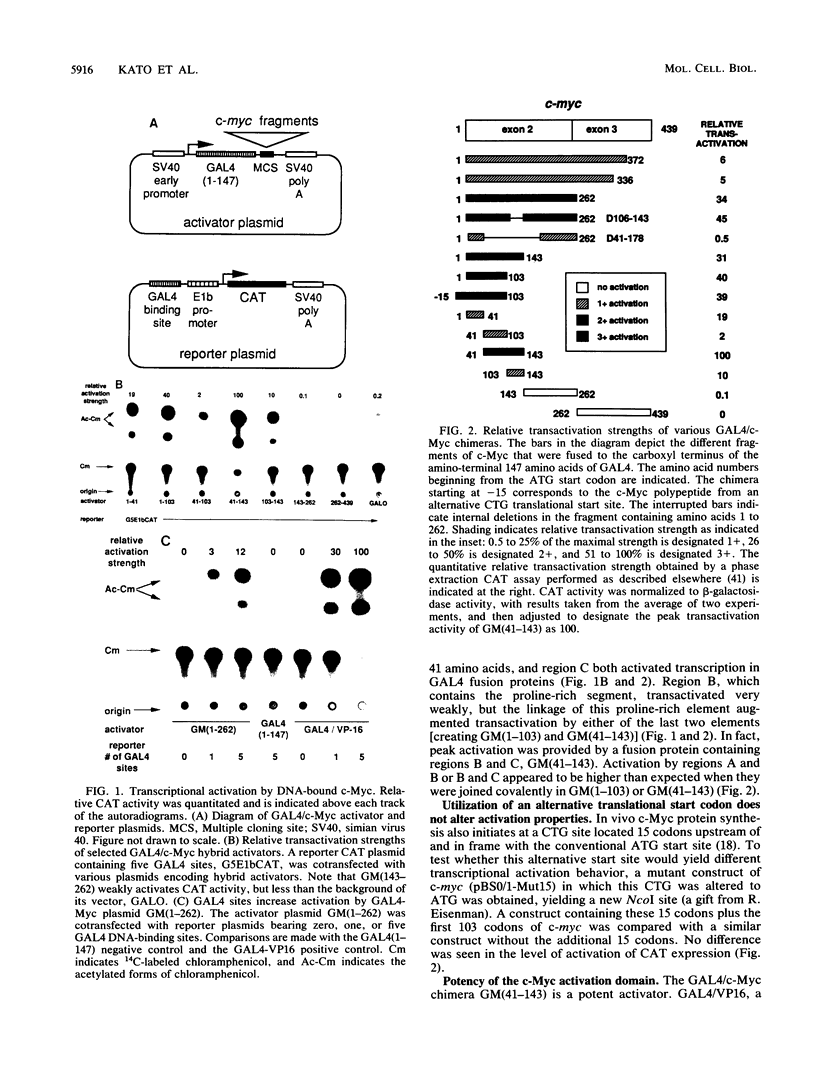
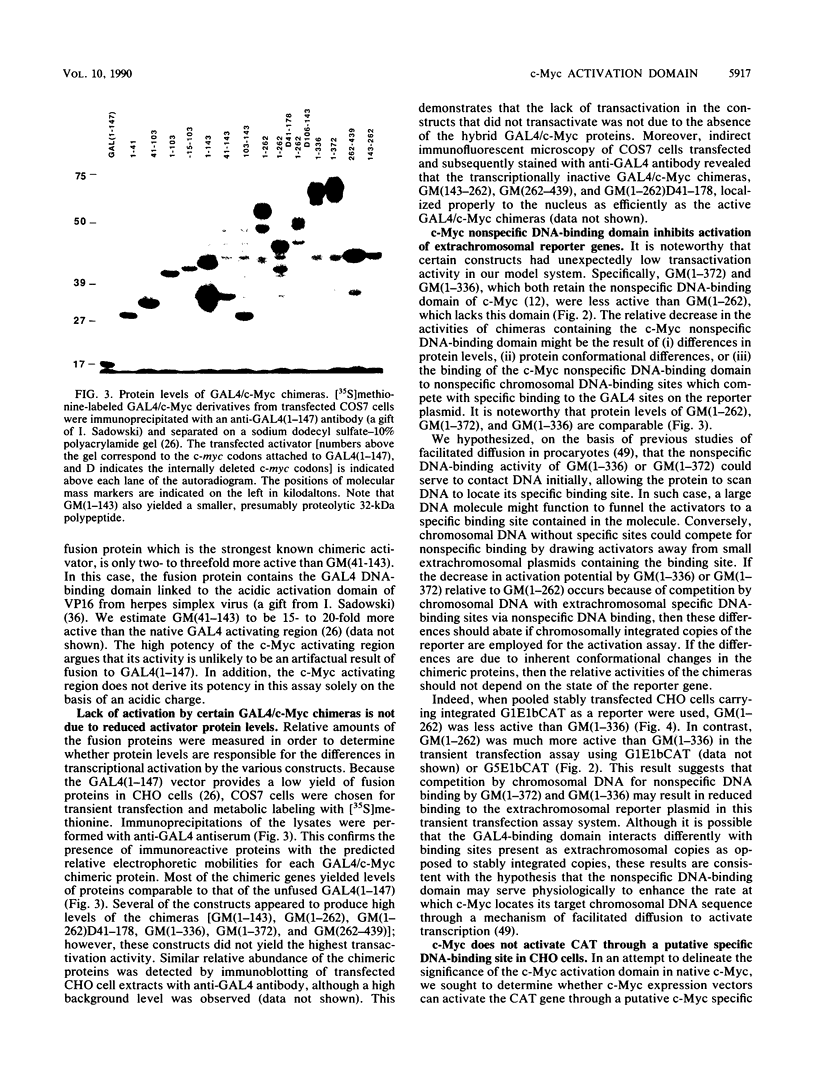
Abstract
The product of the c-myc proto-oncogene is a nuclear phosphoprotein whose normal cellular function has not yet been defined. c-Myc has a number of biochemical properties, however, that suggest that it may function as a potential regulator of gene transcription. Specifically, it is a nuclear DNA-binding protein with a short half-life, a high proline content, segments that are rich in glutamine and acidic residues, and a carboxyl-terminal oligomerization domain containing the leucine zipper and helix-loop-helix motifs that serve as oligomerization domains in known regulators of transcription, such as C/EBP, Jun, Fos, GCN4, MyoD, E12, and E47. In an effort to establish that c-Myc might regulate transcription in vivo, we sought to determine whether regions of the c-Myc protein could activate transcription in an in vitro system. We report here that fusion proteins in which segments of human c-Myc are linked to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4 can activate transcription from a reporter gene linked to GAL4-binding sites. Three independent activation regions are located between amino acids 1 and 143, a region that has been shown to be required for neoplastic transformation of primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with a mutated ras gene. These results demonstrate that domains of the c-Myc protein can function to regulate transcription in a model system and suggest that alterations of Myc transcriptional regulatory function may lead to neoplastic transformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariga H., Imamura Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. DNA replication origin and transcriptional enhancer in c-myc gene share the c-myc protein binding sequences. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4273–4279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Bohmann D., Tsuchie H., Tjian R., Vogt P. K. v-jun encodes a nuclear protein with enhancer binding properties of AP-1. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Van Doren K., Hirsh D., Steitz J. A. Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):559–562. doi: 10.1038/335559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Suzuki M. 'SPKK' motifs prefer to bind to DNA at A/T-rich sites. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4189–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Identification of the human c-myc protein nuclear translocation signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4048–4054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., van Dam H., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. DNA-binding domain of human c-Myc produced in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2477–2486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Webster T., Smith T. F., Paucha E. Prediction of similar transforming regions in simian virus 40 large T, adenovirus E1A, and myc oncoproteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1814–1818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1814-1818.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Definition of the activities and properties of c-myc required to inhibit cell differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jul;1(7):339–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T., Ibanez C., Garcia A., Graf T., Lipsick J. Transformation by v-myb correlates with trans-activation of gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2591–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onclercq R., Gilardi P., Lavenu A., Cremisi C. c-myc products trans-activate the adenovirus E4 promoter in EC stem cells by using the same target sequence as E1A products. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4533-4537.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Land H. Negative autoregulation of c-myc transcription. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1113–1121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Cole M. D. Posttranscriptional regulation of cellular gene expression by the c-myc oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):124–134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):392–392. doi: 10.1038/341392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Visvader J., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Fos-Jun interaction: mutational analysis of the leucine zipper domain of both proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):770–781. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Nagase T., Nakagoshi H., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Delineation of three functional domains of the transcriptional activator encoded by the c-myb protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5758–5762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarid J., Halazonetis T. D., Murphy W., Leder P. Evolutionarily conserved regions of the human c-myc protein can be uncoupled from transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):170–173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweinfest C. W., Fujiwara S., Lau L. F., Papas T. S. c-myc can induce expression of G0/G1 transition genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3080–3087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The DNA-binding domains of the jun oncoprotein and the yeast GCN4 transcriptional activator protein are functionally homologous. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):841–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama A., Kume A., Nemoto K., Lee S. Y., Asami Y., Nemoto F., Nishimura S., Kuchino Y. Isolation and characterization of s-myc, a member of the rat myc gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9144–9148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N., Green C., Pasdar M., Watt R. Characterization and nuclear localization of the v- and c-myc proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:355–361. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidović D., Roglić M., McKune K., Guerder S., MacKay C., Dembić Z. Qa-1 restricted recognition of foreign antigen by a gamma delta T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):646–650. doi: 10.1038/340646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Berg O. G. Facilitated target location in biological systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):675–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]