Abstract
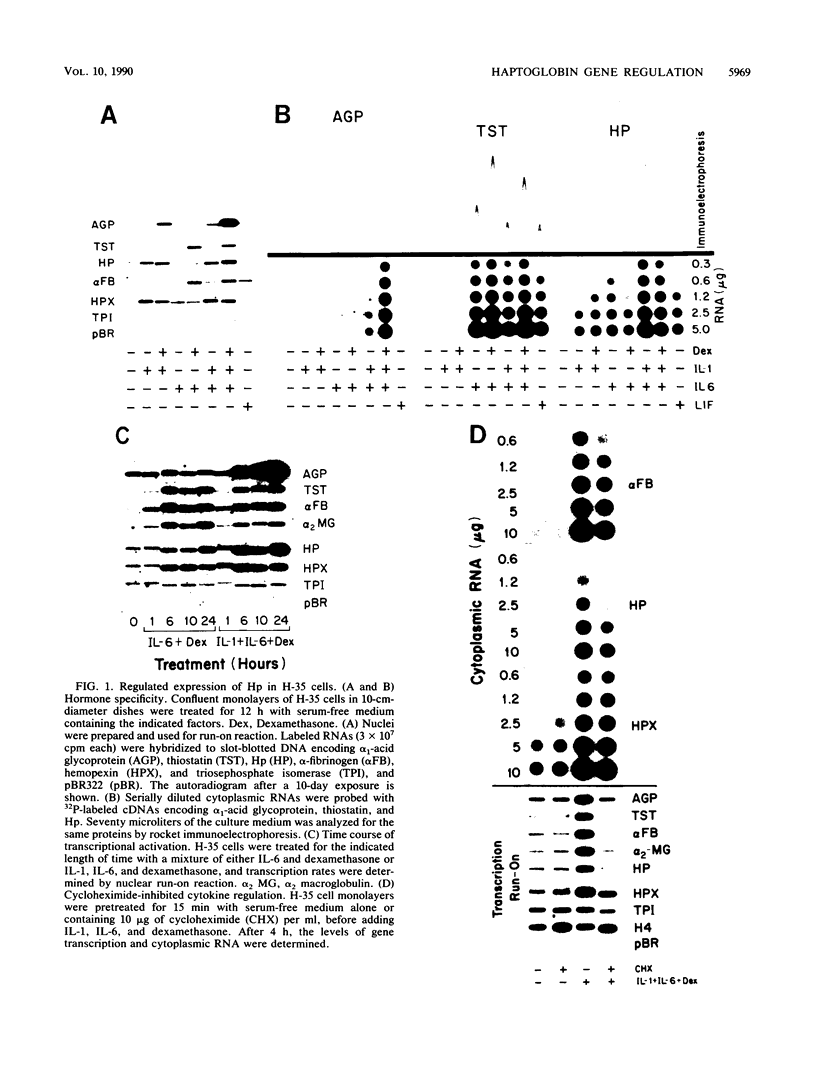
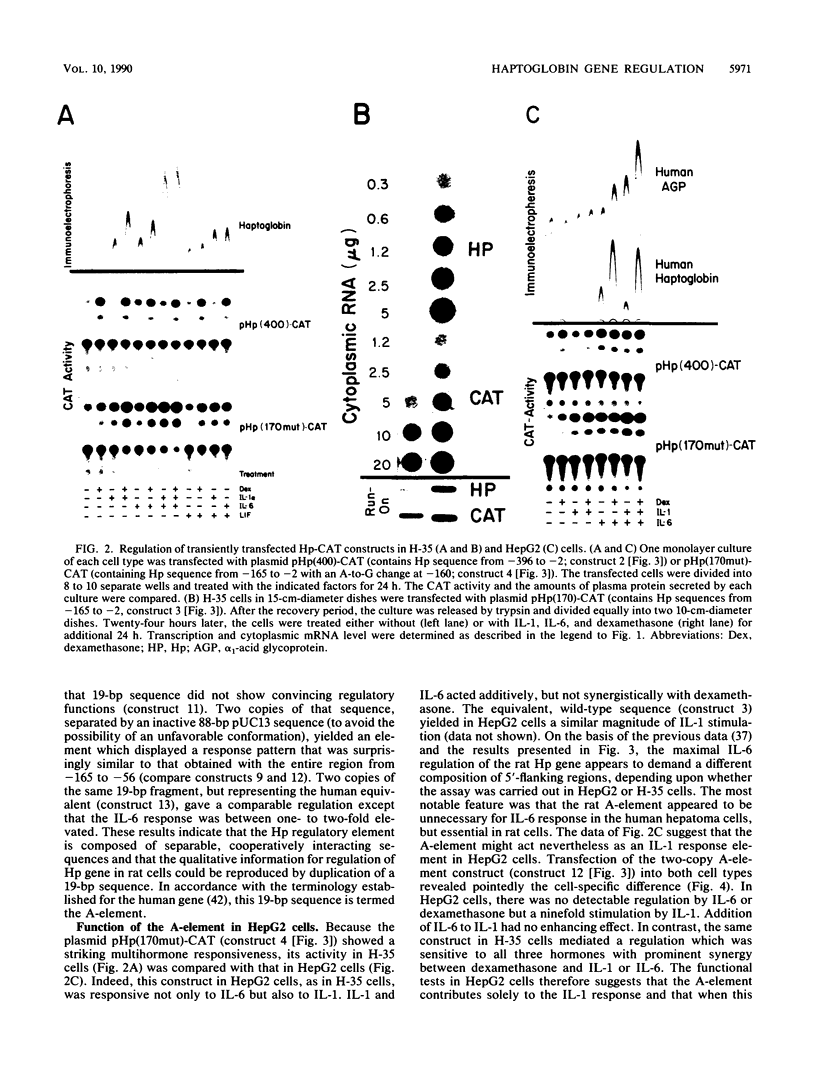
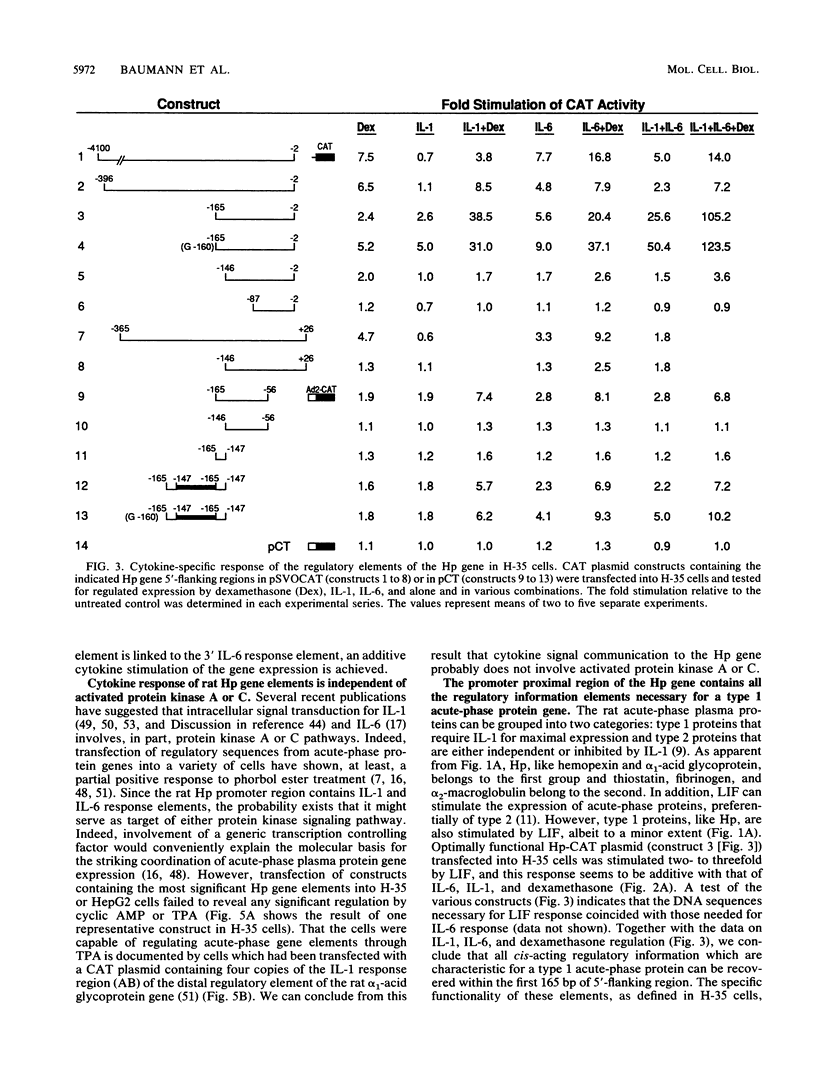
The transcription rate of the haptoglobin (Hp) gene is stimulated by interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and dexamethasone in rat hepatoma (H-35) cells. To identify the cis-acting regulatory elements responsive to these hormones, various lengths of 5' Hp gene-flanking regions, including the promoter, were inserted into chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression vectors and transiently introduced into H-35 cells. The first 4 kb of 5' region mediated a severalfold increase in expression after treatment with IL-6 and dexamethasone. No response to IL-1 was detectable. When, however, upstream sequences were deleted to position -165 relative to the transcription start site, a significant stimulation by IL-1 was gained without appreciably affecting the IL-6 response. With the apparent removal of an inhibitory sequence, the promoter-proximal 165-bp region also displayed a severalfold enhanced response to the combination of dexamethasone, IL-1, and IL-6. The sequence from -165 to -147, termed the A-element, was found to be crucial for all hormone regulatory functions. Two copies of the A-element linked to a heterologous promoter responded to the three hormones, but to a lesser degree than in the Hp gene promoter context. The regulatory elements of the rat Hp gene were similarly active in human hepatoma cells. Optimal regulation by IL-6 in HepG2 cells was, however, independent of the A-element. The A-element functioned in these cells exclusively as an IL-1 response sequence. The results suggest that genomic sequences upstream of the rat Hp gene suppress the regulation by specific cytokines more prominently in transient expression assays than in the normal chromosomal context. Moreover, the functional comparison indicated that specific regulatory regions of the rat Hp gene do not function identically in different hepatic cell types.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcone R., Gualandi G., Ciliberto G. Identification of sequences responsible for acute-phase induction of human C-reactive protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3195–3207. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. Regulation of hepatic acute phase plasma protein genes by hepatocyte stimulating factors and other mediators of inflammation. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H. Hepatic acute phase reaction in vivo and in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02626167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Hill R. E., Sauder D. N., Jahreis G. P. Regulation of major acute-phase plasma proteins by hepatocyte-stimulating factors of human squamous carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):370–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Isseroff H., Latimer J. J., Jahreis G. P. Phorbol ester modulates interleukin 6- and interleukin 1-regulated expression of acute phase plasma proteins in hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17390–17396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Maquat L. E. Localization of DNA sequences involved in dexamethasone-dependent expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2551–2561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Prowse K. R., Marinković S., Won K. A., Jahreis G. P. Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:280-95, discussion 295-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Wong G. G. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor III shares structural and functional identity with leukemia-inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensi G., Raugei G., Klefenz H., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the human haptoglobin locus. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Wilson D. R., Lachman L. B. Monocyte-conditioned medium, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the acute phase response in human hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):787–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Courtois G. M., Kilian P. L., Fuller G. M., Crabtree G. R. Induction of fibrinogen and a subset of acute phase response genes involves a novel monokine which is mimicked by phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10850–10854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G. H., Gauldie J. The acute phase response of the liver in inflammation. Prog Liver Dis. 1990;9:89–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G. H., Hattori M., Northemann W., Abraham L. J., Baumann M., Braciak T. A., Fletcher R. G., Gauldie J., Lee F., Reymond M. F. Regulation of rat liver acute phase genes by interleukin-6 and production of hepatocyte stimulating factors by rat hepatoma cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:317–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., May L. T., Schultz D., Brabenec A., Weinstein J., Sehgal P. B., Kushner I. Role of interleukin-6 in regulating synthesis of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Morrone G., Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3773–3779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring M. R., Shiels B. R., Northemann W., de Bruijn M. H., Kan C. C., Chain A. C., Noonan D. J., Fey G. H. Sequence of rat liver alpha 2-macroglobulin and acute phase control of its messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Abraham L. J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. Acute-phase reaction induces a specific complex between hepatic nuclear proteins and the interleukin 6 response element of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P., Laurent M., Dalmon J. Human beta-fibrinogen gene expression. Upstream sequences involved in its tissue specific expression and its dexamethasone and interleukin 6 stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5695–5701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Tanahashi H., Misumi Y., Sakaki Y. Nuclear factors interacting with an interleukin-6 responsive element of rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9425–9435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D., Zimmermann R., Heisig M., Heinrich P. C. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the interleukin-6 dependent expression of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1121–1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Mackiewicz A. Acute phase proteins as disease markers. Dis Markers. 1987 Mar;5(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. P., Liu T. Y., Goldman N. D. cis-acting elements responsible for interleukin-6 inducible C-reactive protein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4136–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Samols D., Reese J., Kushner I. Regulation of rabbit acute phase protein biosynthesis by monokines. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):851–857. doi: 10.1042/bj2530851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Constitutive and IL-6-induced nuclear factors that interact with the human C-reactive protein promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):457–465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Chilcote R., Ryan P. M. Human triosephosphate isomerase cDNA and protein structure. Studies of triosephosphate isomerase deficiency in man. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic S., Jahreis G. P., Wong G. G., Baumann H. IL-6 modulates the synthesis of a specific set of acute phase plasma proteins in vivo. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):808–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinković S., Baumann H. Structure, hormonal regulation, and identification of the interleukin-6- and dexamethasone-responsive element of the rat haptoglobin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1573–1583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau J. F., Donaldson D. D., Bennett F., Witek-Giannotti J., Clark S. C., Wong G. G. Leukaemia inhibitory factor is identical to the myeloid growth factor human interleukin for DA cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):690–692. doi: 10.1038/336690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Ciliberto G., Oliviero S., Arcone R., Dente L., Content J., Cortese R. Recombinant interleukin 6 regulates the transcriptional activation of a set of human acute phase genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12554–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A., Bird T. A., Gearing A. J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin-1 signal transduction. Increased GTP binding and hydrolysis in membranes of a murine thymoma line (EL4). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3146–3152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Morrone G., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene: transcriptional regulation during development and acute phase induction. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1905–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Haché R. J., Arnemann J., Chalepakis G., Slater E. P., Beato M. Hormonal induction of transfected genes depends on DNA topology. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):625–633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Cortese R. Interleukin 6 induces a liver-specific nuclear protein that binds to the promoter of acute-phase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Baumann H. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 stimulate acute-phase protein production in primary mouse hepatocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jan;45(1):55–61. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Yamashita U., Chedid M., Mizel S. B. Cyclic AMP--an intracellular second messenger for interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8201–8205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Temple P. A., Kriz R., Ferenz C., Hewick R. M., Clark S. C., Ikebuchi K., Ogawa M. Stimulation of murine hemopoietic colony formation by human IL-6. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3040–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]