Abstract
Ras protein requires an intermediate of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway for posttranslational modification and membrane anchorage. This step is necessary for biological activity. Maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes induced by an oncogenic human Ras protein can be inhibited by lovastatin or compactin, inhibitors of the synthesis of mevalonate, an intermediate of cholesterol biosynthesis. This inhibition can be overcome by mevalonic acid or farnesyl diphosphate, a cholesterol biosynthetic intermediate downstream of mevalonate, but not by squalene, an intermediate after farnesyl pyrophosphate in the pathway. This study supports the idea that in Xenopus oocytes, the Ras protein is modified by a farnesyl moiety or its derivative. Furthermore, an octapeptide with the sequence similar to the C-terminus of the c-H-ras protein inhibits the biological activity of Ras proteins in vivo, suggesting that it competes for the enzyme or enzymes responsible for transferring the isoprenoid moiety (prenylation) in the oocytes. This inhibition of Ras prenylation by the peptide was also observed in vitro, using both Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Xenopus oocyte extracts. These observations show that Xenopus oocytes provide a convenient in vivo system for studies of inhibitors of the posttranslational modification of the Ras protein, especially for inhibitors such as peptides that do not penetrate cell membranes.
Full text
PDF

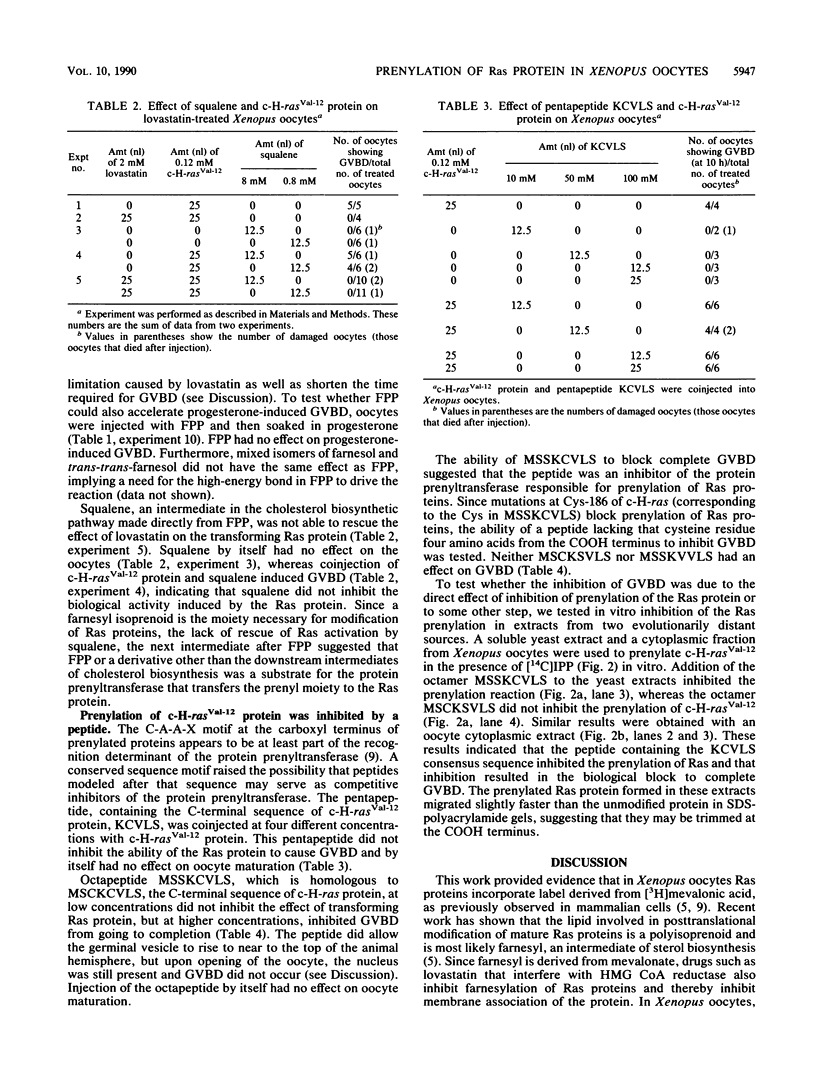
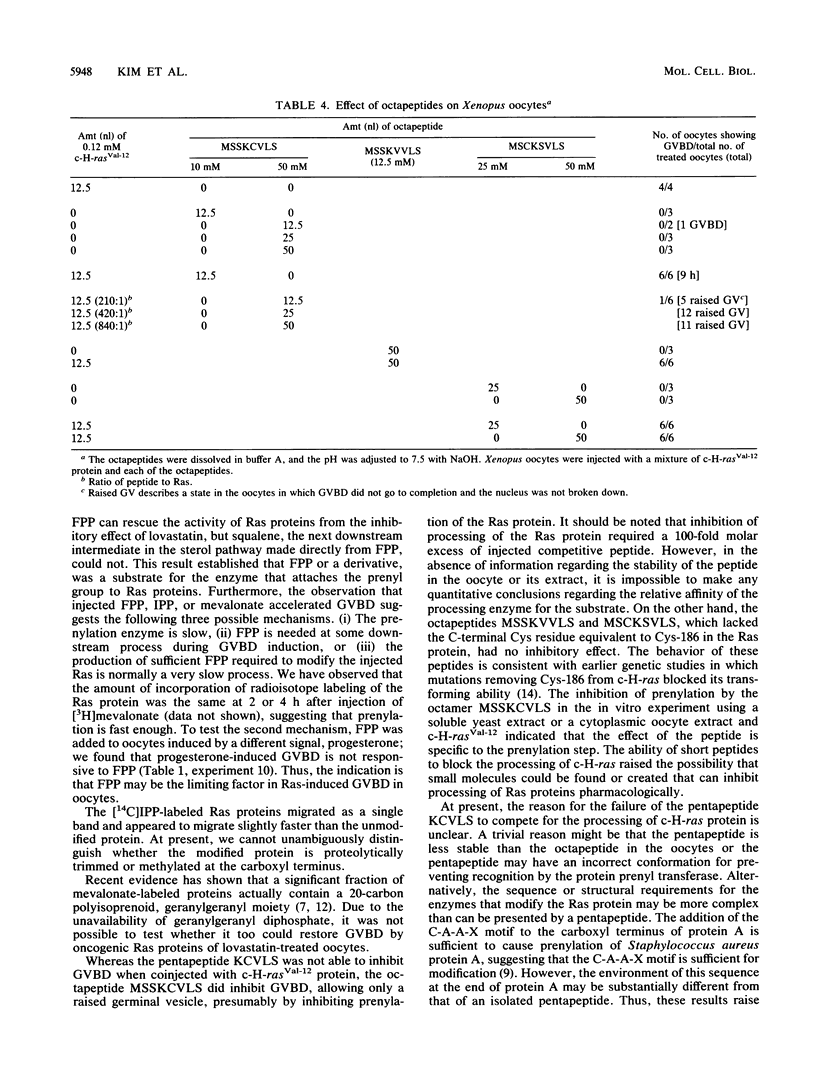

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderegg R. J., Betz R., Carr S. A., Crabb J. W., Duntze W. Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating hormone a-factor. Identification of S-farnesyl cysteine as a structural component. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18236–18240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Direct identification of palmitic acid as the lipid attached to p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Vogel J. P., Deschenes R. J., Stock J. Posttranslational modification of the Ha-ras oncogene protein: evidence for a third class of protein carboxyl methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Identification of geranylgeranyl-modified proteins in HeLa cells. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):320–322. doi: 10.1126/science.2296721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L., Magee A. I., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Post-translational processing of p21ras is two-step and involves carboxyl-methylation and carboxy-terminal proteolysis. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1093–1098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Inoue Y., Nakamori H., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Noguchi S., Nishimura S. Synthesis and expression of a synthetic gene for the activated human c-Ha-ras protein. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;77(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C., Breunger E., Epstein W. W., Crain P. F. Prenylated proteins: the structure of the isoprenoid group. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.2296720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]